Therapy of the lymphatic system
Lymphotherapy (lymphatic physiotherapy) is a method by which pressure applied on specific lymph nodes alters lymphatic response. Proponents state it can be used for lymphedema [1] and breast cancer. [2]
| This article is part of a series on |
| Alternative medicine |
|---|
 |
Lymphotherapy (lymphatic physiotherapy) is a method by which pressure applied on specific lymph nodes alters lymphatic response. Proponents state it can be used for lymphedema [1] and breast cancer. [2]
Lymphotherapy was first suggested in 1918 by Dr. S. Artault de Vevey in the Paris Therapeutic Society as a treatment for infectious diseases, though it had many fans as well as opponents. [3] [ unreliable medical source? ] This treatment was popular in Italy in the 1960s and 1970s. [4] Currently, lymphotherapy practice has been documented in complementary and alternative medicine. [5] [6]
Complete decongestive lymphatic physiotherapy demands substantial time and effort from patients to maintain the benefits; treatments are not always well-accepted, and patients may suffer from a deterioration in quality of life or develop enhanced anxiety. Sudden loss of bowel control was reported, [4] especially with lymphatic physiotherapy applied on the lymph nodes in the lower back.

Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns interstitial fluid to the bloodstream.

Mastectomy is the medical term for the surgical removal of one or both breasts, partially or completely. A mastectomy is usually carried out to treat breast cancer. In some cases, women believed to be at high risk of breast cancer have the operation as a preventive measure. Alternatively, some women can choose to have a wide local excision, also known as a lumpectomy, an operation in which a small volume of breast tissue containing the tumor and a surrounding margin of healthy tissue is removed to conserve the breast. Both mastectomy and lumpectomy are referred to as "local therapies" for breast cancer, targeting the area of the tumor, as opposed to systemic therapies, such as chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, or immunotherapy.

The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphatic tissue and lymph. Lymph is a clear fluid carried by the lymphatic vessels back to the heart for re-circulation. The Latin word for lymph, lympha, refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha".
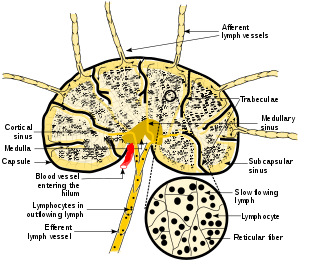
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function.
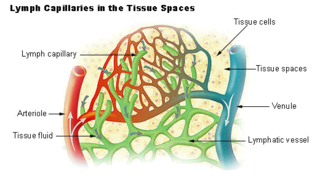
The lymphatic vessels are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavian veins and thus return it to general circulation.

Lymphadenectomy, or lymph node dissection, is the surgical removal of one or more groups of lymph nodes. It is almost always performed as part of the surgical management of cancer. In a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed; in a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed.

The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node or group of nodes draining a cancer. In case of established cancerous dissemination it is postulated that the sentinel lymph nodes are the target organs primarily reached by metastasizing cancer cells from the tumor.
Lymphangiosarcoma is a rare cancer which occurs in long-standing cases of primary or secondary lymphedema. It involves either the upper or lower lymphedematous extremities but is most common in upper extremities. Although its name implies lymphatic origin, it is believed to arise from endothelial cells and may be more accurately referred to as angiosarcoma.

Lymphangitis is an inflammation or an infection of the lymphatic channels that occurs as a result of infection at a site distal to the channel. It may present as long red streaks spreading away from the site of infection. It is a possible medical emergency as involvement of the lymphatic system allows for an infection to spread rapidly. The most common cause of lymphangitis in humans is bacteria, in which case sepsis and death could result within hours if left untreated. The most commonly involved bacteria include Streptococcus pyogenes and hemolytic streptococci. In some cases, it can be caused by viruses such as mononucleosis or cytomegalovirus, as well as specific conditions such as tuberculosis or syphilis, and the fungus Sporothrix schenckii. Lymphangitis is sometimes mistakenly called "blood poisoning". In reality, "blood poisoning" is synonymous with sepsis.

Radical mastectomy is a surgical procedure that treats breast cancer by removing the breast and its underlying chest muscle, and lymph nodes of the axilla (armpit). Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women. During the early twentieth century it was primarily treated by surgery, when the mastectomy was developed. However, with the advancement of technology and surgical skills in recent years, mastectomies have become less invasive. As of 2016, a combination of radiotherapy and breast conserving mastectomy are considered optimal treatment.

