Related Research Articles

A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and to further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylactic, or therapeutic. Some vaccines offer full sterilizing immunity, in which infection is prevented completely.
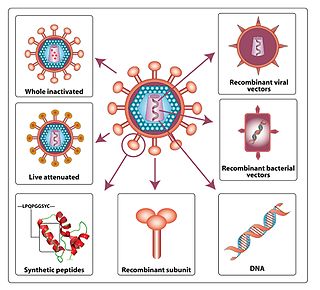
An HIV vaccine is a potential vaccine that could be either a preventive vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine, which means it would either protect individuals from being infected with HIV or treat HIV-infected individuals.
In biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens irrespective of their antigenic make-up. Other components of the immune system adapt themselves to each new disease encountered and can generate pathogen-specific immunity.

Vaccinia virus is a large, complex, enveloped virus belonging to the poxvirus family. It has a linear, double-stranded DNA genome approximately 190 kbp in length, which encodes approximately 250 genes. The dimensions of the virion are roughly 360 × 270 × 250 nm, with a mass of approximately 5–10 fg. The vaccinia virus is the source of the modern smallpox vaccine, which the World Health Organisation used to eradicate smallpox in a global vaccination campaign in 1958–1977. Although smallpox no longer exists in the wild, vaccinia virus is still studied widely by scientists as a tool for gene therapy and genetic engineering.

In immunology, seroconversion is the development of specific antibodies in the blood serum as a result of infection or immunization, including vaccination. During infection or immunization, antigens enter the blood, and the immune system begins to produce antibodies in response. Before seroconversion, the antigen itself may or may not be detectable, but the antibody is absent. During seroconversion, the antibody is present but not yet detectable. After seroconversion, the antibody is detectable by standard techniques and remains detectable unless the individual seroreverts. Seroreversion, or loss of antibody detectability, can occur due to weakening of the immune system or waning antibody concentration over time. Seroconversion refers the production of specific antibodies against specific antigens, meaning that a single infection could cause multiple waves of seroconversion against different antigens. Similarly, a single antigen could cause multiple waves of seroconversion with different classes of antibodies. For example, most antigens prompt seroconversion for the IgM class of antibodies first, and subsequently the IgG class.

Carnivore protoparvovirus 1 is a species of parvovirus that infects carnivorans. It causes a highly contagious disease in both dogs and cats. The disease is generally divided into two major genogroups: CPV-1 containing the classical feline panleukopenia virus (FPLV), and CPV-2 containing the canine parvovirus (CPV) which appeared in the 1970s.
Bovine alphaherpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1) is a virus of the family Herpesviridae and the subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae, known to cause several diseases worldwide in cattle, including rhinotracheitis, vaginitis, balanoposthitis, abortion, conjunctivitis, and enteritis. BoHV-1 is also a contributing factor in shipping fever, also known as bovine respiratory disease (BRD). It is spread horizontally through sexual contact, artificial insemination, and aerosol transmission and it may also be transmitted vertically across the placenta. BoHV-1 can cause both clinical and subclinical infections, depending on the virulence of the strain. Although these symptoms are mainly non-life-threatening it is an economically important disease as infection may cause a drop in production and affect trade restrictions. Like other herpesviruses, BoHV-1 causes a lifelong latent infection and sporadic shedding of the virus. The sciatic nerve and trigeminal nerve are the sites of latency. A reactivated latent carrier is normally the source of infection in a herd. The clinical signs displayed are dependent on the virulence of the strain. There is a vaccine available which reduces the severity and incidence of disease. Some countries in Europe have successfully eradicated the disease by applying a strict culling policy.
Correlates of immunity/protection to a virus or other infectious pathogen are measurable signs that a person is immune, in the sense of being protected against becoming infected and/or developing disease.
A breakthrough infection is a case of illness in which a vaccinated individual becomes infected with the illness, because the vaccine has failed to provide complete immunity against the pathogen. Breakthrough infections have been identified in individuals immunized against a variety of diseases including mumps, varicella, influenza, and COVID-19. The characteristics of the breakthrough infection are dependent on the virus itself. Often, infection of the vaccinated individual results in milder symptoms and shorter duration than if the infection were contracted naturally.

Vaccine efficacy or vaccine effectiveness is the percentage reduction of disease cases in a vaccinated group of people compared to an unvaccinated group. For example, a vaccine efficacy or effectiveness of 80% indicates an 80% decrease in the number of disease cases among a group of vaccinated people compared to a group in which nobody was vaccinated. When a study is carried out using the most favorable, ideal or perfectly controlled conditions, such as those in a clinical trial, the term "vaccine efficacy" is used. On the other hand, when a study is carried out to show how well a vaccine works when they are used in a bigger, typical population under less-than-perfectly controlled conditions, the term "vaccine effectiveness" is used.
An attenuated vaccine is a vaccine created by reducing the virulence of a pathogen, but still keeping it viable. Attenuation takes an infectious agent and alters it so that it becomes harmless or less virulent. These vaccines contrast to those produced by "killing" the virus.

