
The Mastigoteuthidae, also known as whip-lash squid, are a family of small deep-sea squid. Approximately 20 known species in six genera are represented, with members found in both the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zone of most oceans. Originally described by Verill in 1881, it was later lowered by Chun (1920) to a subfamily (Mastigoteuthinae) of the Chiroteuthidae. However, Roper et al. (1969) raised it back to the family level, and this has not been changed since. The taxonomy of this family is extremely unstable, and there have been at times one genus, two genera and four subgenera(Salcedo-Vargas & Okutani, 1994), two genera and several 'groups', five genera and one species with an uncertain placement, or six genera.

Bigfin squids are a group of rarely seen cephalopods with a distinctive morphology. They are placed in the genus Magnapinna and family Magnapinnidae. Although the family was described only from larval, paralarval, and juvenile specimens, numerous video observations of much larger squid with similar morphology are assumed to be adult specimens of the same family.

Taningia danae, the Dana octopus squid, is a species of squid in the family Octopoteuthidae. It is one of the largest known squid species, reaching a mantle length of 1.7 m (5.6 ft) and total length of 2.3 m (7.5 ft). The largest known specimen, a mature female, weighed 161.4 kg (356 lb).[nb a]
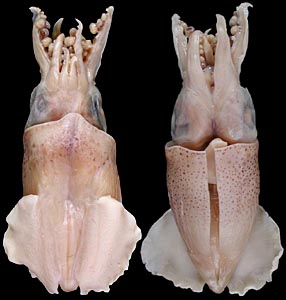
A. aldrichi is a small species of squid found in northern Australian waters. The species was described by Chung Cheng Lu in 2005 based on specimens collected in the inshore waters of Northern Australia. The largest known individual of this species is a mature female measuring 27.6 mm (1.09 in) in mantle length (ML). The holotype is a mature male of 21.3 mm (0.84 in) ML. A live specimen of A. aldrichi has yet to be recorded.

Cephalopods, which include squids and octopuses, vary enormously in size. The smallest are only about 1 centimetre (0.39 in) long and weigh less than 1 gram (0.035 oz) at maturity, while the giant squid can exceed 10 metres (33 ft) in length and the colossal squid weighs close to half a tonne (1,100 lb), making them the largest living invertebrates. Living species range in mass more than three-billion-fold, or across nine orders of magnitude, from the lightest hatchlings to the heaviest adults. Certain cephalopod species are also noted for having individual body parts of exceptional size.

Magnapinna pacifica is a species of bigfin squid known only from three immature specimens; two caught at a depth of less than 300 m (980 ft) and one from a fish stomach. M. pacifica is the type species of the genus Magnapinna. It is characterised primarily by its proximal tentacles, which are wider than adjacent arms and bear numerous suckers.
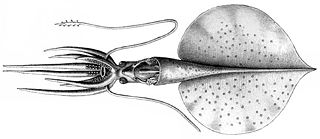
Magnapinna talismani is a species of bigfin squid known only from a single damaged specimen. It is characterised by small white nodules present on the ventral surface of its fins.
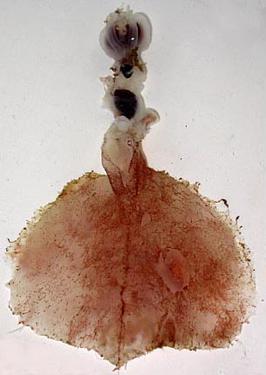
Magnapinna sp. B is an undescribed species of bigfin squid known only from a single immature specimen collected in the northern Atlantic Ocean.

Magnapinna sp. C is an undescribed species of bigfin squid known only from a single specimen of 79-millimetre (3.1 in) mantle length (ML) collected in the southern Atlantic Ocean and held in the Natural History Museum.

Promachoteuthis sloani is a species of squid from the northern Atlantic Ocean. It was known from only three dead specimens until 2024 when a live specimen was observed and photographed in the Nazca Ridge. Very little is understood of its biology. P. sloani is characterised by several morphological features: nuchal fusion is absent between the head and mantle, the arms generally bear 3–4 series of suckers, and papillae are present on the tentacles.
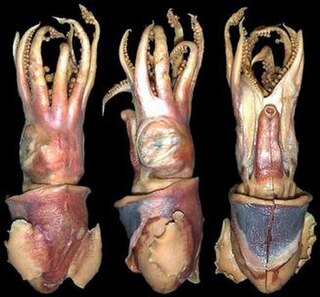
Choneteuthis tongaensis is a species of bobtail squid native to the waters around the Tonga Islands in the southern Pacific Ocean. It is known from only three specimens. Of these, the holotype is the largest, at 33.8 mm mantle length (ML). C. tongaensis is characterised by several distinct morphological features: the mantle is free from the head in the nuchal region, a large, circular visceral photophore and ventral shield are present on the ventral surface of the ink sac, and the broad keel extends the full length of the club.

Asperoteuthis acanthoderma, the thorny whiplash squid, is a large species of squid belonging to the family Chiroteuthidae. It is characterised by the tiny, pointed tubercules present on its skin and a Y-shaped groove in the funnel locking apparatus.
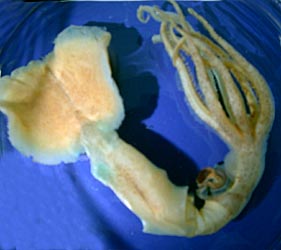
Asperoteuthis mangoldae, previously known as Asperoteuthis sp. A, is a chiroteuthid squid known only from the waters off the Hawaiian Islands. It differs from the closely related Asperoteuthis acanthoderma in lacking integumental tubercles and elongate fins. This species also possesses a characteristic curved groove in its funnel locking apparatus.

Histioteuthis bonnellii, the umbrella squid, is a species of cock-eyed squid belonging to the family Histioteuthidae.
Nephropsis atlantica, sometimes called the scarlet lobsterette or scarlet clawed lobster, is a species of lobster from the Atlantic Ocean.

Illex coindetii, commonly known as the southern shortfin squid or broadtail shortfin squid, is a species of neritic squids in the family Ommastrephidae. They are found in the Mediterranean Sea and on both sides of the north Atlantic Ocean.

Teuthowenia megalops, sometimes known as the Atlantic cranch squid, is a species of glass squid from the subarctic and temperate waters of the northern Atlantic Ocean. They are moderately sized squid with a maximum mantle length of 40 cm (16 in). Their very large eyes are the source for the specific name megalops. Like other members of the genus Teuthowenia, they are easily recognizable by the presence of three bioluminescent organs (photophores) on their eyeballs.
Mastigotragus is a genus of whip-lash squid containing a single species, Mastigotragus pyrodes. This species was originally placed within Mastigoteuthis, but has been subsequently separated from other species in that genus due to multiple morphological characters. This genus is characterized by a lack of antitragus in the funnel-locking cartilage, larger sucker rings on the tentacles, a particular photophore morphology, and relatively large eyelid photophore. This genus is Latin for 'whip-lash goat'.

Slosarczykovia is a monotypic genus of squid, its sole representative being Slosarczykovia circumantarctica. Slosarczykovia is placed in the family Brachioteuthidae.

Grimpoteuthis plena is known from only one specimen, which cannot be easily separated from other species of Grimpoteuthis in the Atlantic Ocean. The specimen was in poor condition. It's similar to Grimpoteuthis wuelkeri, and may be a junior specimen of Grimpoteuthis umbellata.



















