
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root brak. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it can be damaging to the environment.

Monodactylidae is a family of perciform bony fish commonly referred to as monos, moonyfishes or fingerfishes. All are strongly laterally compressed with disc-shaped bodies and tall anal and dorsal fins. Unusually for fish, scales occur on their dorsal fins and sometimes on the anal fins. The pelvic fins are small, sometimes vestigial. They are of moderate size, typically around 25 centimetres (9.8 in) in length, and Monodactylus sebae can be taller than it is long, measuring up to 30 centimetres (12 in) from the tip of the dorsal fin down to the tip of the anal fin. These long, scaly fins have given them the name "fingerfishes". Most are silvery with yellow and black markings; the juveniles are especially attractive, and most species are popular as aquarium fish.

Amphiprion sebae, also known as the sebae clownfish, is an anemonefish found in the northern Indian Ocean, from Java to the Arabian Peninsula. Like all anemonefish it is usually found living in association with sea anemones. While the common name of Heteractis crispa, the sebae anemone, suggests an association, it is normally found with the Stichodactyla haddoni or saddle anemone. A. sebae, like all anemonefish, lives in a symbiotic relationship with the host anemone where the fish is unaffected by the stinging tentacles of the anemone. In a group of clownfish, Only two clownfish, a male and a female, in a group reproduce through external fertilization. Clownfish are sequential hermaphrodites, changing from male to female, with a strict dominance hierarchy and only the largest fish being female.

The sebae anemone, also known as leathery sea anemone, long tentacle anemone, or purple tip anemone, is a species of sea anemone belonging to the family Stichodactylidae and native to the Indo-Pacific area.

The Central African rock python is a species of large constrictor snake in the family Pythonidae. The species is native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of 10 living species in the genus Python.
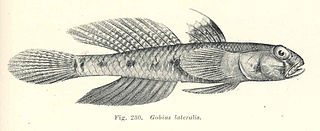
Favonigobius lateralis is a species of goby native to coastal waters of eastern Australia, Tasmania and New Zealand where it can be found in marine and brackish waters of sandy estuaries. It prefers to live in beds of seagrass. This species can reach a length of 9 centimetres (3.5 in) TL.

Monodactylus argenteus is a species of fish in the family Monodactylidae, the moonyfishes. Its common names include silver moonyfish, or natal moony, butter bream, and diamondfish. It is native to the western Pacific and Indian Oceans, including the Persian Gulf, Red Sea, and associated estuaries, such as the Mekong Delta.
The Bot River klipfish is a species of clinid endemic to South Africa where it is found in brackish waters of the Bot River and the Kleinmond Estuary where it lives amongst weeds. This species can reach a length of 17.5 centimetres (6.9 in) TL.

The common goby is a species of ray-finned fish native to fresh and brackish waters along the Atlantic and Baltic Sea coasts of Europe and northern Africa, with a range stretching from Norway to Morocco and Mauritania. It is also found in the Canary Islands. This species reaches a maximum length of 9 centimetres (3.5 in) TL.

Lutjanus sebae, also known as red emperor, emperor red snapper, emperor snapper, government bream, king snapper, queenfish or red kelp, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a snapper belonging to the family Lutjanidae. It is native to the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Cynoglossus quadrilineatus, the fourlined tonguesole, is a species of tonguefish native to the Indian Ocean from Pakistan to the western Pacific Ocean where it occurs from Japan to northern Australia. It can be found in marine and brackish waters in estuaries and coastal waters out to the continental shelf at depths of from 10 to 400 metres. This species can reach a length of 44 centimetres (17 in) SL though most do not exceed 30 centimetres (12 in) SL. It is important in local commercial fisheries.
Awaous grammepomus, the Scribbled goby, is a species of goby native to freshwater streams and rivers and brackish estuaries from Sri Lanka to New Guinea with a report of it occurring in Palau. This species can reach a length of 15 centimetres (5.9 in) SL. It is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries and can also be found in the aquarium trade.

The banded archerfish is a brackish water perciform fish of the archerfish genus Toxotes. It is silvery in colour and has a dorsal fin towards the posterior end. It has distinctive, semi-triangular markings along its sides. It is best known for its ability to spit a jet of water to "shoot down" prey. Larger specimens may be able to hit prey 2 to 3 metres away. The banded archerfish may reach the displaced prey within 50 milliseconds of its hitting the water.

Toxotes chatareus, sometimes known by the common names common archerfish, seven-spot archerfish or largescale archerfish, is a species of perciform fish in the archerfish genus Toxotes.

The smallscale archerfish is a perciform fish of genus Toxotes. As its name suggests, the scales of the smallscale archerfish are smaller than those of other archerfish. They reach a maximum length of 15 centimetres (5.9 in). Smallscale archerfish live in the tropical Indo-Pacific region and are potamodromous, moving between fresh and brackish water through their lifetimes.

The mushroom goby is a species of goby native to the Black Sea where it can be found along the coasts from Bulgaria to the Crimea. Mostly a species of marine and brackish waters, it is known to enter fresh waters in the delta of the Danube River. This species prefers inshore waters with rocks or fallen trees. This species can reach a length of 20 centimetres (7.9 in) TL.

The shuttles hoppfish or shuttles mudskipper is a species of mudskippers native to fresh, marine and brackish waters of the northwestern Pacific Ocean from Vietnam to Korea and Japan. This species occurs in muddy estuaries, tidal flats and swamps and marshes and is capable of remaining out of the water for up to 60 hours so long as it is kept moist. This species can reach a length of 10 centimetres (3.9 in) TL. This species can also be found in the aquarium trade and is also used in traditional Chinese medicine.

Monodactylus is a genus of moonyfishes found in fresh, brackish and marine waters from the eastern Atlantic, through the Indian to the western Pacific oceans.

Ophisternon bengalense the Bengal eel, Bengal mudeel or onegill eel, is a species of fish in the family Synbranchidae. It is endemic to freshwater and brackish water rivers and swamps in Oceania and South Asia. It is normally 100 cm in maximum length.
















