
Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia, or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as Aysheaia and Hallucigenia. However, other genera like Kerygmachela and Pambdelurion are often referred to as “gilled lobopodians”.

Polychaeta is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes. Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm and the sandworm or clam worm Alitta.
Pikaia gracilens is an extinct, primitive chordate animal known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia. Described in 1911 by Charles Doolittle Walcott as an annelid, and in 1979 by Harry B. Whittington and Simon Conway Morris as a chordate, it became "the most famous early chordate fossil", or "famously known as the earliest described Cambrian chordate". It is estimated to have lived during the latter period of the Cambrian explosion. Since its initial discovery, more than a hundred specimens have been recovered.

Wiwaxia is a genus of soft-bodied animals that were covered in carbonaceous scales and spines that protected it from predators. Wiwaxia fossils—mainly isolated scales, but sometimes complete, articulated fossils—are known from early Cambrian and middle Cambrian fossil deposits across the globe. The living animal would have measured up to 5 centimetres (2 in) when fully grown, although a range of juvenile specimens are known, the smallest being 2 millimetres (0.08 in) long.
Aplacophora is a possibly paraphyletic taxon. This is a class of small, deep-water, exclusively benthic, marine molluscs found in all oceans of the world.

Dinocaridida is a proposed fossil taxon of basal arthropods, which flourished during the Cambrian period and survived up to Early Devonian. Characterized by a pair of frontal appendages and series of body flaps, the name of Dinocaridids refers to the suggested role of some of these members as the largest marine predators of their time. Dinocaridids are occasionally referred to as the 'AOPK group' by some literatures, as the group compose of Radiodonta, Opabiniidae, and the "gilled lobopodians" Pambdelurion and Kerygmachelidae. It is most likely paraphyletic, with Kerygmachelidae and Pambdelurion more basal than the clade compose of Opabiniidae, Radiodonta and other arthropods.

Sirius Passet is a Cambrian Lagerstätte in Peary Land, Greenland. The Sirius Passet Lagerstätte was named after the Sirius sledge patrol that operates in North Greenland. It comprises six places in Nansen Land, on the east shore of J.P. Koch Fjord in the far north of Greenland. It was discovered in 1984 by A. Higgins of the Geological Survey of Greenland. A preliminary account was published by Simon Conway Morris and others in 1987 and expeditions led by J. S. Peel and Conway Morris have returned to the site several times between 1989 and the present. A field collection of perhaps 10,000 fossil specimens has been amassed. It is a part of the Buen Formation.

The halkieriids are a group of fossil organisms from the Lower to Middle Cambrian. Their eponymous genus is Halkieria, which has been found on almost every continent in Lower to Mid Cambrian deposits, forming a large component of the small shelly fossil assemblages. The best known species is Halkieria evangelista, from the North Greenland Sirius Passet Lagerstätte, in which complete specimens were collected on an expedition in 1989. The fossils were described by Simon Conway Morris and John Peel in a short paper in 1990 in the journal Nature. Later a more thorough description was undertaken in 1995 in the journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London and wider evolutionary implications were posed.

Pambdelurion is an extinct genus of panarthropod from the Cambrian aged Sirius Passet site in northern Greenland. Like the morphologically similar Kerygmachela from the same locality, Pambdelurion is thought to be closely related to arthropods, combining characteristics of "lobopodians" with those of primitive arthropods.

Halwaxiida or halwaxiids is a proposed clade equivalent to the older orders Sachitida He 1980 and Thambetolepidea Jell 1981, loosely uniting scale-bearing Cambrian animals, which may lie in the stem group to molluscs or lophotrochozoa. Some palaeontologists question the validity of the Halwaxiida clade.

The origin of the brachiopods is uncertain; they either arose from reduction of a multi-plated tubular organism, or from the folding of a slug-like organism with a protective shell on either end. Since their Cambrian origin, the phylum rose to a Palaeozoic dominance, but dwindled during the Mesozoic.

Plumulites is an extinct genus of machaeridians, extinct annelid group.

The Fezouata Formation or Fezouata Shale is a geological formation in Morocco which dates to the Early Ordovician. It was deposited in a marine environment, and is known for its exceptionally preserved fossils, filling an important preservational window beyond the earlier and more common Cambrian Burgess shale-type deposits. The fauna of this geological unit is often described as the Fezouata biota, and the particular strata within the formation which exhibit exceptional preservation are generally termed the Fezouata Lagerstätte.

Myoscolex is an early animal known from the Cambrian Emu Bay Shale in South Australia. It is of unknown affinity but has been interpreted as an annelid and as an arthropod close to Opabinia. Myoscolex is the earliest known example of phosphotized muscle tissue, and as to which shows distinct annulation.
Multiplacophora is a stem-group of chitons with a number of plates arranged in 7 rows along the body. They date to at least the Upper Cambrian, but two lower Cambrian fossils- Ocruranus and Trachyplax - may extend the range downwards.

The annelids, also known as the segmented worms, comprise a large phylum called Annelida. The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments.

Amplectobeluidae is a clade of Cambrian radiodonts. It currently includes five definitive genera, Amplectobelua, Lyrarapax, Ramskoeldia, Guanshancaris and a currently unnamed genus from the lower Cambrian aged Sirius Passet site in Greenland. There is also a potential fifth genus, Houcaris, but that genus has become problematic in terms of its taxonomic placement.

Collinsovermis is a genus of extinct panarthropod belonging to the group Lobopodia and known from the middle Cambrian Burgess Shale in British Columbia, Canada. It is monotypic having only one species, Collinsovermis monstruosus. After its initial discovery in 1983, Desmond H. Collins popularised it as a unique animal and was subsequently dubbed "Collins' monster" for its unusual super armoured body. The formal scientific description and name were given in 2020. A similar lobopodian is known from the Emu Bay Shale, however it remains unnamed.
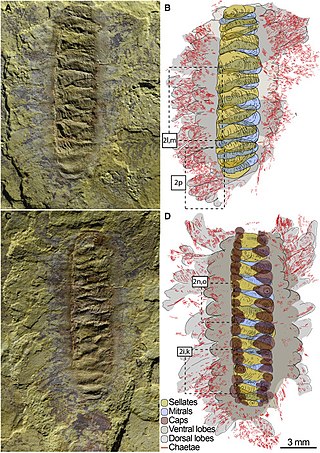
Wufengella is a genus of extinct camenellan "tommotiid" that lived during the Early Cambrian. Described in 2022, the only species Wufengella bengtsonii was discovered from the Maotianshan Shales of Chiungchussu (Qiongzhusi) Formation in Yunnan, China. The fossil indicates that the animal was an armoured worm that close to the common ancestry of the phyla Phonorida, Brachiozoa and Bryozoa, which are collectively grouped into a clade called Lophophorata.
Shishania is a genus of stem-group mollusc from the Cambrian period. It contains a single species, Shishania aculeata. Shishania specimens come from the Wulongqing Formation in China, and date back to around 514 to 509 million years ago. Shishania was a flattened, bilaterally symmetrical slug-like animal with a muscular foot. It had no shell, but was covered in hollow chitinous spines. These sclerites provide a stepping stone between the solid chaetae-like chitinous sclerites of Wiwaxia and the partially hollow, biomineralized sclerites of aculiferan molluscs. This suggests the mollusc ancestor was covered in hollow chitinous sclerites that shared a common origin with annelid chaetae.


















