
Hyoliths are animals with small conical shells, known as fossils from the Palaeozoic era. They are at least considered as lophotrochozoan, and possibly being lophophorates, a group which includes the brachiopods, while others consider them as being basal lophotrochozoans, or even molluscs.

Chitons are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora, formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized.
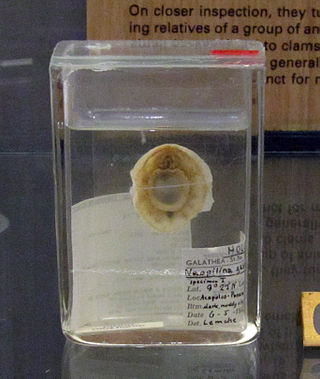
Monoplacophora, meaning "bearing one plate", is a polyphyletic superclass of molluscs with a cap-like shell, inhabiting deep sea environments. Extant representatives were not recognized as such until 1952; previously they were known only from the fossil record, and were thought to have become extinct 375 million years ago.

The Rostroconchia is a class of extinct molluscs dating from the early Cambrian to the Late Permian. They were initially thought to be bivalves, but were later given their own class. They have a single shell in their larval stage, and the adult typically has a single, pseudo-bivalved shell enclosing the mantle and muscular foot. The anterior part of the shell probably pointed downward and had a gap from which the foot could probably emerge. Rostroconchs probably lived a sedentary semi-infaunal lifestyle. There were probably more than 1,000 species of members of this class.
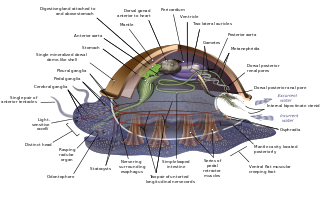
The evolution of the molluscs is the way in which the Mollusca, one of the largest groups of invertebrate animals, evolved. This phylum includes gastropods, bivalves, scaphopods, cephalopods, and several other groups. The fossil record of mollusks is relatively complete, and they are well represented in most fossil-bearing marine strata. Very early organisms which have dubiously been compared to molluscs include Kimberella and Odontogriphus.

Yochelcionella is an extinct genus of basal molluscs which lived during the Tommotian epoch, the first epoch of the Cambrian period. This genus is often reconstructed to resemble snails.

Helcionellid or Helcionelliformes is an order of small fossil shells that are universally interpreted as molluscs, though no sources spell out why this taxonomic interpretation is preferred. These animals are first found about 540 to 530 million years ago in the late Nemakit-Daldynian age, which is the earliest part of the Cambrian period. A single species persisted to the Early Ordovician. These fossils are component of the small shelly fossils (SSF) assemblages.
The small shelly fauna, small shelly fossils (SSF), or early skeletal fossils (ESF) are mineralized fossils, many only a few millimetres long, with a nearly continuous record from the latest stages of the Ediacaran to the end of the Early Cambrian Period. They are very diverse, and there is no formal definition of "small shelly fauna" or "small shelly fossils". Almost all are from earlier rocks than more familiar fossils such as trilobites. Since most SSFs were preserved by being covered quickly with phosphate and this method of preservation is mainly limited to the late Ediacaran and early Cambrian periods, the animals that made them may actually have arisen earlier and persisted after this time span.

Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals, after Arthropoda; members are known as molluscs or mollusks. Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied.

Mattheva is a class of prehistoric mollusc from the late Cambrian, which might be better incorporated in a different class. It was erected to accommodate chiton-like organisms such as Matthevia. Although questionable, phosphatic fossils have been included in this class, even though molluscs do not use phosphate in their bodies.
Robustum nodum is the one species of a problematic genus of Ordovician hemithecellid mollusc proposed by Stinchcomb and Darrough in 1995. Its similarities to Matthevia were outlined by Vendrasco & Runnegar.
Hemithecella is a problematic genus of Ordovician mollusc proposed by Stinchcomb and Darrough in 1995. Hemithecella belongs to what are informally known as multiplated molluscs; it is found in the late Cambrian of the Ozarks and the Lower Ordovician of the same region as well as in Minnesota and the southern Appalachian Mountains. Hemithecella has muscle scars identical to a monoplacophoran and not the musculature of a chiton to which some authors have suggested the multiplated molluscs belong. It is therefore classified in the Mattheviidae.
Echinochiton is an extinct genus of Ordovician chitons with hollow spines on its margins; these spines, which are unique among the chitons, have a strong organic component and show growth lines.
Stenothecidae is an extinct family of fossil univalved Cambrian molluscs which may be either gastropods or monoplacophorans.
The Kirengellids are a group of problematic Cambrian fossil shells of marine organisms. The shells bear a number of paired muscle scars on the inner surface of the valve.
Acrotretides (Acrotretida) are an extinct order of linguliform brachiopods in the class Lingulata. Acrotretida contains 8 families within the sole superfamily Acrotretoidea. They lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Middle Devonian, rapidly diversifying during the middle Cambrian. In the upper Cambrian, linguliforms reached the apex of their diversity: acrotretides and their relatives the lingulides together comprised nearly 70% of brachiopod genera at this time. Though acrotretides continued to diversify during the Ordovician, their proportional dominance declined, as rhynchonelliforms took on a larger role in brachiopod faunas.

Fordilla is an extinct genus of early bivalves, one of two genera in the extinct family Fordillidae. The genus is known solely from Early Cambrian fossils found in North America, Greenland, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia. The genus currently contains three described species, Fordilla germanica, Fordilla sibirica, and the type species Fordilla troyensis.
Watsonella is an extinct genus of mollusc known from early (Terreneuvian) Cambrian strata. It has been hypothesized to be close to the origin of bivalves. It contains a single species, Watsonella crosbyi.
Phthipodochiton is an extinct genus of molluscs, known from several fossils from the upper Ordovician fauna of the Lady Burn Starfish beds of Girvan, Scotland. It shows a mixture of aplacophoran body plan and polyplacophoran-like valves, and it is an informative fossil in the evolution of aculiferan mollusks.

Bruce Norman Runnegar is an Australian-born paleontologist and professor at UCLA. His research centers on using the fossil record to determine how, where, and when life originated and evolved. He has published on a wide variety of topics, including the phylogeny of molluscs, Dickinsonia fossils and oxygen levels, and molecular clock techniques.










