
Taurine, or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is an organic compound that is widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine, and accounts for up to 0.1% of total human body weight. It is named after the Latin taurus which means bull or ox, as it was first isolated from ox bile in 1827 by German scientists Friedrich Tiedemann and Leopold Gmelin. It was discovered in human bile in 1846 by Edmund Ronalds.
Serine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC.

A thiol or thiol derivative is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The –SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols, and the word is a blend of "thio-" with "alcohol", where the first word deriving from Greek θεῖον (theion) meaning "sulfur".

Butyric acid (from Ancient Greek: βούτῡρον, meaning "butter"), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2CO2H. It is an oily, colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Isobutyric acid (2-methylpropanoic acid) is an isomer. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. The acid does not occur widely in nature, but its esters are widespread. It is a common industrial chemical and an important component in the mammalian gut.
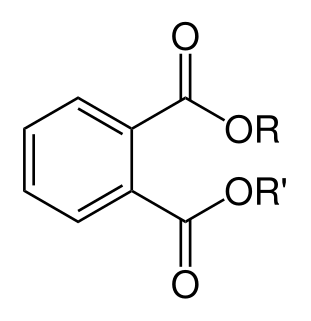
Phthalates, or phthalate esters, are esters of phthalic acid. They are mainly used as plasticizers, i.e., substances added to plastics to increase their flexibility, transparency, durability, and longevity. They are used primarily to soften polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
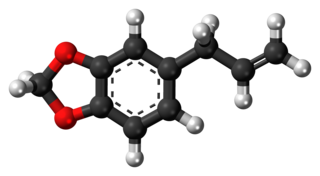
Safrole is an organic compound with the formula CH2O2C6H3CH2CH=CH2. It is a colorless oily liquid, although impure samples can appear yellow. A member of the phenylpropanoid family of natural products, it is found in sassafras plants, among others. Small amounts are found in a wide variety of plants, where it functions as a natural antifeedant. Ocotea pretiosa, which grows in Brazil, and Sassafras albidum, which grows in eastern North America, are the main natural sources of safrole. It has a characteristic "sweet-shop" aroma.
Linoleic acid is an organic compound with the formula COOH(CH2)7CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4CH3. Both alkene groups are cis. It is a fatty acid sometimes denoted 18:2 (n-6) or 18:2 cis-9,12. A linoleate is a salt or ester of this acid.

Myelin basic protein (MBP) is a protein believed to be important in the process of myelination of nerves in the nervous system. The myelin sheath is a multi-layered membrane, unique to the nervous system, that functions as an insulator to greatly increase the velocity of axonal impulse conduction. MBP maintains the correct structure of myelin, interacting with the lipids in the myelin membrane.

Benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) is a phthalate, an ester of phthalic acid, benzyl alcohol, and n-butanol. BBP is a clear liquid with the chemical formula C19H20O4. It was mostly used as a plasticizer for PVC. It is considered a toxicant.

Rebamipide, an amino acid derivative of 2-(1H)-quinolinone, is used for mucosal protection, healing of gastroduodenal ulcers, and treatment of gastritis. It works by enhancing mucosal defense, scavenging free radicals, and temporarily activating genes encoding cyclooxygenase-2.

2-Ethylhexanol is a branched, eight-carbon chiral alcohol. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. It is produced on a massive scale (>2,000,000,000 kg/y) for use in numerous applications such as solvents, flavors, and fragrances and especially as a precursor for production of other chemicals such as emollients and plasticizers. It is encountered in plants, fruits, and wines. The odor has been reported as "heavy, earthy, and slightly floral" for the R enantiomer and "a light, sweet floral fragrance" for the S enantiomer.
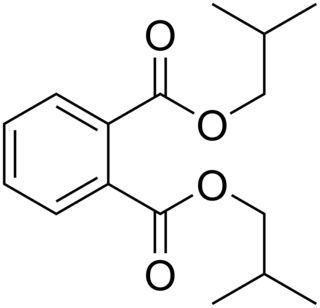
Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP) is prepared by esterification process of isobutanol and phthalic anhydride. Its structural formula is C6H4(COOCH2CH(CH3)2)2.

Butan-1-ol, also known as n-butanol is a primary alcohol with the chemical formula C4H9OH and a linear structure. Isomers of butan-1-ol are isobutanol, butan-2-ol and tert-butanol. The unmodified term butanol usually refers to the straight chain isomer.

Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) is an organic compound which is commonly used as a plasticizer because of its low toxicity and wide liquid range. With the chemical formula C6H4(CO2C4H9)2, it is a colorless oil, although commercial samples are often yellow.

Piceid is a stilbenoid glucoside and is a major resveratrol derivative in grape juices. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis. It can also be isolated from Reynoutria japonica, the Japanese knotweed.

Retinoic acid receptor gamma (RAR-γ), also known as NR1B3 is a nuclear receptor encoded by the RARG gene. Adapalene selectively targets retinoic acid receptor beta and retinoic acid receptor gamma and its agonism of the gamma subtype is largely responsible for adapalene's observed effects.

Glycine N-methyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GNMT gene.

Protocatechuic acid (PCA) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. It is a major metabolite of antioxidant polyphenols found in green tea. It has mixed effects on normal and cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo studies.

Diethyl phthalate (DEP) is a phthalate ester, appears as a clear colorless liquid without significant odor. It is more dense than water and insoluble in water; hence, it sinks in water.

Monobenzyl phthalate (MBzP) also known as benzene-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound with the condensed structural formula C6H5CH2OOCC6H4COOH. It is the major metabolite of butyl benzyl phthalate, more than monobutyl phthalate (MBP). Like many phthalates, MBP has attracted attention as a potential endocrine disruptor.



















