Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. Being a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Symptoms include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks or building up over time. In relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. In progressive forms of MS, bodily function slowly deteriorates once symptoms manifest and will steadily worsen if left untreated.

Fatigue describes a state of tiredness, exhaustion or loss of energy.

Interferon beta-1a is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified E. coli. Some research indicates that interferon injections may result in an 18–38% reduction in the rate of MS relapses.
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have many possible underlying causes. Paresthesias are usually painless and can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly occur in the arms and legs.
A cramp is a sudden, involuntary, painful skeletal muscle contraction or overshortening associated with electrical activity; while generally temporary and non-damaging, they can cause significant pain and a paralysis-like immobility of the affected muscle. A cramp usually goes away on its own over a period of several seconds or (sometimes) minutes. Cramps are common and tend to occur at rest, usually at night. They are also often associated with pregnancy, physical exercise or overexertion, and age ; in such cases, cramps are called idiopathic, because there is no underlying pathology. In addition to those benign conditions cramps are also associated with many pathological conditions.

Osteosclerosis is a disorder characterized by abnormal hardening of bone and an elevation in bone density. It may predominantly affect the medullary portion and/or cortex of bone. Plain radiographs are a valuable tool for detecting and classifying osteosclerotic disorders. It can manifest in localized or generalized osteosclerosis. Localized osteosclerosis can be caused by Legg–Calvé–Perthes disease, sickle-cell disease and osteoarthritis among others. Osteosclerosis can be classified in accordance with the causative factor into acquired and hereditary.

Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) is a disorder of conjugate lateral gaze in which the affected eye shows impairment of adduction. When an attempt is made to gaze contralaterally, the affected eye adducts minimally, if at all. The contralateral eye abducts, however with nystagmus. Additionally, the divergence of the eyes leads to horizontal diplopia. That is if the right eye is affected the patient will "see double" when looking to the left, seeing two images side-by-side. Convergence is generally preserved.
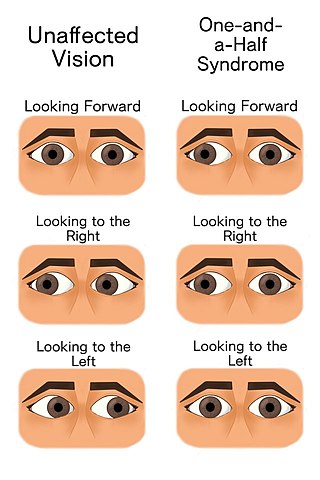
The one and a half syndrome is a rare weakness in eye movement affecting both eyes, in which one cannot move laterally at all, and the other can move only in outward direction. More formally, it is characterized by "a conjugate horizontal gaze palsy in one direction and an internuclear ophthalmoplegia in the other". Nystagmus is also present when the eye on the opposite side of the lesion is abducted. Convergence is classically spared as cranial nerve III and its nucleus is spared bilaterally.
A functional symptom is a medical symptom with no known physical cause. In other words, there is no structural or pathologically defined disease to explain the symptom. The use of the term 'functional symptom' does not assume psychogenesis, only that the body is not functioning as expected. Functional symptoms are increasingly viewed within a framework in which 'biological, psychological, interpersonal and healthcare factors' should all be considered to be relevant for determining the aetiology and treatment plans.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS). Several therapies for it exist, although there is no known cure.
Inflammatory demyelinating diseases (IDDs), sometimes called Idiopathic (IIDDs) due to the unknown etiology of some of them, are a heterogenous group of demyelinating diseases - conditions that cause damage to myelin, the protective sheath of nerve fibers - that occur against the background of an acute or chronic inflammatory process. IDDs share characteristics with and are often grouped together under Multiple Sclerosis. They are sometimes considered different diseases from Multiple Sclerosis, but considered by others to form a spectrum differing only in terms of chronicity, severity, and clinical course.
Ocrelizumab, sold under the brand name Ocrevus, is a medication used for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. It is a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. It targets CD20 marker on B lymphocytes and is an immunosuppressive drug. Ocrelizumab binds to an epitope that overlaps with the epitope to which rituximab binds. It is administered by intravenous infusion. The fixed-dose combination ocrelizumab/hyaluronidase is administered by subcutaneous injection.

Angiofibroma (AGF) is a descriptive term for a wide range of benign skin or mucous membrane lesions in which individuals have:
- benign papules, i.e. pinhead-sized elevations that lack visible evidence of containing fluid;
- nodules, i.e. small firm lumps usually > 1 mm in diameter; and/or
- tumors, i.e. masses often regarded as ~8 mm or larger.

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neurone disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD) in the United States, is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness, twitches, weakness, and wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as limb-onset or bulbar-onset.

Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure. One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud's syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small, dilated blood vessels.

Current standards for diagnosing multiple sclerosis (MS) are based on the 2018 revision of McDonald criteria. They rely on MRI detection of demyelinating lesions in the CNS, which are distributed in space (DIS) and in time (DIT). It is also a requirement that any possible known disease that produces demyelinating lesions is ruled out before applying McDonald's criteria.

Siponimod, sold under the brand name Mayzent, is a selective sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator for oral use that is used for multiple sclerosis (MS). It is intended for once-daily oral administration.
Radiologically isolated syndrome (RIS) is a clinical situation in which a person has white matter lesions suggestive of multiple sclerosis (MS), as shown on an MRI scan that was done for reasons unrelated to MS symptoms. The nerve lesions in these people show dissemination in space with an otherwise normal neurological examination and without historical accounts of typical MS symptoms.

Truncal ataxia is a wide-based "drunken sailor" gait characterised by uncertain starts and stops, lateral deviations and unequal steps. It is an instability of the trunk and often seen during sitting. It is most visible when shifting position or walking heel-to-toe.












