
The Economy of Chile is a market economy and high-income economy as ranked by the World Bank. The country is considered one of South America's most prosperous nations, leading the region in competitiveness, income per capita, globalization, economic freedom, and low perception of corruption. Although Chile has high economic inequality, as measured by the Gini index, it is close to the regional mean.

The economy of Greece is the 51st largest in the world, with a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of $189.410 billion per annum. In terms of purchasing power parity, Greece is the world's 54th largest economy, at $305.005 billion per annum. As of 2020, Greece is the sixteenth-largest economy in the 27-member European Union. According to the International Monetary Fund's figures for 2021, Greece's GDP per capita is $19,827 at nominal value and $31,821 at purchasing power parity.

The economy of Malaysia is the fourth largest in Southeast Asia and the 38th largest in the world according to the International Monetary Fund. Labour productivity in Malaysia is significantly higher than in neighbouring Thailand, Indonesia, the Philippines or Vietnam, due to a high density of knowledge-based industries and adoption of cutting-edge technology for manufacturing and digital economy. According to the Global Competitiveness Report 2019, the Malaysian economy is the 27th most competitive country economy in the world, and of the top ten countries in the world to adopt a digital legal framework.

Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, also called Burma, is a country in Southeast Asia. It is the largest country in Mainland Southeast Asia, and has a population of about 54 million as of 2017. Myanmar is bordered by Bangladesh and India to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (Rangoon).

The economy of Myanmar has a nominal GDP of USD $76.09 billion in 2019 and an estimated purchasing power adjusted GDP of USD $327.629 billion in 2017 according to the World Bank. For the 2020 estimate, GDP per capita in Myanmar would be USD $5142.20 in PPP per capita and USD $1,608.50 in nominal per capita. This would make Myanmar one of the poorest countries in Southeast Asia.

The economy of South Korea is a highly developed mixed economy dominated by family-owned conglomerates called chaebols. By nominal GDP, it has the 4th largest economy in Asia and the 10th largest in the world. South Korea is notable for its emergence of economic development from one of the poorest countries in the world to a developed, high-income country in just a few generations. This economic growth has been described as the Miracle on the Han River, which has brought South Korea to the ranks of countries in the OECD and the G-20. South Korea still remains one of the fastest growing developed countries in the world, following the Great Recession. It is included in the group of Next Eleven countries as having the potential to play a dominant role in the global economy by the middle of the 21st century.

The economy of Thailand is dependent on exports, which accounted in 2019 for about sixty per cent of the country's gross domestic product (GDP). Thailand itself is a newly industrialized country, with a GDP of 16.316 trillion baht (US$505 billion) in 2018, the 8th largest economy of Asia, according to the World Bank. As of 2018, Thailand has an average inflation of 1.06% and an account surplus of 7.5% of the country's GDP. The Thai economy was expected to post 3.8% growth in 2019. Its currency, the Thai Baht, ranked as the tenth most frequently used world payment currency in 2017.

The economy of Trinidad and Tobago is the third wealthiest in the Caribbean and the fifth-richest by GDP (PPP) per capita in the Americas. Trinidad and Tobago is recognised as a high-income economy by the World Bank. Unlike most of the English-speaking Caribbean, the country's economy is primarily industrial, with an emphasis on petroleum and petrochemicals. The country's wealth is attributed to its large reserves and exploitation of oil and natural gas.

The economy of the United Kingdom is a highly developed social market and market-oriented economy. It is the fifth-largest national economy in the world measured by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), tenth-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP), and twenty first-highest by GDP per capita, constituting 3.3% of world GDP.

The United States is a developed country with a market economy and has the world's largest nominal GDP and net wealth. It has the second-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP) behind China. It had the world's ninth-highest per capita GDP (nominal) and the fifteenth-highest per capita GDP (PPP) in 2021. The United States has the most technologically powerful and innovative economy in the world. Its firms are at or near the forefront in technological advances, especially in artificial intelligence, computers, pharmaceuticals, and medical, aerospace, and military equipment. The U.S. dollar is the currency most used in international transactions and is the world's foremost reserve currency, backed by its economy, its military, the petrodollar system and its linked eurodollar and large U.S. treasuries market. Several countries use it as their official currency and in others it is the de facto currency. The largest U.S. trading partners are China, the European Union, Canada, Mexico, India, Japan, South Korea, the United Kingdom, and Taiwan. The U.S. is the world's largest importer and the second-largest exporter. It has free trade agreements with several countries, including the USMCA, Australia, South Korea, Switzerland, Israel and several others that are in effect or under negotiation.
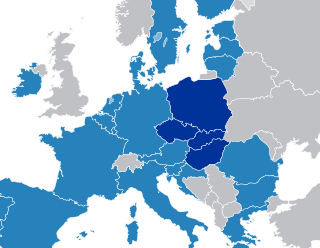
The Visegrád Group, Visegrád Four, V4, or European Quartet, is a cultural and political alliance of four countries of Central Europe, all of which are members of the EU and of NATO, to advance co-operation in military, cultural, economic and energy matters with one another and to further their integration to the EU.

