Kalinga is a historical region of India. It is generally defined as the eastern coastal region between the Mahanadi and the Godavari rivers, although its boundaries have fluctuated with the territory of its rulers. The core territory of Kalinga now encompasses a large part of Odisha and northerneastern part of Andhra Pradesh. At its widest extent, the Kalinga region also included parts of present-day southwestern West Bengal and Chhattisgarh.

Rayagada is a district in southern Odisha, a state in India, which became a separate district in October 1992. Its population consists mainly of tribes, primarily the Khonds and the Soras. In addition to Odia, Kui and Sora are spoken by the district's indigenous population. It was founded by Maharajah Vishwanath Dev Gajapati of the Suryavansh dynasty of Jeypore.

Jeypore is one of the largest towns and a place of historical significance in Koraput district in the Indian state of Odisha. It was established as a capital of king Vir Vikram Dev in the mid 17th century. The kingdom was defeated by the East India Company in 1777 and was made a Zamindari and later was promoted to a Princely state until its dissolution in the Dominion of India in 1947.
Quli Qutb Mulk, known by the regnal name Quli Qutb Shah, was the founder of the Qutb Shahi dynasty, which ruled the Sultanate of Golconda in southern India from 1518 to 1687.

Nabarangpur district, also known as Nabarangapur district and Nawarangpur district, is a district of Odisha, India. The city of Nabarangpur is the district capital. Most of its population is tribal and the land is heavily forested. It borders Kalahandi and Koraput districts. Nabarangpur district is situated at 19.14′ latitude and 82.32′ longitude at an average elevation of 572 metres (1,877 ft).

Gajapati is a district of Odisha, India. It was created from Ganjam District on 2 October, 1992. Gajapati district was named after Krushna Chandra Gajapati Narayan Deb, the King of the Paralakhemundi estate and the first Prime Minister of Orissa, who is remembered for his contribution in the formation of a separate state, and inclusion of his estate in Odisha. The district headquarters at Paralakhemundi, formerly a Zamindari, has been clustered within a radius of approximately 5 kilometers around the geometric centre of Paralakhemundi. The District is a part of the Red Corridor.

Rayagada is a municipality in Rayagada district in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the administrative headquarters of Rayagada district.

Bissam Cuttack is a census town in the Rayagada district, within the state of Odisha, India. It is one of the identified Tourist Centres of Odisha.

Gunupur is a Municipality and one of the sub-divisional headquarters of Rayagada district in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the second biggest town in Rayagada district.

The Gajapati Empire was a Royal dynasty established by the Suryavamsa or Routray dynasty, who were a medieval Hindu dynasty from the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Odradesha from 1434 to 1541 CE. Under Kapilendra Deva, Gajapatis became an empire stretching from the lower Ganga in the north to the Kaveri in the south.

Madugula is a village in Visakhapatnam district in the state of Andhra Pradesh in India. It was also known as Vaddadi or Vaddadimadugula and was founded by the rulers of the Matsya dynasty. Later, it merged into the kingdom of Nandapur - Jeypore and during the British Raj it remained an independent Zamindari for sometime. Later, in 1915 the zamindaris of Madugula and Pachipenta were purchased by Maharaja Vikram Dev III and they became a part of Jeypore Samasthanam until 1947.

Uttarandhra is a region consisting of three north coastal districts of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It comprises the districts of Srikakulam, Vizianagaram and Visakhapatnam. As of 2011 census of India, the region with three districts has a population of 9,338,177.

The Eastern Ganga dynasty also known as Rudhi Gangas or Prachya Gangas were a large medieval era Indian royal dynasty that reigned from Kalinga from as early as the 5th century to the early 15th century. The territory ruled by the dynasty consisted of the whole of the modern-day Indian state of Odisha as well as major parts of West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. The early rulers of the dynasty ruled from Dantapuram; the capital was later moved to Kalinganagara, and ultimately to Kataka . Today, they are most remembered as the builders of the world renowned Puri Jagannath Temple and Konark Sun Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site at Konark, Odisha.

Purunagada or Purnagarh is the easternmost locality of Jeypore in Odisha, India. It is a place of historical significance as it was once the main fort of the Maharajas of Jeypore. It was constructed by Maharaja Vir Vikram Dev after he shifted the capital of his kingdom from Nandapur to Jeypore. In modern era, the place is known for its numerous ancient temples built by the erstwhile kings.
Poosapati / Pusapati was the ruling clan of the Northern Andhra region, Vizianagaram.

Biswanathpur is a village in Ganjam district in the south of Odisha, India, bordering Andhra Pradesh. This village owes its name to Vishwanath Dev Gajapati, the Suryavanshi king of Kalinga who founded this place after conducting a royal anicent ritual known as 'Vajapeya Yagna'. It is located southeast of Berhampur and northeast of Ichchapuram.
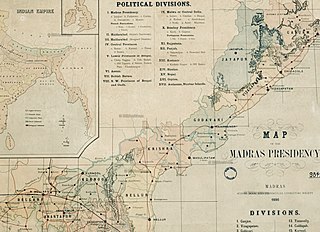
Jeypore Estate or Jeypore Zamindari was a Zamindari estate of the Madras Presidency in British India. Earlier, it was known as Jeypore Kingdom, located in the Kalinga region. The kingdom was independent from the mid-15th century to 1777 CE, when it became a vassal state of the British. It was also a tributary of Qutb Shahi Sultanate for some years. It eventually formed a part of the linguistic Orissa Province in 1936 upon transfer from the Madras Province and became a part of the independent Union of India in 1947.
Vishwanath Dev Gajapati was the king of Kalinga who established a kingdom in the region of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh, historically known as Kalinga. He belonged to the Suryavansh dynasty that was installed in the region by his grandfather Vinayak Dev who was a prince of the ancient branch of the dynasty, he migrated from Kashmir to Nandapur - a kingdom in Southern Odisha.

Maharaja of Jeypore was the principal title used by the rulers of the Kingdom of Jeypore until its dissolution in 1947. The title was used by the titular rulers until the removal of titles and privileges of all princely states and estates of India by the 26th amendment of the Constitution of India. However, due to the significance given to the cultural and religious role of a king, evidently, Vishweshwar Dev in 2013 became the Maharaja of Jeypore in pretense.

Maharajah Vikram Dev I or Vikram Dev was the king of Jeypore kingdom from 1758 to 1781. He was born in the Suryavansh Shankara Dynasty that ruled the region since 1443. He succeeded his brother Maharaja Lal Krishna Dev in a military coup in what is described as a critical period when the kingdom was under attack from all directions. The king battled and protected his kingdom from the French East India Company in Malkangiri, Marathas in Umerkote belt and the East India Company - Pusapati alliance in Jeypore and Rayagada. He retransferred the capital from Narayanapatna to Jeypore which had been deserted from the time of Balaram Dev in 1711. In the last years of his reign, the kingdom was demoted to a zamindari after they were defeated by the British. He was the 19th king of the Suryavansh dynasty of Kalinga that previously ruled the kingdom from Nandapur.
















