| monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDAR) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.6.5.4 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9029-26-9 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In enzymology, a monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDAR) (EC 1.6.5.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
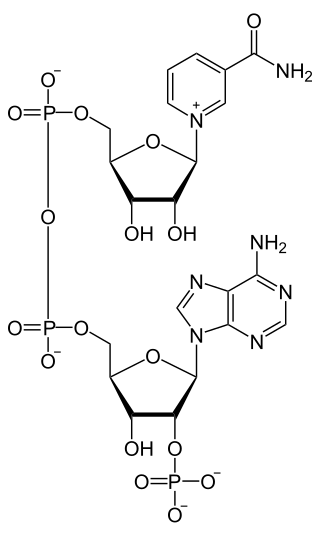
- NADH + H+ + 2 monodehydroascorbate NAD+ + 2 ascorbate
The 3 substrates of this enzyme are NADH, H+, and monodehydroascorbate, whereas its two products are NAD+ and ascorbate.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on NADH or NADPH, with a quinone or similar compound as an acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is NADH: monodehydroascorbate oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include NADH: semidehydroascorbic acid oxidoreductase, MDHA, semidehydroascorbate reductase, AFR, AFR-reductase, ascorbic free radical reductase, ascorbate free radical reductase, SOR, MDAsA reductase (NADPH), SDA reductase, NADH: ascorbate radical oxidoreductase, NADH-semidehydroascorbate oxidoreductase, ascorbate free-radical reductase, NADH: AFR oxidoreductase, and monodehydroascorbate reductase (NADH2). This enzyme participates in ascorbate and aldarate metabolism.
In plants, the monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDAR) is an enzymatic component of the glutathione-ascorbate cycle that is one of the major antioxidant systems of plant cells for the protection against the damages produced by reactive oxygen species (ROS). The MDAR activity has been described in several cell compartments, such as chloroplasts, cytosol, mitochondria, glyoxysomes, and leaf peroxisomes. [1]