The economy of Singapore is a highly developed free-market economy. Singapore's economy has been ranked by the World Economic Forum as the most open in the world, the 3rd-least corrupt, and the most pro-business. Singapore has low tax-rates and the second-highest per-capita GDP in the world in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is headquartered in Singapore.

Yangon, also known as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar. Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government relocated the administrative functions to the purpose-built capital city of Naypyidaw in north central Myanmar. With over 7 million people, Yangon is Myanmar's most populous city and its most important commercial centre.

Australia is a highly developed country with a market economy. As of 2021, Australia was the 13th-largest national economy by nominal GDP, the 18th-largest by PPP-adjusted GDP, and was the 25th-largest goods exporter and 20th-largest goods importer. Australia took the record for the longest run of uninterrupted GDP growth in the developed world with the March 2017 financial quarter. It was the 103rd quarter and the 26th year since the country had a technical recession. As of June 2021, the country's GDP was estimated at A$1.98 trillion.
The world economy or the global economy is the economy of all humans of the world, referring to the global economic system which includes all economic activities which are conducted both within and between nations, including production, consumption, economic management, work in general, exchange of financial values and trade of goods and services. In some contexts, the two terms are distinct "international" or "global economy" being measured separately and distinguished from national economies while the "world economy" is simply an aggregate of the separate countries' measurements. Beyond the minimum standard concerning value in production, use and exchange, the definitions, representations, models and valuations of the world economy vary widely. It is inseparable from the geography and ecology of planet Earth.
The economies of Canada and the United States are similar because both are developed countries. While both countries feature in the top ten economies in the world in 2022, the U.S. is the largest economy in the world, with US$24.8 trillion, with Canada ranking ninth at US$2.2 trillion.

The economy of India is a middle income developing mixed economy. It is the world's sixth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), on a per capita income basis, India ranked 145th by GDP (nominal) and 122th by GDP (PPP). From independence in 1947 until 1991, successive governments promoted protectionist economic policies, with extensive state intervention and economic regulation. This is characterised as dirigism, in the form of the License Raj. The end of the Cold War and an acute balance of payments crisis in 1991 led to the adoption of a broad economic liberalisation in India. Since the start of the 21st century, annual average GDP growth has been 6% to 7%, and from 2013 to 2018 and in 2021, India is the world's fastest growing major economy, surpassing China. Historically, India was the largest economy in the world for most of the two millennia from the 1st until the 19th century.

The People's Republic of China has a developing market-oriented mixed economy that incorporates economic planning through industrial policies and strategic five-year plans. Dominated by state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and mixed-ownership enterprises, the economy also consists of a large domestic private sector and openness to foreign businesses in a system described as a socialist market economy. State-owned enterprises accounted for over 60% of China's market capitalization in 2019 and generated 40% of China's GDP of US$15.97 trillion(101.36 trillion yuan) in 2020, with domestic and foreign private businesses and investment accounting for the remaining 60%. As of the end of 2019, the total assets of all China's SOEs, including those operating in the financial sector, reached US$78.08 trillion. Ninety-one (91) of these SOEs belong to the 2020 Fortune Global 500 companies. China has the world's second largest economy when measured by nominal GDP, and the world's largest economy since 2014 when measured by Purchasing Power Parity (PPP). It has been the second largest by nominal GDP since 2010, with data relying on fluctuating market exchange rates. A forecast states that China will become the world's largest economy in nominal GDP by 2028. Historically, China was one of the world's foremost economic powers for most of the two millennia from the 1st until the 19th century.
Not to confuse with Asia World in Manila
Beijing's economy ranks among the most developed and prosperous cities in China. In 2013, the municipality's nominal gross domestic product (GDP) was CN¥1.95 trillion. It was about 3.43% of the country's total output, and ranked 13th among province-level administrative units. Per capita GDP, at CN¥93,213 (US$15,051) in nominal terms and Int $21,948 at purchasing power parity, was 2.2 times the national average and ranked second among province-level administrative units.



















