
Cutthroat eels are a family, Synaphobranchidae, of eels, the only members of the suborder Synaphobranchoidei. They are found worldwide in temperate and tropical seas.

Dysomma is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. These eels are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Dysommina is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. These eels are known from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Meadia is a genus of eels in the cutthroat eel family Synaphobranchidae. It currently contains the following species:
Coloconger cadenati is an eel in the family Colocongridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1961. It is a marine, deep-water dwelling eel which is known from Senegal to the Gulf of Guinea in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. It is known from a depth range of 270–600 m. Males can reach a maximum total length of 90 cm. The diet of C. cadenati consists primarily of benthic crustaceans.
Atractodenchelys phrix, known under the common name "arrowtooth eel" is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins and Charles Richard Robins in 1970. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from its type locality in the eastern Caribbean, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 385–425 metres.

Dysomma anguillare, the shortbelly eel, stout moray, mustard eel or arrowtooth eel, is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Keppel Harcourt Barnard in 1923. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean and Indo-Western Pacific, including the United States, Venezuela, South Africa, Zanzibar, and Japan. It lives at a depth range of 30 to 270 metres, and inhabits muddy sediments in coastal waters and large rivermouths. Males can reach a maximum total length of 52 centimetres (20 in).
Dysomma bucephalus is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Alfred William Alcock in 1889. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 353 metres.
Dysomma goslinei is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins and Charles Richard Robins in 1976. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific. Males can reach a maximum total length of 19.7 centimetres.
Dysomma longirostrum is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Chen Yu-Yun and Michael Hin-Kiu Mok in 2001. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling eel which is known from Taiwan, in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 100–150 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 19.6 centimetres.
Dysomma melanurum is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Johnson T. F. Chen and Herman Ting-Chen Weng in 1967. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western Pacific Ocean. Males can reach a maximum total length of 23.7 centimetres.
Dysomma muciparus is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Alfred William Alcock in 1891. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 439–505 metres.
Dysomma opisthoproctus is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Chen Yu-Yun and Michael Hin-Kiu Mok in 1995. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known only from northeastern Taiwan, in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 200 metres. Males are known to reach a total length of 42.1 centimetres.
Dysomma tridens is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins, Eugenia Brandt Böhlke, and Charles Richard Robins in 1989. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from off Belize, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 348 metres.
Ilyophis arx is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins in 1976. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern Pacific and northeastern Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 1,790 to 3,225 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 44.7 centimetres (17.6 in).
Ilyophis saldanhai is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Emma Stanislavovna Karmovskaya and Nikolai Vasilyevich Parin in 1999, and is the most recently described of the six species in the genus Ilyophis. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 3,020 metres (9,910 ft).
Meadia abyssalis, the abyssal cutthroat eel, is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Toshiji Kamohara in 1938. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific, including Brazil, the Hancock Seamount, the Hawaiian and Society islands, Japan, Mauritius, and Réunion. It is found off the continental slope, and dwells at a depth range of 100–329 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 73 centimetres.
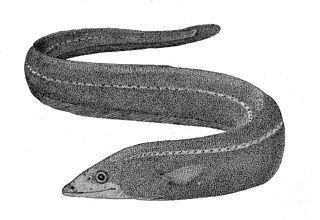
The shortdorsal cutthroat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and western central Atlantic Ocean, including Zanzibar, Maldives, Australia, Japan, Suriname, and the Gulf of Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 900 to 3,000 metres, most often between 1,000 to 2,500 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).

Donn Eric Rosen (1929-1986) was a member of the staff of the American Museum of Natural History. He was a Distinguished Fellow of the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists.

Ilyophinae, the arrowtooth ells or mustard eels, is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes belongiing to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. Within its family this subfamily shows greatest number of species and the greatest morphological diversity.




