
Oio is a region in Guinea-Bissau. Its capital is Farim. Other major cities and towns include Nhacra, Mansôa, Bissorã and Cumeré. The region borders Senegal to the north, the Guinea-Bissau regions of Bafatá, Bissau and Biombo to the east, the Rio Geba/Guinea-Bissau region of Quinara to the south and the Guinea-Bissau region of Cacheu to the west. There has not been any local administration since the civil war of 1998-99 and all the social services are done by organs of civil society and other government agencies. It is a coastal region covered with Mangrove swamps, rain forest and tangled forest and receives an annual rainfall of more than 1,000 mm (39 in), while the inland has Savannah woodlands.
Hymenaea protera is an extinct prehistoric leguminous tree, the probable ancestor of present-day Hymenaea species. Most neotropical ambers come from its fossilized resin, including the famous Dominican amber.

Hymenaea L. is a genus in the flowering plant family Fabaceae. Of fourteen living species in the genus, all but one are native to the tropics of the Americas, with one additional species on the east coast of Africa. Some authors place the African species in a separate monotypic genus, Trachylobium. In the Neotropics, Hymenaea is distributed through the Caribbean islands, and from southern Mexico to Brazil. Linnaeus named the genus in 1753 in Species Plantarum for Hymenaios, the Greek god of marriage ceremonies. The name is a reference to the paired leaflets.
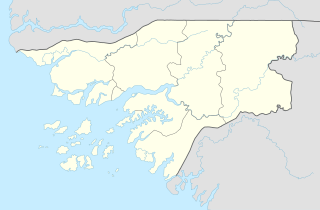
Mansôa is a town located in the Oio Region of Guinea-Bissau. Population 7,376. The Sua language is spoken in Mansôa.

There are 39 sectors of Guinea-Bissau which subdivide the regions. The sectors are further subdivided into smaller groups called sections ; which are further subdivided into populated places. Here are the following listed below, by region:

Hymenaea courbaril, the courbaril or West Indian locust, is a tree common in the Caribbean, Central America, and South America. It is a hardwood that is used for furniture, flooring, and decoration. Its hard fruit pods have edible dry pulp surrounding the seeds. Its sap, called animé, is used for incense, perfume, and varnish.
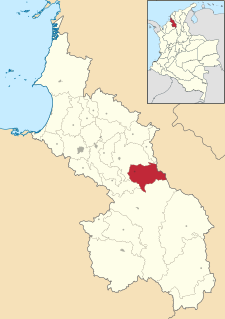
Galeras is a town and municipality located in the Sucre Department, northern Colombia. The main economic activities are agriculture and cattle raising. Galeras is 50 km away from the department's capital, Sincelejo.
Clube de Futebol Os Balantas is a Guinea-Bissauan football club based in Mansôa. They play in the top division in Guinean football, the Campeonato Nacional da Guiné-Bissau. The club is named after the Balanta people, the club location where the people inhabit. Mansoa is the main city of the Balantas in Guinea-Bissau. It is being the most popular club of the Oio Region.
Indio Maíz Biological Reserve is situated on the southeastern corner of Nicaragua bordering the San Juan River and Costa Rica. Measuring about 3,180 square kilometers, it is one of the largest protected lowland forest system in Central America, the second largest lowland rainforest reserve in Nicaragua and is a key component in the proposed Mesoamerican Biological Corridor. It has previously been referred to as "the gem of Central American nature reserves" by UCLA biologists. Indio Maíz is rich in biodiversity, holding a higher number in species of trees, birds, and insects than all of Europe. In recent years, a growing timber and oil palm industry has led to increasing rates of deforestation along the northern and western flanks of Indio Maíz.

Pantala hymenaea is a dragonfly of the family Libellulidae. It is a migratory species and is native to North, Central and South America, travelling widely and breeding in temporary water bodies. It looks very similar to the wandering glider, with the addition of a dark basal spot on the hindwing. It is a common species with a very large range and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has listed it as being of "least concern".
Hymenaea martiana is a tree species in the genus Hymenaea found in Brazil and Paraguay.
Sua, also known as Mansoanka or Kunante, is a divergent Niger–Congo language spoken in the Mansôa area of Guinea-Bissau.

Mansoa is a genus of tropical, flowering vines in the family Bignoniaceae.
Mansoa difficilis is a species of neotropical liana in the family Bignoniaceae. It is native to Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay. Its flowers range in colour from fuchsia to purple.

Mansoa verrucifera is a species of liana in the family Bignoniaceae. It is native to Mexico, Guyana, and Venezuela. M. verrucifera bears long, narrow fruit, and has trifoliolate leaves that grow oppositely.
Hymenaea mexicana is an extinct legume species in the family Fabaceae described from a series of isolated fossil petals, leaflets, and amber. The species is known from a group of Late Oligocene to Early Miocene locations in southern Mexico. It is one of two extinct Hymenaea species placed close to the living species Hymenaea verrucosa and along with Hymenaea allendis, is one of the two extinct species which have been found in Mexican amber.
Hymenaea allendis is an extinct legume species in the family Fabaceae described from a single isolated fossil flower in amber. The species is known from a Late Oligocene to Early Miocene location in southern Mexico. Unlike the coeval extinct species Hymenaea mexicana and Hymenaea protera which are placed closer to the living species Hymenaea verrucosa of Africa, H. allendis is closer in relation to the neotropical species of Hymenaea.

Hymenaea stiginocarpa is an irregularly shaped, mostly 6–9 m (20–30 ft) high tree that has been assigned to the pea family. It has a twisted spindle-shaped trunk, a very rough grey bark, and reddish-brown twigs. The deciduous leaves consist of two large asymmetrical leaflets with an entire margin. The flowers occur in clusters of up to thirty at the end of the branches. It produces edible, highly appreciated fruits, which are often collected from the wild and used by local people. The vernacular name of this species in Brazil is jatobá do cerrado.










