
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, including A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes.

The M16 rifle is a family of military rifles adapted from the ArmaLite AR-15 rifle for the United States military. The original M16 rifle was a 5.56×45mm automatic rifle with a 20-round magazine.

A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of 1,435 mm. The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge, international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it.

The 5.56×45mm NATO is a rimless bottlenecked intermediate cartridge family developed in the late 1970s in Belgium by FN Herstal. It consists of the SS109, L110, and SS111 cartridges. On 28 October 1980, under STANAG 4172, it was standardized as the second standard service rifle cartridge for NATO forces as well as many non-NATO countries. Though they are not entirely identical, the 5.56×45mm NATO cartridge family was derived from and is dimensionally similar to the .223 Remington cartridge designed by Remington Arms in the early 1960s.

The M4 Sherman, officially Medium Tank, M4, was the most widely used medium tank by the United States and Western Allies in World War II. The M4 Sherman proved to be reliable, relatively cheap to produce, and available in great numbers. It was also the basis of several other armored fighting vehicles including self-propelled artillery, tank destroyers, and armored recovery vehicles. Tens of thousands were distributed through the Lend-Lease program to the British Commonwealth and Soviet Union. The tank was named by the British after the American Civil War General William Tecumseh Sherman.

The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths.

The Florida Keys are a coral cay archipelago off the southern coast of Florida, forming the southernmost part of the continental United States. They begin at the southeastern coast of the Florida peninsula, about 15 miles (24 km) south of Miami, and extend in a gentle arc south-southwest and then westward to Key West, the westernmost of the inhabited islands, and on to the uninhabited Dry Tortugas. The islands lie along the Florida Straits, dividing the Atlantic Ocean to the east from the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest, and defining one edge of Florida Bay. At the nearest point, the southern part of Key West is just 93 miles (150 km) from Cuba. The Keys are between about 24.3 and 25.5 degrees North latitude.
5.1 surround sound is the common name for surround sound audio systems. 5.1 is the most commonly used layout in home theatres. It uses five full bandwidth channels and one low-frequency effects channel. Dolby Digital, Dolby Pro Logic II, DTS, SDDS, and THX are all common 5.1 systems. 5.1 is also the standard surround sound audio component of digital broadcast and music.
AC power plugs and sockets connect electric equipment to the alternating current (AC) mains electricity power supply in buildings and at other sites. Electrical plugs and sockets differ from one another in voltage and current rating, shape, size, and connector type. Different standard systems of plugs and sockets are used around the world.

The B-series are a family of inline four-cylinder DOHC automotive engines introduced by Honda in 1988. Sold concurrently with the D-series which were primarily SOHC engines designed for more economical applications, the B-series were a performance option featuring dual overhead cams along with the first application of Honda's VTEC system, high-pressure die cast aluminum block, cast-in quadruple-Siamese iron liners.

In geology, hotspots are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them.

The Ferret armoured car, also commonly called the Ferret scout car, is a British armoured fighting vehicle designed and built for reconnaissance purposes. The Ferret was produced between 1952 and 1971 by the UK company Daimler. It was widely used by regiments in the British Army, as well as the RAF Regiment and Commonwealth countries throughout the period.

The Honda K-series engine is a line of four-cylinder four-stroke car engine introduced in 2001. The K-series engines are equipped with DOHC valvetrains and use roller rockers on the cylinder head to reduce friction. The engines use a coil-on-plug, distributorless ignition system with a coil for each spark plug. This system forgoes the use of a conventional distributor-based ignition timing system in favor of a computer-controlled system that allows the ECU to control ignition timings based on various sensor inputs. The cylinders have cast iron sleeves similar to the B- and F-series engines, as opposed to the FRM cylinders found in the H- and newer F-series engines found only in the Honda S2000.

Dactylorhiza viridis, the frog orchid, is a species of flowering plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae. It has also been treated as the only species Coeloglossum viride of the monotypic genus Coeloglossum.

Eucalyptus dives, commonly known as the broad-leaved peppermint or blue peppermint, is a species of tree that is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It has rough, finely fibrous bark on the trunk and larger branches, smooth bark above, lance-shaped or curved adult leaves, flower buds in groups of eleven or more, white flowers and cup-shaped, hemispherical or conical fruit.

The Carniolan sausage is a Slovenian sausage similar to what is known as kielbasa or Polish sausage in North America.
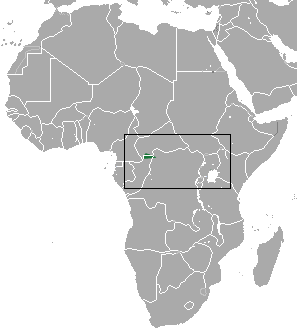
The Ugandan musk shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in Uganda, the Democratic Republic of Congo and the Central African Republic. Its range, population size and habits are poorly known.

Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class of soil or soil type; i.e., a soil containing more than 85 percent sand-sized particles by mass.

Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectric power plants, crop irrigation, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems.

Hypericum buckleyi, known as Blue Ride St. John's wort and Buckley's St. Johnswort, is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Hypericaceae found only in the Appalachian Mountains of the southeastern United States. The species is listed in the state of Georgia (S1), South Carolina (SX), and North Carolina (S3).



















