
Laramie is a city in and the county seat of Albany County, Wyoming, United States. The population was estimated 32,711 in 2019, making it the third-largest city in Wyoming after Cheyenne and Casper. Located on the Laramie River in southeastern Wyoming, the city is north west of Cheyenne, at the junction of Interstate 80 and U.S. Route 287.

The Medicine Bow Mountains are a mountain range in the Rocky Mountains that extend 100 miles (160 km) from northern Colorado into southern Wyoming. The northern extent of this range is the sub-range the Snowy Range. From the northern end of Colorado's Never Summer Mountains, the Medicine Bow mountains extend north from Cameron Pass along the border between Larimer and Jackson counties in Colorado and northward into south central Wyoming. In Wyoming, the range sits west of Laramie, in Albany and Carbon counties to the route of the Union Pacific Railroad and U.S. Interstate 80. The mountains often serve as a symbol for the city of Laramie. The range is home to Snowy Range Ski Area.

Cheyenne Regional Airport is a civil-military airport a mile north of downtown Cheyenne, in Laramie County, Wyoming. It is owned by the Cheyenne Regional Airport Board.
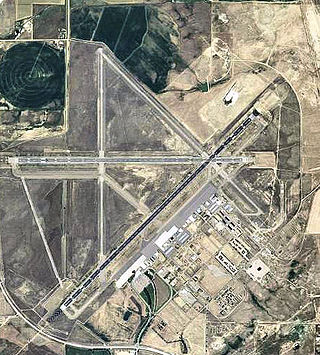
Casper–Natrona County International Airport is 7 miles (11 km) northwest of Casper, in Natrona County, Wyoming. Before December 19, 2007 the airport was called Natrona County International Airport.

Idaho Falls Regional Airport is two miles north-northwest of downtown Idaho Falls, Idaho, United States. It is locally known as Fanning Field. It is the second-busiest airport in Idaho after Boise Airport.

United Air Lines Flight 409 was a scheduled flight which originated in New York City, New York. The final flight destination was San Francisco, California, with stops in Chicago, Denver and Salt Lake City. The aircraft operating the service, a Douglas DC-4 propliner, registration N30062, crashed into Medicine Bow Peak, near Laramie, Wyoming, on October 6, 1955, killing all 66 people on board. The victims included five female members of the Mormon Tabernacle Choir and military personnel. At the time, this was the deadliest airline crash in the history of American commercial aviation. Another 66 lives had been lost earlier that year in the March 22 crash in Hawaii of a United States Navy Douglas R6D-1 Liftmaster military transport aircraft, and 66 had also died in the mid-air collision of two United States Air Force C-119G Flying Boxcars over West Germany on August 11, placing the three crashes in a three-way tie as the deadliest aviation incidents in 1955.

This is a list of properties and historic districts in Montana that are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The state's more than 1,100 listings are distributed across all of its 56 counties.

Fort Fetterman was constructed in 1867 by the United States Army on the Great Plains frontier in Dakota Territory, approximately 11 miles northwest of present-day Douglas, Wyoming. Located high on the bluffs south of the North Platte River, it served as a major base for the start of several United States military expeditions against warring Native American tribes. The fort is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

An airway beacon (US) or aerial lighthouse was a rotating light assembly mounted atop a tower. These were once used extensively in the United States for visual navigation by airplane pilots along a specified airway corridor. In Europe, they were used to guide aircraft with lighted beacons at night.
Challenger Airlines was a United States airline incorporated in Wyoming, December 31, 1941, by Charles W. Hirsig II, as Summit Airways Inc., a non-scheduled carrier. In 1944, Hirsig filed an application with the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) Docket No. 1091, for a Certificate of Public Convenience and Necessity to engage in air transportation in Wyoming, Colorado, and Nebraska.

Field Club is a neighborhood located in the Midtown region of Omaha, Nebraska. Roughly bounded by Pacific Street, 32nd Avenue, Center St., and 36th Street, the neighborhood was placed on the National Register of Historic Places as a historic district on November 15, 2000. Field Club is the location of dozens of historically significant homes in the Omaha area, including the Gerald R. Ford Birthsite and Gardens.

The Holman Field Administration Building is a Kasota limestone building designed by Clarence Wigington and built in 1939 by WPA employees. It serves as the control building for the St. Paul Downtown Airport in Saint Paul in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The airport was named for Charles W. Holman, who won the U.S. air speed trials in 1930. The airfield was built on the former site of Lamprey Lake, which was filled with dredged material from the adjacent Mississippi River, which regularly floods the airport. Across the river in Indian Mounds Park is one of the last remaining airway beacons in the country.

The Brooklyn Lodge or Brooklyn Lake Lodge was built in 1922–23 for former rodeo performer Harry "Hoot" Jones. The log lodge, located near Centennial, Wyoming in the Snowy Range of Medicine Bow National Forest, was operated by the Jones family until the late 1930s.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Carbon County, Wyoming.

The Virginian Hotel is a historic hotel in Medicine Bow, Wyoming, United States. Construction on the hotel began in 1901 and was completed in 1911. It was built by August Grimm, the first mayor of Medicine Bow, and his partner George Plummer. The hotel is thought to be named for the famous novel written in Medicine Bow, The Virginian by Owen Wister. Although it provided a place for cowboys and railroad workers to stay while they were in town, the hotel was actually built to serve a much broader clientele. It became a headquarters for all to meet and eat as well as a setting for many business dealings.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Salt Lake City, Utah.

The Transcontinental Airway System was a navigational aid deployed in the United States during the 1920s.
Walter Ellsworth Ware was an American architect who established a firm in 1891 in Salt Lake City, Utah and practiced until 1949, over a period of almost 60 years. He designed numerous buildings of diverse styles and functions that remain standing, many of which are listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

The Airway Radio Station in Gallatin County, Montana was built by the Aeronautics Bureau of the U.S. Department of Commerce in 1933. Located on Pogreba Field at Three Forks Airport, the radio station was part of a series of federally-constructed airway stations built during the early years of U.S. civil aviation. The station housed the radio range and ground-to-air radio systems that aided airmail pilots flying on the Minneapolis-Spokane-Seattle civil airway. The station was moved from its original location at Seifert Field, near Belgrade, Montana, to Pogreba Field in 1953, where it now serves as a terminal at Three Forks Airport. The Airway Radio Station was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on November 5, 1998.
Union Pacific Depot or variations such as Union Pacific Station or Union Pacific Railroad Depot may refer to:


















