
A squid is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.

Myopsida is one of the four orders of squid. It consists of two families: the monotypic Australiteuthis and the diverse and commercially important Loliginidae. Some taxonomists classify this taxon as a suborder of the order Teuthida, in which case it is known as Myopsina. This reclassification is due to Myopsina and Oegopsina not being demonstrated to form a clade.

Loligo is a genus of squid and one of the most representative and widely distributed groups of myopsid squid.

The European squid or common squid is a large squid belonging to the family Loliginidae. It occurs abundantly in coastal waters from the North Sea to at least the west coast of Africa. This species lives from sea level to depths of 500 m (1,600 ft). Its mantle is up to 40 cm (16 in) long. The species is extensively exploited by commercial fisheries.

Doryteuthis opalescens, the opalescent inshore squid or market squid, is a small squid in the family Loliginidae. It is a myopsid squid, which is the near shore group and that means that they have corneas over their eyes. The species lives in the eastern Pacific Ocean from Mexico's Baja California peninsula to Alaska, United States, and as an inshore squid it can be found with a range of 200 miles (320 km) off the coast.
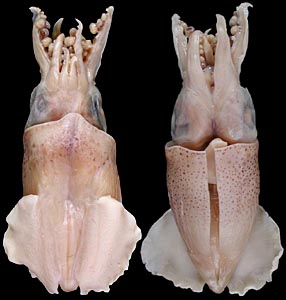
A. aldrichi is a small species of squid found in northern Australian waters. The species was described by Chung Cheng Lu in 2005 based on specimens collected in the inshore waters of Northern Australia. The largest known individual of this species is a mature female measuring 27.6 mm (1.09 in) in mantle length (ML). The holotype is a mature male of 21.3 mm (0.84 in) ML. A live specimen of A. aldrichi has yet to be recorded.

Idiosepius pygmaeus, also known as the two-toned pygmy squid, Tropical Pygmy squid, is a species of bobtail squid native to the Indo-Pacific. It occurs in waters of the South China Sea, Japan, Philippines, Palau, Indonesia, Northern Mariana Islands, as well as northern and northeastern Australia. It inhabits shallow, inshore waters.
Loligo reynaudii, commonly known as the Cape Hope squid, is a 20–30 cm (7.9–11.8 in) long squid belonging to the family Loliginidae. In South Africa it is known as either calamari or chokka.

Thysanoteuthis rhombus, also known as the diamond squid,diamondback squid, or rhomboid squid, is a large species of squid from the family Thysanoteuthidae which is found worldwide, throughout tropical and subtropical waters. T. rhombus is given its name for the appearance of the fins that run the length of the mantle. They are a fast growing species with a lifespan of approximately 1 year. The diamond squid is the only cephalopod species known to be monogamous. T. rhombus often preys on fish and other small cephalopods at varying water depths. This species is commercially fished in Japan, specifically in the Sea of Japan and Okinawa.

The Japanese flying squid, Japanese common squid or Pacific flying squid, scientific name Todarodes pacificus, is a squid of the family Ommastrephidae. This animal lives in the northern Pacific Ocean, in the area surrounding Japan, along the entire coast of China up to Russia, then spreading across the Bering Strait east towards the southern coast of Alaska and Canada. They tend to cluster around the central region of Vietnam.

Alloteuthis subulata, the European common squid, is a species of squid in the family Loliginidae.

Todaropsis eblanae, also known as the lesser flying squid, is a species of short finned squid in the monotypic genus Todaropsis of the family Ommastrephidae.

Sepioteuthis lessoniana, commonly known as the bigfin reef squid, glitter squid or oval squid, is a species of loliginid squid. It is one of the three currently recognized species belonging to the genus Sepioteuthis. Studies in 1993, however, have indicated that bigfin reef squids may comprise a cryptic species complex. The species is likely to include several very similar and closely related species.

Illex coindetii, commonly known as the southern shortfin squid or broadtail shortfin squid, is a species of neritic squids in the family Ommastrephidae. They are found in the Mediterranean Sea and on both sides of the north Atlantic Ocean.

Illex illecebrosus, commonly known as the northern shortfin squid, is a species of neritic squids in the family Ommastrephidae. Squids of the genus Illex account for 65% of the world's cephalopod captures. Illex is formed by four taxa distributed throughout the Atlantic Ocean, whose identification and phylogenetic relationships based on morphological characters remain controversial.They are found in the northwest Atlantic Ocean, from off the coast of eastern North America to Greenland, Iceland, and west of Ireland and the United Kingdom. They are a highly migratory and short-lived species, with lifespans of less than a year. They are commercially important and are fished extensively, mostly for the Canadian and Japanese markets.

Heterololigo is a monotypic genus of squids containing the single species Heterololigo bleekeri. It was formerly classified in the genus Loligo; some authors still include it there, but DNA evidence supports its separation into a genus of its own. This species is known by the common name spear squid.

Alloteuthis media, the midsize squid or little squid, is a species of squid in the family Loliginidae from the eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea. It is generally a by-catch species in trawl fisheries, although there is an active fishery in the western Mediterranean.
Loliolus is a genus of squid from the family Loliginidae from the Indo-Pacific region. The genus is divided into two subgenera Loliolus and Nipponololigo. They are small squids of less than 150 mm (5.9 in) in mantle length which have an expanded tentacular club. This club has 4 series of suckers. The sucker rings have plate-like teeth which are square in shape all around them. The males' hectocotylus has a ventral crest which is created by the fusion of the protective membrane with the ventral series of papillae and this crest completely obscures the conical shape of the papillae. The mantle is rounded posteriorly and lacks the posterior tail-like lobe while the fins are positioned on the rear of the mantle and extend to the posterior tip of the mantle. Their eggs are small and the males' spermatophore has a short cement body. They do not possess photophores. The two subgenera are distinguished by the hectocotylus which in Loliolus encompasses the entire arm and there are no unmodified suckers while in Nipponololigo the arm is only partly hectocotylsed and has normal suckers at its base.

Doryteuthis gahi, also known as the Patagonian longfin squid and Patagonian squid, is a small-sized squid belonging to the family Loliginidae. It occurs in coastal waters in the southeastern Pacific Ocean and the southwestern Atlantic Ocean where it is caught and eaten for food.
Loliolus Japonica, the Japanese squid, is a species of squid from the family Loliginidae. As the name suggests, it lives around Japan, but has also been found around Vietnam and China. They are pelagic, living 1–30 m down in the ocean.
