Hepatitis B vaccine is a vaccine that prevents hepatitis B. The first dose is recommended within 24 hours of birth with either two or three more doses given after that. This includes those with poor immune function such as from HIV/AIDS and those born premature. It is also recommended that health-care workers be vaccinated. In healthy people routine immunization results in more than 95% of people being protected.
A Cytomegalovirus vaccine is a vaccine to prevent cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection or curb virus re-activation in persons already infected. Challenges in developing a vaccine include adeptness of CMV in evading the immune system and limited animal models. As of 2018 no such vaccine exists, although a number of vaccine candidates are under investigation. They include recombinant protein, live attenuated, DNA and other vaccines.
Herpes simplex research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure herpes, as well as fundamental research about the nature of herpes. Examples of particular herpes research include drug development, vaccines and genome editing. HSV-1 and HSV-2 are commonly thought of as oral and genital herpes respectively, but other members in the herpes family include chickenpox (varicella/zoster), cytomegalovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus. There are many more virus members that infect animals other than humans, some of which cause disease in companion animals or have economic impacts in the agriculture industry.
Dengue vaccine is a vaccine used to prevent dengue fever in humans. Development of dengue vaccines began in the 1920s, but was hindered by the need to create immunity against all four dengue serotypes.
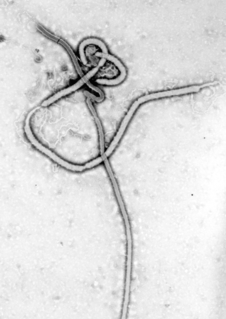
Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus–Zaire Ebola virus (rVSV-ZEBOV), also known as Ebola Zaire vaccine live and sold under the brand name Ervebo, is an Ebola vaccine for adults that prevents Ebola caused by the Zaire ebolavirus. When used in ring vaccination, rVSV-ZEBOV has shown a high level of protection. Around half the people given the vaccine have mild to moderate adverse effects that include headache, fatigue, and muscle pain.

Ebola vaccines are vaccines either approved or in development to prevent Ebola. The first vaccine to be approved in the United States was rVSV-ZEBOV in December 2019. It had been used extensively in the Kivu Ebola epidemic under a compassionate use protocol. During the early 21st century, several vaccine candidates displayed efficacy to protect nonhuman primates against lethal infection.
Raccoonpox virus (RCN) is a double-stranded DNA virus and a member of the orthopoxviruses in the family Poxviridae and subfamily Chordopoxvirinae which consists of eight genera: Avipoxvirus, Capripoxvirus, Leporipoxvirus, Molluscipoxvirus, Orthopoxvirus, Parapoxvirus, Suipoxvirus and Yatapoxvirus Vertebrates are the natural host of Chordopoxvirinae subfamily viruses. More specifically, raccoons are the natural hosts of RCN. RCN was isolated in 1961 from the upper respiratory tissues of 2 raccoons in a group of 92 observably healthy raccoons trapped close to Aberdeen, Maryland.

Animal vaccination is the immunisation of a domestic, livestock or wild animal. The practice is connected to veterinary medicine. The first animal vaccine invented was for chicken cholera in 1879 by Louis Pasteur. The production of such vaccines encounter issues in relation to the economic difficulties of individuals, the government and companies. Regulation of animal vaccinations is less compared to the regulations of human vaccinations. Vaccines are categorised into conventional and next generation vaccines. Animal vaccines have been found to be the most cost effective and sustainable methods of controlling infectious veterinary diseases. In 2017, the veterinary vaccine industry was valued at USD$7 billion and it is predicted to reach USD$9 billion in 2024.
Vaccine resistance is the evolutionary adaptation of pathogens to infect and spread through vaccinated individuals, analogous to antimicrobial resistance. It concerns both human and animal vaccines. Although the emergence of a number of vaccine resistant pathogens has been well documented, this phenomenon is nevertheless much more rare and less of a concern than antimicrobial resistance.
References
- ↑ van Oirschot, J. T.; Rziha, H. J.; Moonen, P. J.; Pol, J. M.; van Zaane, D. (July 1986). "Differentiation of serum antibodies from pigs vaccinated or infected with Aujeszky's disease virus by a competitive enzyme immunoassay". The Journal of General Virology. 67 (6): 1179–1182. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1179 . ISSN 0022-1317. PMID 3011974.
- ↑ Blodörn, Krister; Hägglund, Sara; Fix, Jenna; Dubuquoy, Catherine; Makabi-Panzu, Boby; Thom, Michelle; Karlsson, Per; Roque, Jean-Louis; Karlstam, Erika; Pringle, John; Eléouët, Jean-François; Riffault, Sabine; Taylor, Geraldine; Valarcher, Jean François (2014). "Vaccine Safety and Efficacy Evaluation of a Recombinant Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV) with Deletion of the SH Gene and Subunit Vaccines Based On Recombinant Human RSV Proteins: N-nanorings, P and M2-1, in Calves with Maternal Antibodies". PLOS ONE. 9 (6): –100392. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j0392B. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100392 . ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4063758 . PMID 24945377.