Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores, and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, Vandellia cirrhosa. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus Corydoras, are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, but others are crepuscular or diurnal.

Callichthyidae is a family of catfishes, called armored catfishes due to the two rows of bony plates along the lengths of their bodies. It contains some of the most popular freshwater aquarium fish, such as many species in the genus Corydoras.

The Mochokidae are a family of catfishes that are known as the squeakers or known as upside-down catfish. There are nine genera and about 200 species of mochokids. All the mochokids are freshwater species originating from Africa.

Loricariidae is the largest family of catfish, with 92 genera and just over 680 species. Loricariids originate from freshwater habitats of Costa Rica, Panama, and tropical and subtropical South America. These fish are noted for the bony plates covering their bodies and their suckermouths. Several genera are sold as "plecos", notably the suckermouth catfish, Hypostomus plecostomus, and are popular as aquarium fish.

The eeltail catfish are a family (Plotosidae) of catfish whose tails are elongated in an eel-like fashion. These catfishes are native to the Indian Ocean and western Pacific from Japan to Australia and Fiji. The family includes about 41 species in 10 genera. About half of the species are freshwater, occurring in Australia and New Guinea.

Trichomycteridae is a family of catfishes commonly known as pencil catfishes or parasitic catfishes. This family includes the candiru fish, feared by some people for its alleged habit of entering into the urethra of humans. They are one of the few parasitic chordates. Another species is the life monsefuano which was important to the Moche culture and still an important part of Peruvian cuisine.

The Doradidae are a family of catfishes also known as thorny catfishes, raphael catfishes or talking catfishes. These fish are native to South America, primarily the Amazon basin and the Guianas.

The Cetopsidae are a small family of catfishes, commonly called the whale catfishes.

The stream catfishes comprise the family Akysidae of catfishes.

The Bagridae are a family of catfish that are native to Africa (Bagrus) and Asia from Japan to Borneo. It includes about 245 species. These fish are commonly known as naked catfishes or bagrid catfishes.

Erethistidae are a family of catfishes that originate from southern Asia. It includes about 45 species.

Pseudolaguvia is a genus of South Asian river catfishes. These species inhabit hill streams and large rivers. P. tenebricosa is found in fast running, clear water; the river has a sandy bottom and numerous rocks and boulders and aquatic vegetation is absent. P. inornata is from clear, shallow, moderately flowing streams with a predominantly sandy bottom. P. muricata is found in clear, shallow, slow-flowing streams with a mixed substrate of sand and detritus; these fish are found amongst detritus in areas with current. P. ferula is also found in swift flowing waters with a mixed rocky/sandy bottom.

Loricariinae is a subfamily of the family Loricariidae of catfish. This subfamily is divided into two tribes and about 30 genera. They are mainly native to freshwater habitats in South America, but there are also several species in Panama and a single (Fonchiiichthys) in Costa Rica.
Parakysis is a genus of catfishes of the family Akysidae. It includes six species.

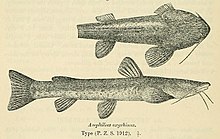
Amphilius is a genus of catfishes of the family Amphiliidae.

The bayad, is a species of bagrid catfish from Africa.
The Somalia catfish is a species of catfish in the family Bagridae. The Somalia catfish is native to the Jubba River in Somalia.

Phractura is a genus of loach catfishes that occur in Africa.

Galeichthys is a genus of sea catfishes in the family Ariidae, the only genus in the subfamily Galeichthyinae. It includes four predominantly marine species distributed in Southern Africa and northwestern South America:
Amissidens hainesi, the ridged catfish, is the only species of catfish in the genus Amissidens of the family Ariidae. This species occurs in marine and brackish waters on the southern coast of New Guinea and Northern Australia, between Darwin and southern Gulf of Carpentaria.