
The Sonoran Desert is a North American desert which covers large parts of the Southwestern United States in Arizona and California and of Northwestern Mexico in Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur. It is the hottest desert in Mexico. It has an area of 260,000 square kilometers (100,000 sq mi). The western portion of the United States–Mexico border passes through the Sonoran Desert.

The ecology of California can be understood by dividing the state into a number of ecoregions, which contain distinct ecological communities of plants and animals in a contiguous region. The ecoregions of California can be grouped into four major groups: desert ecoregions, Mediterranean ecoregions, forested mountains, and coastal forests.
The North Western Ghats moist deciduous forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of southwestern India.
The South Western Ghats moist deciduous forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of southern India. It covers the southern portion of the Western Ghats range and the Nilgiri Hills between 250 and 1000 meters elevation in Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu states.

The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.

The Baja California Desert is a desert ecoregion of Mexico's Baja California Peninsula. This ecoregion occupies the western portion of the Baja California peninsula, and occupies most of the Mexican states of Baja California Sur and Baja California. It covers 77,700 square kilometers. The climate is dry, but the close proximity of the Pacific Ocean provides humidity and moderates the temperature. The flora mostly consists of xeric shrubs and over 500 species of recorded vascular plants.
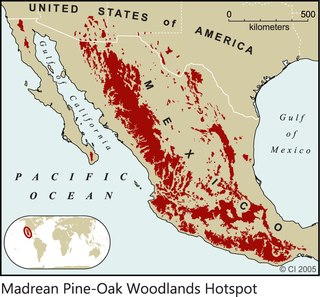
The Madrean pine-oak woodlands is an ecoregion of the Tropical and subtropical coniferous forests biome, located in North America. They are subtropical woodlands found in the mountains of Mexico and the southwestern United States.

The Sierra de Juárez, also known as the Sierra Juarez, is a mountain range located in Tecate Municipality and northern Ensenada Municipality, within northern Baja California state of northwestern Mexico.

The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca pine-oak forests is an ecoregion of the Tropical and subtropical coniferous forests biome, in Southern Mexico.

The Petén-Veracruz moist forests ecoregion, of the Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest Biome, is found in Belize, Guatemala, and Mexico.

The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt pine-oak forests is a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt of central Mexico.
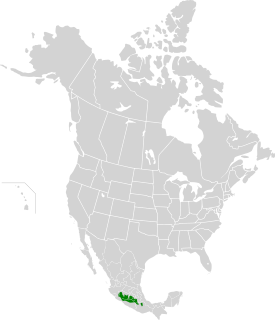
The Balsas dry forests are a tropical ecoregion, of the Tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests Biome, located in western and central Mexico.
The Central America bioregion is a biogeographic region comprising southern Mexico and Central America.

The Central Mexican matorral is an ecoregion of the deserts and xeric shrublands biome of central Mexico.
The Sonoran-Sinaloan transition subtropical dry forest is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in northwestern Mexico.
The Sierra Madre del Sur pine-oak forests is a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion of the Sierra Madre del Sur mountain range of southern Mexico.

The Chiapas Depression dry forests form one of the ecoregions that belong to the tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests biome, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund, in northwestern Central America.

The forests of Mexico cover a surface area of about 64 million hectares, or 34.5% of the country. These forests are categorized by the type of tree and biome: tropical forests, temperate forests, cloud forests, riparian forests, deciduous, evergreen, dry, moist, etc.. The agency in charge of Mexico's forests is the Comisión Nacional Forestal.

The Tumbes-Piura dry forests (NT0232) is an arid tropical ecoregion along the Pacific coasts of southern Ecuador and northern Peru. The ecoregion contains many endemic species of flora and birds adapted to the short wet season followed by a long dry season. Threats include extraction of wood for fuel or furniture, and capture of wild birds for sale.