
Mangalore, officially known as Mangaluru, is a major industrial port city in the Indian state of Karnataka and on the west coast of India. It is located between the Laccadive Sea and the Western Ghats about 352 km (219 mi) west of Bangalore, the state capital, 14 km north of Karnataka–Kerala border and 297 km south of Goa. Mangalore is the state's only city to have all four modes of transport—air, road, rail and sea. The population of the urban agglomeration was 619,664 according to the 2011 national census of India. It is known for being one of the locations of the Indian strategic petroleum reserves.

Dakshina Kannada district is located in the state of Karnataka in India, with its headquarters in the coastal city of Mangalore. The district covers an area nestled in between the Western Ghats to its east and the Arabian Sea to its west. Dakshina Kannada receives abundant rainfall during the Indian monsoon. It is bordered by Udupi district to the north, Chikmagalur district to the northeast, Hassan district to the east, Kodagu to the southeast and Kasaragod district of Kerala to the south. According to the 2011 census of India, Dakshina Kannada district had a population of 2,083,625. It is the only district in Karnataka state to have all modes of transport like road, rail, water and air due to the presence of a major hub, Mangalore. This financial district is also known as the Cradle of Indian banking.

Surathkal is one of the major localities in the northern part of Mangalore city located on National Highway 66 in the Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka state, India on the shore of Arabian sea. It is a municipality merged with Mangalore City Corporation. It lies between Gurupura (Phalguni) and Pavanje (Nandini) rivers. It is the northern suburb and can be considered as the northernmost area of Mangalore City until Mukka. Surathkal has a railway station on Konkan railway route which connects cities of Mumbai to Mangaluru. Surathkal is 8 km north of New Mangalore seaport, 4 km west of Mangalore Refinery and Petrochemicals Limited and 16 km west of Mangalore International Airport This region has developed educationally, industrially and commercially can be regarded as one of the crucial localities in Mangaluru and coastal Karnataka. The only NIT of Karnataka is situated here which is adjacent to the national highway NH 66. Mukka a popular name in Indian surfing is also situated close to Surathkal. Surathkal beach is well known for its cleanliness and well maintained like other beaches in Mangalore.

The Government of Karnataka, abbreviated as GoK or GoKA, formerly known as Government of Mysore (1956–1974), is a democratically elected state body with the governor as the ceremonial head to govern the Southwest Indian state of Karnataka. The governor who is appointed for five years appoints the chief minister and on the advice of the chief minister appoints their council of ministers. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day-to-day running of the government is taken care of by the chief minister and their council of ministers in whom a great amount of legislative powers are vested.

Deralakatte is a major educational, healthcare, commercial and residential locality in the south-eastern part of Mangalore City in the Dakshina Kannada district of Karnataka state. It is 9 km (5.6 mi) away from the Karnataka-Kerala state border. It is popularly known as the University Town owing to its student population and universities. The stretch from Thokottu junction to Konaje is known as the Medical corridor road due to the presence of many premium educational institutions and healthcare facilities. It is close to Mangalore University, Konaje, Mudipu Infosys, Soorya Infratech Park, Thokottu and Ullal. Ullal beach, Someshwar Beach, Pilikula Nisargadhama are some of the nearest tourist destinations. This locality houses the NITTE University, Yenepoya University, Father Muller Charitable Institutions, Fathers Mullers Homeopathic Medical college Hospital and Kanachur Groups of Institutions and Hospital. It is a largest University locality in Mangalore after Manipal university in terms of students from all over the country and other parts of the world.

Mangalore Central railway station (station code: MAQ) is an NSG–3 category Indian railway station in Palakkad railway division of Southern Railway zone. It is the main railway terminus in the city of Mangalore which lies in the heart of the city. It is one of the major railway stations in Karnataka state and it is the biggest terminal station under Palakkad railway division. There is also another railway station named Mangalore Junction railway station, previously known as Kankanady railway station. The Mangalore region provides the highest freight revenue to the Palakkad division, which sums up to 90 per cent of the total revenue which the Palakkad division generates. Mangalore Central comes under the Southern Railway and also provides connectivity for Konkan Railway and South Western Railway of the Indian Railways. It is one of the 5 central railway stations of India.

The Thrissur Municipal Corporation is the civic body that governs Thrissur city in Kerala, India. It is the third largest city Corporation in the state of Kerala by area and fourth largest in population. Established as a Municipality since 1921 under the Cochin Municipal Regulations, it is responsible for civic infrastructure and administration; the distribution of electricity and water for Thrissur city. The Corporation manages 101.42 km of Thrissur city limits of through 55 wards through five zones Ayyanthole, Vilvattom, Ollukkara, Ollur and Koorkanchery. Thrissur Municipal Corporation has been formed with functions to improve the infrastructure of town.

Bondel is a residential locality in Mangalore city, Karnataka, India. It is one of the upscale residential localities of Mangalore. Bondel along with Maryhill houses many highrise buildings and also developing rapidly as a commercial center. It lies in Airport road, which originates in KPT Junction and extends till Mangalore International Airport. Kavoor, one of the major localities of Mangalore is located nearby. This locality is close to the airport too.

