
The aorta is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at the aortic bifurcation into two smaller arteries. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation.

The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that carries sensory fibers that create a pathway that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem.

Coronary artery bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass graft, is a surgical procedure to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), the buildup of plaques in the arteries of the heart. It can relieve chest pain caused by CAD, slow the progression of CAD, and increase life expectancy. It aims to bypass narrowings in heart arteries by using arteries or veins harvested from other parts of the body, thus restoring adequate blood supply to the previously ischemic heart.

In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.
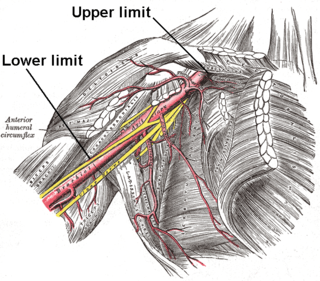
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

In human anatomy, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), also known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurcation as the superior epigastric and musculophrenic arteries.

In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.

In the human body, the lateral thoracic artery is a blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to approximately one-third of the lateral structures of the thorax and breast.

The thoracic aorta is a part of the aorta located in the thorax. It is a continuation of the aortic arch. It is located within the posterior mediastinal cavity, but frequently bulges into the left pleural cavity. The descending thoracic aorta begins at the lower border of the fourth thoracic vertebra and ends in front of the lower border of the twelfth thoracic vertebra, at the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm where it becomes the abdominal aorta.

In human anatomy, the superior epigastric artery is a terminal branch of the internal thoracic artery that provides arterial supply to the abdominal wall, and upper rectus abdominis muscle. It enters the rectus sheath to descend upon the inner surface of the rectus abdominis muscle. It ends by anastomosing with the inferior epigastric artery.

In human anatomy, the internal thoracic vein is the vein that drains the chest wall and breasts.

The thyrocervical trunk is a short artery of the neck. It arises from the subclavian artery, then promptly divides into its branches: the inferior thyroid artery, suprascapular artery, and (sometimes) the transverse cervical artery.

The pericardiacophrenic artery is a long slender branch of the internal thoracic artery.

The superior thoracic artery is a small artery located near the armpit. It usually originates from the axillary artery, but can instead originate from the thoracoacromial artery. It supplies the pectoralis minor and major muscles, and the chest wall.

The costocervical trunk arises from the upper and back part of the second part of subclavian artery, behind the scalenus anterior on the right side, and medial to that muscle on the left side.

The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries passing within an intercostal space. There are 9 anterior and 11 posterior intercostal arteries on each side of the body. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery and its terminal branch - the musculophrenic artery. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the supreme intercostal artery and thoracic aorta.

Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is a type of minimally-invasive endovascular surgery used to treat pathology of the aorta, most commonly an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). When used to treat thoracic aortic disease, the procedure is then specifically termed TEVAR for "thoracic endovascular aortic/aneurysm repair." EVAR involves the placement of an expandable stent graft within the aorta to treat aortic disease without operating directly on the aorta. In 2003, EVAR surpassed open aortic surgery as the most common technique for repair of AAA, and in 2010, EVAR accounted for 78% of all intact AAA repair in the United States.
Subclavian loop, also known as Vieussens' ansa after French anatomist Raymond Vieussens (1635-1715), is a nerve cord that is a connection between the middle and inferior cervical ganglion which is commonly fused with the first thoracic ganglion and is then called the stellate ganglion. The subclavian ansa forms a loop around the subclavian artery; whence its name. This communicating branch downwards anteromedial to the vertebral artery makes a loop around the subclavian artery from anterior to posterior and then lies medially to the internal thoracic artery respectively. Sometimes there are two communicating branches encompassing the vertebral artery, one from anterior and the other from posterior.
The perforating branches of the internal thoracic artery pierce through the internal intercostal muscles of the superior six intercostal spaces. These small arteries run with the anterior cutaneous branches of the intercostal nerves.













