Related Research Articles

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science which deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated over immediate (embryology) and long (evolution) timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study (respectively) the structure and function of organisms and their parts, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and they are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine.
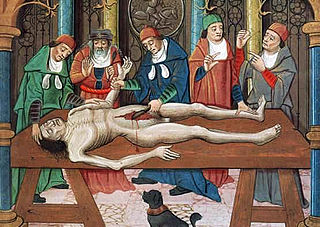
The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern scientists. The study of human anatomy can be traced back thousands of years, at least to the Egyptians, but the science of anatomy, as we know it today, did not develop until far later. The development of the study of anatomy gradually built upon concepts that were understood during the time of Galen and slowly became a part of the traditional medical curriculum. It has been characterized, over time, by a continually developing understanding of the functions of organs and structures in the body.
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.

The palate is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separate. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior bony hard palate and the posterior fleshy soft palate.

A joint or articulation is the connection made between bones in the body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally.

Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny.
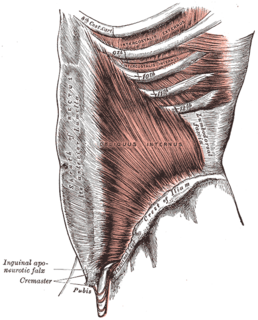
A fascia is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. Fascia is classified by layer, as superficial fascia, deep fascia, and visceral or parietal fascia, or by its function and anatomical location.
Grey's Anatomy is an American medical drama television series that premiered on March 27, 2005, on the American Broadcasting Company (ABC) as a mid-season replacement. The fictional series focuses on the lives of surgical interns, residents, and attending physicians, as they develop into seasoned doctors while trying to maintain personal lives and relationships. The title is a play on Gray's Anatomy, a classic human anatomy textbook first published in 1858 in London and written by Henry Gray. Shonda Rhimes developed the pilot and continues to write for the series; she is also one of the executive producers, along with Betsy Beers, Mark Gordon, Krista Vernoff, Rob Corn, Mark Wilding, and Allan Heinberg. Although the series is set in Seattle, it is filmed primarily in Los Angeles, California.
Ellen Kathleen Pompeo is an American actress, director, and producer. She is one of the highest paid television actors, having signed a $20 million annual contract with the American Broadcasting Company in late 2017. She was honored with the 2007 Special Achievement in Entertaining by the National Italian American Foundation for her contributions to the entertainment industry.

Sara Elena Ramírez is a Mexican American actress, singer, and songwriter. Born in Mazatlán, Sinaloa, she graduated with a fine arts degree from the Juilliard School. She began acting in Broadway productions, making her debut with Paul Simon's The Capeman, and later ventured into film and television roles. Ramirez is a recipient of a Tony Award, a Screen Actors Guild Award, and a Satellite Award, among other accolades.

Chandra Danette Wilson is an American actress and director, known for her role as Dr. Miranda Bailey in the ABC television drama Grey's Anatomy since 2005, for which she has been nominated for the Emmy for Best Supporting Actress four times. She also played the character of Bailey on Private Practice and Station 19. She made her New York stage debut in 1991 and began to land guest spots on a variety of prime-time television shows. She made her first film appearance in the 1993 film Philadelphia.

Plant anatomy or phytotomy is the general term for the study of the internal structure of plants. Originally it included plant morphology, the description of the physical form and external structure of plants, but since the mid-20th century plant anatomy has been considered a separate field referring only to internal plant structure. Plant anatomy is now frequently investigated at the cellular level, and often involves the sectioning of tissues and microscopy.

Isobel "Izzie" KatherineStevens, M.D. is a fictional character from the medical drama television series Grey's Anatomy, which airs on the American Broadcasting Company (ABC) in the United States. The character was created by series producer Shonda Rhimes, and was portrayed by actress Katherine Heigl from 2005 to 2010. Introduced as a surgical intern at the fictional Seattle Grace Hospital, Izzie worked her way up to resident level, while her relationships with her colleagues Meredith Grey, Cristina Yang, George O'Malley and Alex Karev formed a focal point of the series.
The Foundational Model of Anatomy Ontology (FMA) is a reference ontology for the domain of anatomy. It is a symbolic representation of the canonical, phenotypic structure of an organism; a spatial-structural ontology of anatomical entities and relations which form the physical organization of an organism at all salient levels of granularity.
A cadaver is a dead human body that is used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Students in medical school study and dissect cadavers as a part of their education. Others who study cadavers include archaeologists and artists.

Katherine Marie Heigl is an American actress, film producer, and former fashion model. She started her career as a child model with Wilhelmina Models before turning her attention to acting, making her film debut in That Night (1992) and later appearing in My Father the Hero (1994) as well as Under Siege 2: Dark Territory (1995). Heigl then landed the role of Isabel Evans on The WB television series Roswell (1999–2002), for which she received nominations for Saturn and Teen Choice Awards.

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 600 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Gray's Anatomy is an English language textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical, Anatomy of the Human Body and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and has continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.
| This cardiovascular system article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |