
Davao del Sur, officially the Province of Davao del Sur, is a province in the Philippines located in the Davao Region in Mindanao. Its capital is Digos. Davao City is the largest city in terms of area and population within the province's jurisdiction, yet it is administratively independent from the province; as such, Davao City is only grouped for geographical and statistical purposes and serves as the regional center of Davao Region.

Davao Oriental, officially the Province of Davao Oriental, is a province in the Philippines located in the Davao Region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Mati which is the most populous, and it borders the province of Davao de Oro to the west, and Agusan del Sur and Surigao del Sur to the north. The province is the traditional homeland of the Mandaya and Kalagan/Kaagan.

Davao de Oro, officially the Province of Davao de Oro, is a province in the Philippines located in the Davao Region in Mindanao. Its capital is Nabunturan while Monkayo is the most populous. It used to be part of the province of Davao del Norte until it was made a separate province in 1998.

San Isidro, officially the Municipality of San Isidro, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Davao Oriental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,664 people.

Pototan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Iloilo, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 78,298 people.
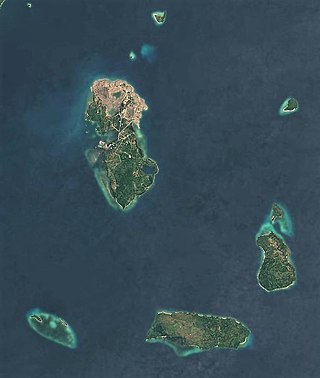
Caluya, officially the Municipality of Caluya, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Antique, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 38,908 people, making it the sixth most populous municipality in the province.

Tibiao, officially the Municipality of Tibiao, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Antique, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 28,703 people.

Tagum, officially the City of Tagum, is a 1st class component city and capital of the Davao del Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 296,202 people making it the most populous component city in Mindanao and in Davao del Norte, as well as the second most populous in Davao Region after Davao City.

Arakan, officially the Municipality of Arakan is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 50,558 people.

Kidapawan, officially the City of Kidapawan, is a 3rd class component city and capital of the province of Cotabato, Philippines. According to the 2020 Census, it has a population of 160,791 people making it the most populous in the province.

Compostela, officially the Municipality of Compostela, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Davao de Oro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 89,884 people.
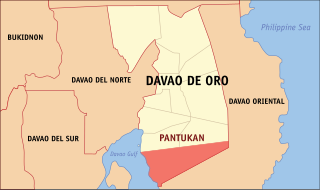
Pantukan, officially the Municipality of Pantukan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Davao de Oro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 90,786 people.

Montevista, officially the Municipality of Montevista, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Davao de Oro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 46,558 people.

Kitaotao, officially the Municipality of Kitaotao, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Bukidnon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 53,796 people.

San Fernando, officially the Municipality of San Fernando, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Bukidnon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,045 people.

Malita, officially the Municipality of Malita, is a 1st class municipality and capital of the province of Davao Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 118,197 people making it the most populous town in the province.

Santa Maria, officially the Municipality of Santa Maria, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Davao Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 57,526 people.

Sulop, officially the Municipality of Sulop, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Davao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 35,151 people.

Banaybanay, officially the Municipality of Banaybanay, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Davao Oriental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 44,451 people.

Tolosa, officially the Municipality of Tolosa, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Leyte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 20,708 people.























