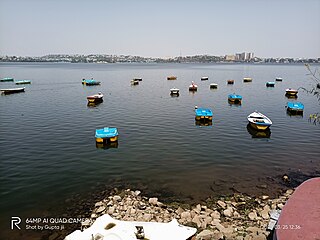Madhya Pradesh is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second largest Indian state by area and the fifth largest state by population with over 72 million residents. It borders the states of Uttar Pradesh to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the east, Maharashtra to the south, Gujarat to the west, and Rajasthan to the northwest.

Bhopal is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the City of Lakes due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It is also one of the greenest cities in India. It is the 16th largest city in India and 131st in the world. After the formation of Madhya Pradesh, Bhopal was part of the Sehore district. It was bifurcated in 1972 and a new district, Bhopal, was formed. Flourishing around 1707, the city was the capital of the former Bhopal State, a princely state of the British ruled by the Nawabs of Bhopal. Numerous heritage structures from this period include the Taj-ul-Masajid and Taj Mahal palace. In 1984, the city was struck by the Bhopal disaster, one of the worst industrial disasters in history.

The Yamuna, also spelt Jamuna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about 4,500 m (14,800 ft) on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Lower Himalaya in Uttarakhand, it travels a total length of 1,376 kilometres (855 mi) and has a drainage system of 366,223 square kilometres (141,399 sq mi), 40.2% of the entire Ganges Basin. It merges with the Ganges at Triveni Sangam, Allahabad, which is a site of the Kumbh Mela, a Hindu festival held every 12 years.

Pachmarhi is a hill station in Narmadapuram district of Madhya Pradesh state of central India. It has been the location of a cantonment since British Raj.

The Bhoj Wetland consists of two lakes located in the city of Bhopal, the capital of the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. The two lakes are the Bhojtal & the Lower Lake, which lie to the west of the city center. The Bhojtal has an area of 31 km², and drains a catchment or watershed of 361 km². The watershed of the Bhojtal is mostly rural, with some urbanized areas around its eastern end. The lower lake has an area of 1.29 km². Its catchment is 9.6 km² and is mostly urbanized; the Lower Lake also receives subsurface seepage from the Bhojtal.

The Chambal River is a tributary of the Yamuna River in Central and Northern India, and thus forms part of the drainage system of the Ganges. The river flows north-northeast through Madhya Pradesh, running for a time through Rajasthan then forming the boundary between Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh before turning southeast to join the Yamuna in Uttar Pradesh state.

Bhopal District is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. The city of Bhopal serves as its administrative headquarters. The district is part of Bhopal Division.
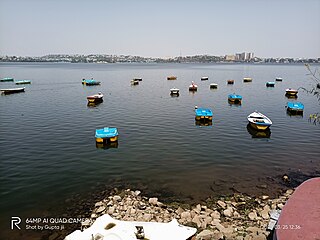
Bhojtal, formerly known as Upper Lake, is a large lake which lies on the western side of the capital city of Madhya Pradesh, Bhopal, India. It is a major source of drinking water for the residents of the city, serving around 40% of the residents with nearly 30 million imperial gallons (140,000 m3) of water per day. Bada talaab, along with the nearby Chhota Talaab, meaning small lake in Hindi, constitute Bhoj Wetland, which is now a Ramsar site.

Pollution of the Ganges, the largest river in India, poses significant threats to human health and the larger environment. The river, which is severely polluted with human waste and industrial contaminants, provides water to about 40% of India's population across 11 states, serving an estimated population of 500 million people, which is more than any other river in the world.
The Bhadbhada dam is a set of 11 sluice gates at the south-east corner of Upper lake in Bhopal. It was constructed in 1965. The gates are used to control the outflow of water from the lake to Kaliasote river, and are usually opened only when the city receives heavy rainfall during the monsoon season. It has a full tank level of 1666.80 feet.
Budha Nullah or Budha Naala is a seasonal water stream, which runs through the Malwa region of Punjab, India, and after passing through highly populated Ludhiana district, Punjab, India, it drains into Sutlej River, a tributary of the Indus river. Today, it has also become a major source of pollution in the region as well the main Sutlej river, as it gets polluted after entering the highly populated and industrialized Ludhiana city, turning it into an open drain. Also, since large area in south-western Punjab solely depend on the canal water for irrigation, and water from Budha Nullah enters various canals after Harike waterworks near Firozpur, thus affecting far-reaching areas such as Malout, Zira, upper Lambi, while the areas being fed by Sirhind feeder, are the most-affected by its pollution.

Lai Nullah, commonly called Nullah Lai, is a rain water fed natural stream flowing through the city of Rawalpindi. Every monsoon season the stream floods after being fed by its catchment basin in the Margalla Hills bordering Islamabad, Pakistan.

The Upper Wardha Dam is an earthfill straight gravity dam across the Wardha River, a tributary of the Godavari River, near Simbhora village in Morshi taluk in Amravati district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The dam provides multipurpose benefits of irrigation, drinking water supply, flood control and hydropower generation.
Chennai Metropolitan Water Supply and Sewerage Board, known shortly as CMWSSB, is a statutory board of Government of Tamil Nadu which provides water supply and sewage treatment to the city of Chennai and its metropolitan region.

Jagdishpur is a panchayat village in the Bhopal district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located in the Huzur tehsil and the Phanda block.
The Halali reservoir is a reservoir in Madhya Pradesh state of India, spanning Bhopal, Raisen, and Vidisha districts. It is built on the Halali River, and lies 40 km northwards from the state capital Bhopal.

Hussainsagar Lake and Catchment Area Improvement Project is a project led by Hyderabad Metropolitan Development Authority to improve the quality of Hussain Sagar Lake (pictured) in Hyderabad, India.

The Kolar is a right bank tributary of the Narmada River. It flows for a total length of 101 km, all of which is in the state of Madhya Pradesh.

The Government of India (GoI) constituted a common tribunal on 10 April 1969 to solve the river water utilization disputes about the river basin states of Godavari and Krishna rivers under the provisions of Interstate River Water Disputes Act – 1956. The common tribunal was headed by Sri RS Bachawat as its chairman with Sri DM Bhandari and Sri DM Sen as its members. Godavari river basin spreads through the states of Telangana (TS), Maharashtra (MR), Orissa, old Madhya Pradesh {later bifurcated into present Madhya Pradesh (MP) and Chhattisgarh}, Karnataka (K) and Andhra Pradesh (AP). Krishna river basin states Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh insisted on the quicker verdict as it had become more expedient for the construction of irrigation projects in Krishna basin. So the of Godavari Water Disputes Tribunal (GWDT) could not proceed till the Krishna Water Disputes Tribunal final verdict was submitted to GoI on 27 May 1976.
Bhauri is a village in the Bhopal district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located in the Huzur tehsil and the Phanda block. Bhauri has been included in Bhopal Municipal Corporation in 2015 by Gazette Notification of Government of Madhya Pradesh. The IISER Bhopal is located in Bhauri, beside the Bhopal Bypass Road. School of Planning and Architecture (SPA) Bhopal, an Institute of National Importance under Ministry of Human Resource Development, is located in Bhauri village. SPA is accessed by Neelbad Road from Bhopal Bypass. The road is under construction. Madhya Pradesh Police Academy is also situated in Bhauri village.