
Dickinsonia is an extinct genus of lifeforms that lived during the late Ediacaran period in what is now Australia, China, Russia and Ukraine, most likely a basal animal. The individual Dickinsonia typically resembles a bilaterally symmetrical ribbed oval. Its affinities are presently unknown; its mode of growth is consistent with a stem-group bilaterian affinity, though some have suggested that it belongs to the fungi, or even an "extinct kingdom". The discovery of cholesterol molecules in fossils of Dickinsonia lends support to the idea that Dickinsonia was an animal.

Tribrachidium heraldicum is a tri-radially symmetric fossil animal that lived in the late Ediacaran (Vendian) seas. In life, it was hemispherical in form. T. heraldicum is the best known member of the extinct group Trilobozoa.

Yorgia waggoneri is a discoid Ediacaran organism. It has a low, segmented body consisting of a short wide "head", no appendages, and a long body region, reaching a maximum length of 25 cm (9.8 in). It is classified within the extinct animal phylum Proarticulata.
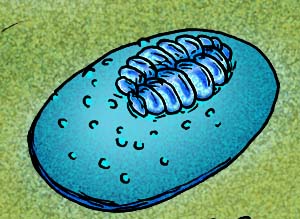
Cephalonega stepanovi is a fossil organism from Ediacaran deposits of the Arkhangelsk Region, Russia. It was described by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1976
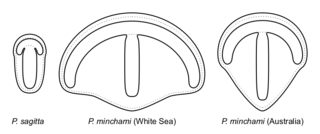
Parvancorina is a genus of shield-shaped bilaterally symmetrical fossil animal that lived in the late Ediacaran seafloor. It has some superficial similarities with the Cambrian trilobite-like arthropods.

Vendia is a genus of oval-shaped, Ediacaran fossils ranging from 4.5 to 12.5 mm long. The body is completely segmented into isomers, which are arranged alternately in two rows longitudinal to the axis of the body. The larger isomers cover the smaller ones externally but the posterior ends of all the isomers remain free. The transverse elements decrease in size from anterior to posterior and are all inclined in the same direction.

Trilobozoa is a phylum of extinct, sessile animals that were originally classified into the Cnidaria. The basic body plan of trilobozoans is often a tri-radial or radial sphere-shaped form with lobes radiating from its centre. Fossils of trilobozoans are restricted to marine strata of the Late Ediacaran period.

Albumares brunsae is a tri-radially symmetrical fossil animal that lived in the late Ediacaran seafloor. It is a member of the extinct group Trilobozoa.

Anfesta stankovskii is a tri-radially symmetrical fossil animal that lived in the late Ediacaran (Vendian) seafloor. It is a member of the extinct group Trilobozoa.

Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately 567 to 550 million years ago. The name comes from the Greek προ = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as Dickinsonia, Vendia, Cephalonega, Praecambridium and currently many other Proarticulata are described.

Vendiamorpha is a class of extinct animals within the Ediacaran phylum Proarticulata.
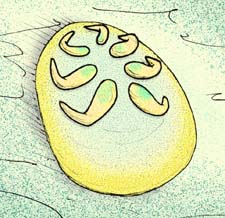
Tamga hamulifera is a disk-shaped fossil from Precambrian strata of the White Sea area, in Russia, the only member of the genus Tamga.

Isomer is an element of transverse body articulation of the bilateral fossil animals of the Phylum Proarticulata from the Ediacaran (Vendian) period. This term has been proposed by Andrey Yu. Ivantsov, a Russian paleontologist from the Laboratory of the Precambrian organisms, Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences.

Solza margarita is an extinct animal of uncertain phylogeny which lived about 555 mya in the Ediacaran period.

Keretsa brutoni is a fossil bilaterian from the Late Precambrian-aged Zimnie Gory Formation near Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, along the Winter coast of the White Sea. The first specimens were found in 2005. This rounded oblong-shaped organism resembles Naraoia, in having its body divided into an anteriorly positioned headshield, and a trunkshield. A pair of antennae-like structures emanate from underneath the base of the headshield, and there are numerous oblique grooves along the trunkshield that suggest legs.
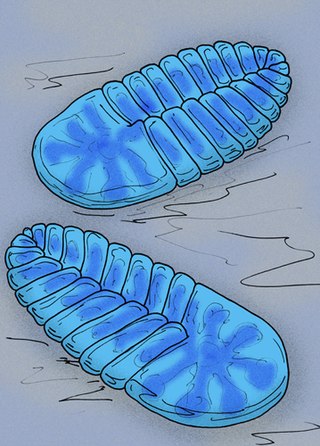
Cyanorus singularis is a small proarticulatan, closely related to Spriggina and Marywadea. Its two largest pairs of appendages are located on the anterior part of the body. The anterior part of the body was most likely not segmented. The axial structure of it combines features of the Vendia species and Dickinsonia species. It was found in the Upper Vendian of the White Sea area, Arkhangel'sk Region. It is a White Sea Ediacaran fossil and it became extinct during the Late Precambrian.

Armillifera parva is a species of Ediacaran proarticulate first described by Mikhail Fedonkin in 1980. Its fossils were discovered in the White Sea area, Arkhangelsk Region, Russia. These fossils of A. parva were restricted to almost the same stratigraphic range as Kimberella, although fossils of both organisms have been rarely found.

Archaeaspinus fedonkini is an extinct proarticulatan organism from the Late Precambrian (Ediacaran) period.

Temnoxa molluscula is a small creature approximately 8 mm wide found in the Ediacaran period in Russia. The Temnoxa has a resemblance to a vertically cut penny bun mushroom. Due to the lack of information regarding the fossils of this organism, researchers are unable to place Temnoxa molluscula into any known phylum. The genus was originally discovered by Russian paleontologist Andrey Yu. Ivantsov in 2004.

Cephalozoa are an extinct class of primitive segmented marine organisms within the Phylum Proarticulata from the Ediacaran period. They possessed bilateral symmetry and were characterized by a thin, rounded body.














