
Mamallapuram, also known as Mahabalipuram, is a town in Chengalpattu district in the southeastern Indian state of Tamil Nadu, best known for the UNESCO World Heritage Site of 7th- and 8th-century Hindu Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram. It is one of the famous tourist sites in India. The ancient name of the place is Thirukadalmallai. It is a part of Chennai Metropolitan Area. It is a satellite town of Chennai.

The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The Pallavas played a crucial role in shaping in particular southern Indian history and heritage. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahana Empire, whom they had formerly served as feudatories.

Simhavishnu also known as Avanisimha son of Simhavarman III and one of the Pallava kings of India, was responsible for the revival of the Pallavan dynasty. He was the first Pallava monarch whose domain extended beyond Kanchipuram (Kanchi) in the South. He was portrayed as a great conqueror in Mattavilasa Prahasana, a drama written by his son Mahendravarman I.

Vikramaditya II was the son of King Vijayaditya and ascended the Badami Chalukya throne following the death of his father. This information comes from the Lakshmeshwar inscriptions in Kannada dated 13 January 735 A.D. From inscriptions it has come to be known that even before his coronation, Vikramaditya II, as a crown prince (Yuvaraja), had conducted successful military campaigns against their arch enemy, the Pallavas of Kanchipuram. His most important achievements were the capture of Kanchipuram on three occasions, the first time as a crown prince, the second time as an emperor and the third time under the leadership of his son and crown prince Kirtivarman II. This is attested to by another Kannada inscription, known as the Virupaksha Temple inscription which alludes to the emperor as the conqueror of Kanchi on three occasions and reads Sri Vikramaditya-bhatarar-mume-Kanchiyan-mume parajisidor. The other notable achievement was the consecration of the famous Virupaksha Temple and Mallikarjuna Temple by his queens Lokadevi and Trilokadevi at Pattadakal. These two monuments are the centre piece of the UNESCO World Heritage Monuments at Pattadakal. Vikramaditya II was a powerful ruler and was in power for 40 years. In order to maintain peace he entered into marriage alliance with Rashtrakutas.

Narasimhavarman I was a Pallava emperor who reigned from 630 CE to 668 CE. He shared his father Mahendravarman I's love of art and completed the works started by Mahendravarman in Mamallapuram. During his reign, the famous Pancha Rathas, a monolithic rock-cut temple complex and a UNESCO World Heritage Site was constructed.

Kanchipuram also known as Kanjeevaram, is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu in the Tondaimandalam region, 72 km (45 mi) from Chennai – the capital of Tamil Nadu. Known as the City of Thousand Temples, Kanchipuram is known for its temple architectures, 1000-pillared halls, huge temple towers and silk saris. Kanchipuram serves as one of the most important tourist destinations in India. Kanchipuram has become a centre of attraction for foreign tourists as well. The city covers an area of 36.14 km2 (13.95 sq mi) and an estimated population of more than 300,000 in 2021. It is the administrative headquarters of Kanchipuram District. Kanchipuram is well-connected by road and rail.

Sholinghur is a municipality under Sholinghur taluk in Ranipet District of Tamil Nadu, India. The town is famous in Tamil Nadu and other neighboring states for the Lakshmi Narasimha Swamy temple.

The Kailasanathar Temple, Kanchipuram, also referred to as the Kailasanatha temple, is a Pallava-era historic Hindu temple in Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu, India. Dedicated to Shiva, it is one of the oldest surviving monuments in Kanchipuram. It reflects a Dravidian architecture and was built about 700 CE by Narasimhavarman II with additions by Mahendravarman III. A square-plan temple, it has a mukha-mandapa, a maha-mandapa and a primary garbha-griya (sanctum) topped with a four-storey vimana. The main sanctum is surrounded by nine shrines, seven outside and two inside flanking the entrance of the sanctum, all with forms of Shiva. The outer walls of the temple's prakara (courtyard) is also surrounded by cells.

The Sri Kamakshi Amman Temple is an ancient Hindu Temple dedicated to the goddess Kamakshi, one of the highest aspects of Adi Parashakti, the mighty goddess in Shaktism. The temple is located in the historic city of Kanchipuram, near Chennai, India. The temple houses one of the 108 Divya Desams of Vishnu and is called Tirukalavanur. The temple is dedicated mainly to Kamakshi and then to Vishnu in his form of Varaha. The temple is glorified by the 6th-9th century Vaishnavite Alvars in the Naalayira Divya Prabandham. Its construction is credited to the Pallava kings, whose capital was in the same city. This temple, along with the goddesses of Madurai and either Varanasi or Thiruvanaikovil, are the important centers of Shaktism in the state of Tamil Nadu. The present temple is also known as Kamakoti Peetha or Kamakota Nayaki Kovil, where Tripura Sundari had settled after killing a demon. This ancient temple was mentioned in Perunaraatrupadai, an ancient Tamil literature that praises the renowned Sangam era. King Thondaiman Ilandiraiyan of the Pallava dynasty, who ruled Kanchipuram, constructed the temple. Kamakshi is worshipped in the shrine in 5 forms, one of them was a golden idol, which was transported to Thanjavur due to the Muslim invasions of Kanchipuram. There are no other goddess temples in the city of Kanchipuram, apart from this one, which is unusual in a city that has hundreds of traditional temples. There are various legends that account for this fact.

