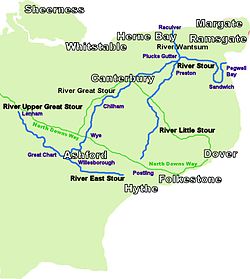
The River Stour(, rhymes with "flour") is a river in Kent, England that flows into the North Sea at Pegwell Bay. Above Plucks Gutter, where the Little Stour joins it, the river is normally known as the Great Stour. The upper section of the river, above its confluence with the East Stour at Ashford is sometimes known as the Upper Great Stour or West Stour. In the tidal lower reaches, the artificial Stonar Cut short cuts a large loop in the natural river.

The River Stour is a 61 mi (98 km) river which flows through Wiltshire and Dorset in southern England, and drains into the English Channel. The catchment area for the river and its tributaries is listed as 480 square miles (1,240 km2).

The Stour(, rhymes with "flour") is a river flowing through the counties of Worcestershire, the West Midlands and Staffordshire in the West Midlands region of England. The Stour is a major tributary of the River Severn, and it is about 25 miles (40 km) in length. It has played a considerable part in the economic history of the region.

The River Rother, a waterway in the northern midlands of England, gives its name to the town of Rotherham and to the Rother Valley parliamentary constituency. It rises in Pilsley in Derbyshire and flows in a generally northwards direction through the centre of Chesterfield, where it feeds the Chesterfield Canal, and on through the Rother Valley Country Park and several districts of Sheffield before joining the River Don at Rotherham in Yorkshire. Historically, it powered mills, mainly corn or flour mills, but most had ceased to operate by the early 20th century, and few of the mill buildings survive.

Canterbury, commonly called the City of Canterbury, is a local government district with city status in Kent, England. As well as Canterbury itself, the district extends north to the coastal towns of Whistable and Herne Bay.

Four major rivers drain the county of Kent, England.

Foudry Brook is a small stream in southern England. It rises from a number of springs near the Hampshire village of Baughurst, and flows to the east and then the north, to join the River Kennet to the south of Reading. The upper section is called Silchester Brook, and beyond that, Bishop's Wood Stream. The underlying geology is chalk, covered by a layer of clay, and so it has the characteristics of a clay stream, experiencing rapid increases in level after heavy rain due to run-off from the surrounding land. It passes a number of listed buildings and scheduled monuments, including the site of the Roman town of Calleva Atrebatum or Silchester.

Noonday Creek is a 20.2-mile-long (32.5 km) stream in Cobb and Cherokee counties in the U.S. state of Georgia. The stream begins near Kennesaw Mountain and ends at Lake Allatoona.

Etchinghill is a village in Kent, England, about 5 km north of Hythe, and 1 km north of the Channel Tunnel terminal at Cheriton, near Folkestone. It is in the civil parish of Lyminge.

Barham is a village and civil parish in the City of Canterbury district of Kent, England. Barham village is approximately 6 miles (10 km) south-east from Canterbury and 8 miles (13 km) north from Folkestone.

Lyminge is a village in southeast Kent, England. It lies about five miles (8 km) from Folkestone and the Channel Tunnel, on the road passing through the Elham Valley. At the 2011 Census the population of Etchinghill was included. The Nailbourne stream begins in the village and flows north through the Valley, to become one of the tributary streams of the Great Stour. The hamlet of Ottinge lies to the NE on the road to Elham. Lyminge is home to the Grade II* listed Sibton Park, now owned by the Holiday Property Bond but previously a school.

The Stour Valley Walk is a recreational walking route that follows the River Stour, through the Low Weald and Kent Downs, from its source at Lenham to its estuary at Pegwell Bay.
PUB, Singapore's National Water Agency, commonly known as PUB, an acronym for Public Utilities Board, is a statutory board under the Ministry of Sustainability and the Environment of the Government of Singapore responsible for ensuring a sustainable and efficient water supply in Singapore.

Rawa is a minor river in Silesia, Poland. It is the largest right tributary of the Brynica, itself a tributary of the Przemsza, which in turn is a tributary of the Vistula. The entire length of the Rawa is within the Upper Silesian Metropolitan Union. It has its source in Ruda Śląska and crosses the cities of Świętochłowice, Chorzów and Katowice. Finally in Sosnowiec it joins the Brynica River only several hundred metres before the latter joins with Czarna Przemsza.

The Elham Valley Railway was a line connecting Folkestone and Canterbury in Kent, England. It opened between 1887 and 1889 and closed in 1947.

The River Stour has been used for centuries as a source of power. Many different processes were performed by the use of water power:- Corn milling, fulling, paper making and electricity generation. Many of the mills survive today as house conversions, with two of them still working commercially.
The Smestow Brook, sometimes called the River Smestow, is a small river that plays an important part in the drainage of Wolverhampton, South Staffordshire, and parts of Dudley in the United Kingdom, and has contributed to the industrial development of the Black Country. It is the most important tributary of the River Stour, Worcestershire and part of the River Severn catchment.

The Cut is a river in England that rises in North Ascot, Berkshire. It flows for around 14 miles (23 km), through the rural Northern Parishes of Winkfield, Warfield and Binfield in Bracknell Forest on its way down to Bray, where it meets the River Thames just above Queens Eyot on the reach below Bray Lock, having been joined by the Maidenhead Waterways.

Stodmarsh SSSI is a 623.2-hectare (1,540-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest near Stodmarsh, north-east of Canterbury in Kent. Parts of it are a Nature Conservation Review site, Grade I, a National Nature Reserve, a Ramsar internationally important wetland site, a Special Area of Conservation and a Special Protection Area under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds.