
A squid is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.

Ommastrephidae is a family of squid containing three subfamilies, 11 genera, and over 20 species. They are widely distributed globally and are extensively fished for food. One species, Todarodes pacificus, comprised around half of the world's cephalopod catch annually.

Psychroteuthis glacialis, the glacial squid, is the only known species in the monotypic genus Psychroteuthis, in the family Psychroteuthidae. While only one species has been confirmed, two undescribed species also probably exist. The species occurs in coastal waters near Antarctica and South America. It grows to a mantle length of 44 cm (1.44 ft).

Onykia ingens, the greater hooked squid, is a species of squid in the family Onychoteuthidae. It occurs worldwide in subantarctic oceans.
Moroteuthopsis longimana, also known as Kondakovia longimana, the giant warty squid or longarm octopus squid, is a large species of hooked squid. It attains a mantle length of at least 85 cm and probably over 1.15 m. The largest complete specimen of this species, measuring 2.3 m in total length, was found in Antarctica in 2000.
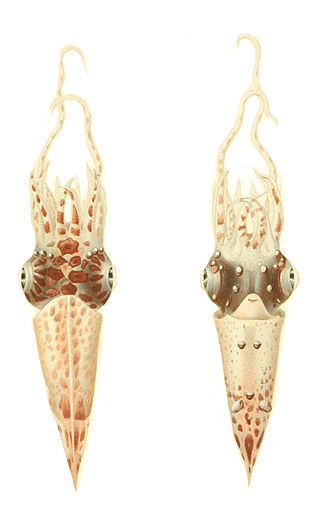
Pterygioteuthis giardi is a species of squid in the family Pyroteuthidae. It is known as the roundear enope squid. The specific name honors the French zoologist and marine biologist Alfred Mathieu Giard (1846-1908).

Nototodarus sloanii is a species of squid commonly known as the New Zealand arrow squid or Wellington flying squid. It is also known by its Māori name of wheketere. It is a favoured prey species of a number of marine mammals and diving birds. It is an important food source for the New Zealand fur seal and two endangered species: the New Zealand sea lion and the yellow-eyed penguin. Nototodarus sloanii is sought by trawler fishermen for human consumption; New Zealand sea lions are frequently caught in trawl nets and drowned when feeding on N. sloanii.
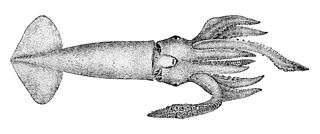
Nototodarus is a genus of squid. Example species in this genus include Nototodarus sloanii, a species sought for human food. In the process of harvesting N. sloanii, Australian sea lions are frequently killed, since that marine mammal preys upon this squid species. Furthermore, New Zealand arrow squid, N. sloanii, is an important food source for the endangered yellow-eyed penguin, Megadyptes antipodes.

Todaropsis eblanae, also known as the lesser flying squid, is a species of short finned squid in the monotypic genus Todaropsis of the family Ommastrephidae.
The Antarctic neosquid is the only neosquid in the genus Alluroteuthis. The tentacles are relatively short compared to the arms.

Todarodinae is a squid subfamily in the family Ommastrephidae.

Galiteuthis glacialis is a species of glass squid from the Antarctic Convergence. It is in the family Cranchiidae and subfamily Taoniinae. They are endemic to the Antarctic and are found in the Southern Ocean, around the Weddell Sea and the South Shetland Islands. Galiteuthis glacialis are one of the most plentiful and widely dispersed species of Antarctic squid. These squids are found in the mesopelagic and bathypelagic layers of the open ocean and demonstrate vertical migration. They can reach a maximum mantle length of 500 mm (0.5m).

Gonatus antarcticus is a squid in the family Gonatidae. The species is known with certainty only from southern Atlantic waters but it may have a circum-Antarctic distribution.
Brachioteuthis riisei is a species of squid in the family Brachioteuthidae.
Richard E. Young is a teuthologist. He is an Emeritus Professor of Oceanography at the University of Hawaii's School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology.

Ornithoteuthis antillarum, the Atlantic bird squid, is a species of flying squid from the family Ommastrephidae which is found in the warmer waters of the Atlantic Ocean. This species is an important component of the diet of many species of fish and of cetaceans. It is taken as a bycatch in fisheries but has the potential to be commercially important if appropriate fishing methods can be developed.
The Angolan flying squid is a species of squid from the subfamily Todarodinae, part of the family Ommastrephidae. Due to taxonomic confusion with the Antarctic flying squid the exact limits of its distribution are uncertain but it is thought to be restricted to waters off Southern Africa.

The Antarctic flying squid is a species of squid from the subfamily Todarodinae of the family Ommastrephidae, a family of pelagic squid from the order Oegopsida. It has a circumglobal distribution in the seas around the lower latitudes of the Southern Ocean.

The European flying squid is a species of squid from the continental slope and oceanic waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is the type species of the genus Todarodes, the type genus of the subfamily Todarodinae of the pelagic squid family Ommastrephidae. It is a species which is targeted by some fisheries, although it is more often a bycatch.
A micronekton is a group of organisms of 2 to 20 cm in size which are able to swim independently of ocean currents. The word 'nekton' is derived from the Greek νήκτον, translit. nekton, meaning "to swim", and was coined by Ernst Haeckel in 1890.