Mysuru City Corporation (MCC) is the administrative body responsible for civic amenities and infrastructural assets of Mysuru in Karnataka, India. It is the third-largest municipal corporation in Karnataka, serving a population of 1,000,000 in an area of 235 km2. The city's boundaries have expanded more than twice between 2010 and 2020.
John Richard Lobo, popularly known as J. R. Lobo, is an Indian politician with the Indian National Congress and former MLA of Mangalore South constituency in Karnataka, India. MLA J.R Lobo proposed the installation of musical fountain with laser show at Kadri Park, which is the largest lung space in the city. J.R Lobo also proposed the construction of the 3D 8K Planetarium at Pilikula in Mangalore, which was inaugurated in March 2018.

Shimla Municipal Corporation (SMC) is the municipal corporation of Shimla, the capital of Himachal Pradesh, and is the chief nodal agency for the administration of the city. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Shimla Municipal Corporation is headed by Mayor of city and governed by Commissioner. Shimla Municipal Corporation has been formed with functions to improve the infrastructure of town.

Srikakulam Municipal Corporation is the civic body that governs the city of Srikakulam in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It was formed as a municipality in the year 1856 and was upgraded to corporation on 9 December 2015. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Srikakulam Municipal Corporation Municipal Corporation is headed by Mayor of city and governed by Commissioner.

Vizianagaram Municipal Corporation is the civic body that governs the city of Vizianagaram in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. The municipality was first constituted in the year 1888 and was upgraded to corporation on 9 December 2015. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Vizianagaram Municipal Corporation is headed by Mayor of city and governed by Commissioner.

Surathkal railway station is one of the main railway stations of Mangalore city along with Mangalore Central railway station and Mangalore Junction railway station and is located in north Mangaluru on Konkan Railway route. Twenty-two trains stop here.KRCL operates RO-RO services from Suratkal to Verna, Kolad, and Karembeli. As per the Konkan railway map, Surathkal railway station is at a distance of 733.825 kilometers from the northern starting point of the Konkan railway line at Roha and 4.615 kilometers from Thokur which is the southern endpoint of Konkan railway jurisdiction. The Surathkal railway station is at distance of 26.285 Kilometre from Mangaluru Central(MAQ) railway station.

Mangalore City North Assembly constituency is one of the Karnataka Legislative Assemblies or Vidhan Sabha constituencies in Karnataka. Mangalore City North is part of Dakshina Kannada Lok Sabha constituency along with seven other Vidhan Sabha segments, namely: 201. Moodabidri, 203. Mangalore City South, 204. Mangalore, 205. Bantwal, 206. Puttur and 207. Sullia.
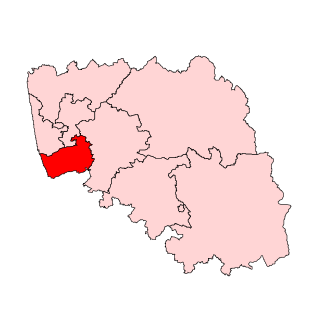
Mangalore Assembly constituency is one of the Karnataka Legislative Assemblies or Vidhan Sabha constituencies in Karnataka, India which belongs to Dakshina Kannada Lok Sabha constituency. Mangalore constituency, along with Mangalore City South and Mangalore City North, represents Mangalore City. The constituency has 45% Muslims population and 6% Christians.

The Kannur Municipal Corporation is the municipal corporation that administers the city of Kannur, Kerala. Established in 2015, the Corporation's first mayor was E. P. Latha. Kannur Corporation has two assembly constituencies – Kannur Assembly constituency and Azhikode Assembly constituency – both of which are part of the Kannur parliamentary constituency. The Corporation is headed by a Mayor and council, and manages 78.35 km2 of Kannur city, with a population of about 232,486 within that area. Kannur Municipal Corporation has been formed with functions to improve the infrastructure of town.
Mohiuddin Bava is an Indian politician from the state of Karnataka. He represented the Mangalore City North seat as a member of the Indian National Congress party in the Karnataka Legislative Assembly from 2013 to 2018.

Kalaburagi City Corporation (KCC) is the municipal corporation responsible for looking after the city administration of the Indian city of Kalaburagi. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. It consists of a legislative and an executive body. The legislative body is headed by the city mayor while the executive body is headed by a Chief Commissioner.

Davanagere City Corporation (DCC) is the civic organisation that manages the municipal affairs of Davanagere City in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the 6th largest Urban Local Body in Karnataka. The town administration of Davanagere city was upgraded as a Municipality in c.1870 and later as a City Corporation on 6 January 2006. The Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with the formation of municipal corporations in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. It has a territorial area of 68.63 km2 and a population of 4,34,971, as per the 2011 Census of India. The territorial limits of the City Corporation fall under the Davanagere North and Davanagere South legislative assembly constituencies.




