The Pallava script or Pallava Grantha is a Brahmic script named after the Pallava dynasty of Southern India and is attested to since the 4th century CE. In India, the Pallava script evolved into the Tamil and Grantha script. Pallava also spread to Southeast Asia and evolved into local scripts such as Balinese, Baybayin, Javanese, Kawi, Khmer, Lanna, Lao, Mon–Burmese, New Tai Lue alphabet, Sundanese, and Thai.
Narasimhavarman II, popularly known as Rajasimha and as Rajamalla, was a Pallava monarch who reigned from 690 CE to 725 CE. He is credited with the construction of the Shore Temple Complex, the Isvara and Mukunda Temples in Mamallapuram, the Talagirisvara Temple in Panamalai and the Kailasanathar Temple in Kanchi. He is further credited with the construction of a Buddhist Vihara at Nagipattinam, which is commonly known as ‘China-pagoda'.

The Tondaiman family were Tamil rulers of the ancient Tondai Nadu (Tondaimandalam) division of Tamilakkam in South India. Their capital was at Kanchipuram.

Ulagalandha Perumal Temple is a temple dedicated to Vishnu located in Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu, India. Constructed in the Dravidian style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Naalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th through 9th centuries CE. It is one of the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to Vishnu, who is worshipped as Ulagalantha Perumal, and his consort Lakshmi as Amuthavalli. The temple is believed to have been built by the Pallavas, with later contributions from the medieval Cholas, Vijayanagara kings, and Madurai Nayaks.

Thiru Parameswara Vinnagaram or Vaikunta Perumal Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to the God Vishnu, located in Kanchipuram in the Southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Constructed in the Dravidian style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Nalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th through the 9th centuries CE. It is one among the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to the God Vishnu, who is worshipped as Vaikuntanathan and his consort, the Goddess Lakshmi as Sri Vaikundavalli. The temple is considered the second oldest extant temple in Kanchipuram after the Kailasanathar temple.
Kailasanathar Temple is the name of several famous megalith rock cut kovils dedicated to the deity Shiva in the form Kailasanathar, whose primary abode is Mount Kailash from which the temples take their names and inspiration.
Aiyadigal Kadavarkon, was a ruler of the kadava dynasty and was ruling from Kanchipuram. Later he became the 46th Nayanar Saint in Tamil Nadu.

Pallava art and architecture represent an early stage of Dravidian art and architecture which blossomed to its fullest extent under the Chola Dynasty. The first stone and mortar temples of South India were constructed during Pallava rule and were based on earlier brick and timber prototypes.

Trilokyanatha Temple, also called Thirupparuthikundram Jain temple or Jeenaswamy Trilokyanathar temple, is an 8th-century Digambara Jain temple in Thiruparthikundram, in northeast Kanchipuram in Tamil Nadu, India. The suburb and the area around this temple is also called Jain Kanchi. The stone temple is dedicated to the Jain Tirthankaras, but is notable for integrating Hindu deities with Jain deities within the premises of the temple, particularly as Ksetrapalas. Constructed in Dravidian architecture, the temple was built during the reign of Narasimhavarman II of the Pallava dynasty. The temple was expanded by the Jain community with financial support of Medieval Cholas, later Pallavas and Vijayanagar kings.
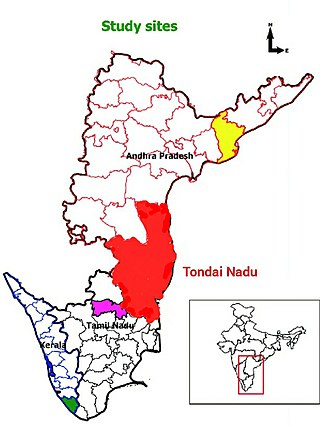
Tondaimandalam, also known as Tondai Nadu, is a historical region located in the northernmost part of Tamil Nadu and southernmost part of Andhra Pradesh. The region comprises the districts which formed a part of the legendary kingdom of Athondai Chakravarti. The boundaries of Tondaimandalam are ambiguous – between the river basins of Penna River and Ponnaiyar River. During the reign of Rajaraja I, this region was called as Jayankonda Cholamandalam.
Manimangalam is a small town located in the Kanchipuram district of Tamil Nadu state in Southern India, famous for its ancient temples and inscriptions documenting the history of the ancient Tamil kings

