The axillary lymph nodes or armpit lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human armpit. Between 20 and 49 in number, they drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast, the superficial lymph vessels from thin walls of the chest and the abdomen above the level of the navel, and the vessels from the upper limb. They are divided in several groups according to their location in the armpit. These lymph nodes are clinically significant in breast cancer, and metastases from the breast to the axillary lymph nodes are considered in the staging of the disease.
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a type of manual manipulation of the skin, not to be confused with massage, based on the hypothesis that it will encourage the natural drainage of the lymph, which carries waste products away from the tissues back toward the heart. The lymph system depends on intrinsic contractions of the smooth muscle cells in the walls of lymph vessels (peristalsis) and the movement of skeletal muscles to propel lymph through the vessels to lymph nodes and then to the lymph ducts, which return lymph to the cardiovascular system. Manual lymph drainage uses a specific amount of pressure, and rhythmic circular movements to stimulate lymph flow.
Breast cancer management takes different approaches depending on physical and biological characteristics of the disease, as well as the age, over-all health and personal preferences of the patient. Treatment types can be classified into local therapy and systemic treatment. Local therapy is most efficacious in early stage breast cancer, while systemic therapy is generally justified in advanced and metastatic disease, or in diseases with specific phenotypes.
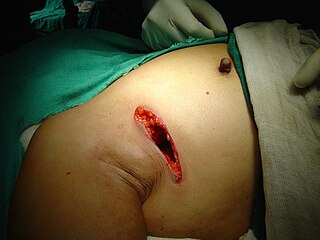
Breast-conserving surgery refers to an operation that aims to remove breast cancer while avoiding a mastectomy. Different forms of this operation include: lumpectomy (tylectomy), wide local excision, segmental resection, and quadrantectomy. Breast-conserving surgery has been increasingly accepted as an alternative to mastectomy in specific patients, as it provides tumor removal while maintaining an acceptable cosmetic outcome. This page reviews the history of this operation, important considerations in decision making and patient selection, and the emerging field of oncoplastic breast conservation surgery.
Cancer of unknown primary origin (CUP) is a cancer that is determined to be at the metastatic stage at the time of diagnosis, but a primary tumor cannot be identified. A diagnosis of CUP requires a clinical picture consistent with metastatic disease and one or more biopsy results inconsistent with a tumor cancer
Cancer treatments are a wide range of treatments available for the many different types of cancer, with each cancer type needing its own specific treatment. Treatments can include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy including small-molecule drugs or monoclonal antibodies, and PARP inhibitors such as olaparib. Other therapies include hyperthermia, immunotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and stem-cell therapy. Most commonly cancer treatment involves a series of separate therapies such as chemotherapy before surgery. Angiogenesis inhibitors are sometimes used to enhance the effects of immunotherapies.
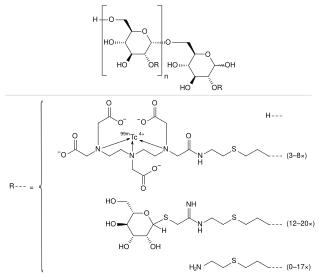
Technetium (99mTc) tilmanocept, sold under the brand name Lymphoseek, is a radiopharmaceutical diagnostic imaging agent used to locate lymph nodes which may be draining from tumors, and assist doctors in locating lymph nodes for removal during surgery.

Elisa Rush Port FACS is Associate Professor of Surgery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital, as well as cofounder and director of the Dubin Breast Center at the Tisch Cancer Institute at Mount Sinai Health System, since 2010. She has received four research grants, has served as an investigator or co-investigator on 15 clinical trials, published 44 peer-reviewed articles, and published a total of 12 book chapters and books. She has specialized in sentinel-node biopsy, a diagnostic method that determines cancer stages based on spread to regional lymph nodes, nipple sparing mastectomy, and the use of MRI for breast cancer.

Armando Elario Giuliano is a surgical oncologist, surgeon scientist and medical professor in Los Angeles, California, United States of America. He is the Linda and Jim Lippman Chair in Surgical Oncology and co-director of Saul and Joyce Brandman Breast Center at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles.
Gary Herbert Lyman is an American academic hematologist, medical oncologist, and cancer researcher.