
Hernando de Soto was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula, and played an important role in Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, but is best known for leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States. He is the first European documented as having crossed the Mississippi River.

DeSoto County is a county located on the northwest border of the U.S. state of Mississippi. As of the 2010 census, the population was 161,252, making it the third-most populous county in Mississippi. Its county seat is Hernando.

Chicot County is a county located in the southeastern corner of the U.S. state of Arkansas. As of the 2010 census, the population was 11,800. The county seat is Lake Village. Chicot County is Arkansas's 10th county, formed on October 25, 1823, and named after Point Chicot on the Mississippi River. It is part of the Arkansas Delta, lowlands along the river that have been historically important as an area for large-scale cotton cultivation.

Lake Village is a city in and the county seat of Chicot County, Arkansas, United States. The population was 2,575 at the 2010 census. It is located in the Arkansas Delta. Lake Village is named for its location on Lake Chicot, an oxbow lake formed by the Mississippi River.

Louis Jolliet was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jesuit Father Jacques Marquette, a Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore and map the Mississippi River.

The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United States in Colorado, specifically the Arkansas River Valley, where the headwaters derive from the snowpack in the Sawatch and Mosquito mountain ranges. It then flows east into the Midwest via Kansas, and finally into the South through Oklahoma and Arkansas.

Pacaha was a Native American polity encountered in 1541 by the Hernando de Soto expedition. This group inhabited fortified villages in what is today the northeastern portion of the U.S. state of Arkansas.

The Mississippian culture was a Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages (suburbs) linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center located in what is present-day southern Illinois.

The Quapaw people are a tribe of Native Americans that coalesced in the Midwest and Ohio Valley. The Dhegiha Siouan-speaking tribe historically migrated from the Ohio Valley area to the west side of the Mississippi River and resettled in what is now the state of Arkansas; their name for themselves refers to this migration and traveling downriver.
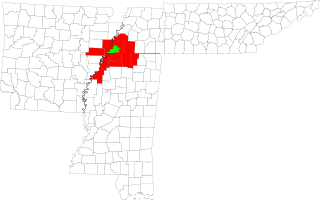
The Memphis–Forrest City Combined Statistical Area, TN–MS–AR (CSA) is the commercial and cultural hub of The Mid-South or Ark-Miss-Tenn. The census defined combined statistical area covers ten counties in three states – Tennessee, Mississippi, and Arkansas. As of census 2010 the MSA had a population of 1,324,108. The Forrest City Micropolitan area was added to the Memphis area in 2012 to form the Memphis–Forrest City Combined Statistical area and had a population of 1,369,548 according to census estimates. The greater Mid-South area as a whole has a population of 2.4 million according to 2013 census estimates. This area is covered by Memphis local news channels and includes the Missouri Bootheel, Northeast Arkansas, West Tennessee, and North Mississippi.

The Hernando de Soto Bridge is a through arch bridge carrying Interstate 40 across the Mississippi River between West Memphis, Arkansas, and Memphis, Tennessee. The architectural design is a continuous cantilevered cable-stayed steel through arch, with bedstead endposts. Memphians also call the bridge the "New Bridge", as it is newer than the Memphis & Arkansas Bridge downstream, and the "M Bridge", due to its distinctive shape. It is of similar construction to the Sherman Minton Bridge between Louisville, Kentucky, and New Albany, Indiana.

The Nodena Site is an archeological site east of Wilson, Arkansas and northeast of Reverie, Tennessee in Mississippi County, Arkansas, United States. Around 1400–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed in the Nodena area on a meander bend of the Mississippi River. The Nodena site was discovered and first documented by Dr. James K. Hampson, archaeologist and owner of the plantation on which the Nodena site is located. Artifacts from this site are on display in the Hampson Museum State Park in Wilson, Arkansas. The Nodena Site is the type site for the Nodena Phase, believed by many archaeologists to be the province of Pacaha visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542.
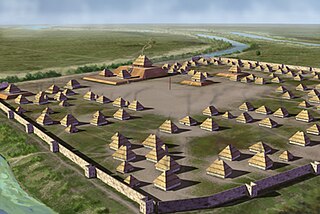
Parkin Archeological State Park, also known as Parkin Indian Mound, is an archeological site and state park in Parkin, Cross County, Arkansas. Around 1350–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed at the site, at the confluence of the St. Francis and Tyronza rivers. Artifacts from this site are on display at the site museum. The Parkin Site is the type site for the Parkin phase, an expression of the Mississippian culture from the Late Mississippian period. Many archeologists believe it to be part of the province of Casqui, documented as visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542. Archeological artifacts from the village of the Parkin people are dated to 1400–1650 CE.
The Koroa were one of the groups of indigenous people who lived in the Mississippi Valley prior to the European settlement of the region. They lived in the northwest of present-day Mississippi in the Yazoo River basin.

The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture centered on the Lower Mississippi River valley. It had a deep history in the area stretching back through the earlier Coles Creek and Troyville cultures to the Marksville culture. The Natchez and related Taensa peoples were their historic period descendants. The type site for the culture is the Medora Site in Louisiana; while other examples include the Anna, Emerald, Holly Bluff, and Winterville sites in Mississippi.

The Tunica people were a group of linguistically and culturally related Native American tribes in the Mississippi River Valley, which include the Tunica ; the Yazoo; the Koroa ; and possibly the Tioux. They first encountered Europeans in 1541 - members of the Hernando de Soto expedition.

The Nodena Phase is an archaeological phase in eastern Arkansas and southeastern Missouri of the Late Mississippian culture which dates from about 1400–1650 CE. The Nodena Phase is known from a collection of villages along the Mississippi River between the Missouri Bootheel and Wapanocca Lake. They practiced extensive maize agriculture and artificial cranial deformation and were members of a continent wide trade and religious network known as the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex, which brought chert, whelk shells, and other exotic goods to the area.
The Carson Mounds,, also known as the Carson Site and Carson-Montgomery- is a large Mississippian culture archaeological site located near Clarksdale in Coahoma County, Mississippi in the Yazoo Basin. Only a few large earthen mounds are still present at Carson to this day. Archaeologists have suggested that Carson is one of the more important archaeological sites in the state of Mississippi.
Kevin Edward Blackwell is a Republican member of the Mississippi State Senate. Since January 2016, he has represented District 19, including parts of DeSoto and Marshall counties in northern Mississippi.
Quigualtam or Quilgualtanqui was a powerful Native American Plaquemine culture polity encountered in 1542-1543 by the Hernando de Soto expedition. The capital of the polity and its chieftain also bore the same name; although neither the chief nor his settlements were ever visited in person by the expedition. Their encounters consisted of messages sent by runners and a three-day long canoe battle on the Mississippi River. Multiple archaeological cultures, archaeological sites, and protohistoric and early historic period Native American groups have been proposed by historians and archaeologists to identify the polity, but their identity will probably never be known with any degree of certainty.


















