
The snow bunting is a passerine bird in the family Calcariidae. It is an Arctic specialist, with a circumpolar Arctic breeding range throughout the northern hemisphere. There are small isolated populations on a few high mountain tops south of the Arctic region, including the Cairngorms in central Scotland and the Saint Elias Mountains on the southern Alaska-Yukon border, as well as the Cape Breton Highlands. The snow bunting is the most northerly recorded passerine in the world.

The least weasel, little weasel, common weasel, or simply weasel is the smallest member of the genus Mustela, family Mustelidae and order Carnivora. It is native to Eurasia, North America and North Africa, and has been introduced to New Zealand, Malta, Crete, the Azores, and São Tomé. It is classified as least concern by the IUCN, due to its wide distribution and large population throughout the Northern Hemisphere.

The white-winged snowfinch, or snowfinch, is a small passerine bird. Despite its name, it is a sparrow rather than a true finch.

Galanthus nivalis, the snowdrop or common snowdrop, is the best-known and most widespread of the 20 species in its genus, Galanthus. Snowdrops are among the first bulbs to bloom in spring and can form impressive carpets of white in areas where they are native or have been naturalised. They should not be confused with the snowflakes, in the genera Leucojum and Acis.

Chlamydomonas nivalis, also referred to as Chloromonas typhlos, is a unicellular red-coloured photosynthetic green alga that is found in the snowfields of the alps and polar regions all over the world. They are one of the main algae responsible for causing the phenomenon of watermelon snow, where patches of snow appear red or pink. The first account of microbial communities that form red snow was made by Aristotle. Researchers have been active in studying this organism for over 100 years.

Gentiana nivalis, the snow gentian or Alpine gentian, is a species of the genus Gentiana. It grows to a height of 3–15 centimetres.

Pyrus nivalis, commonly known as yellow pear or snow pear, is a species of tree in the family Rosaceae that grows naturally from South-East Europe to Western Asia. Like most pears, its fruit can be eaten raw or cooked; it has a mild sour taste. The fruit is picked in October, when it is still dry and unripe; it will not become soft and sweet until the end of November or December, hence the name snow pear.

Chionomys is a genus of rodent in the family Cricetidae.

The European snow vole or snow vole is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It has dense, pale grey fur and a pale-coloured tail and can reach about 14 cm (5.5 in) long, with a tail which is 7 cm (2.8 in) long.

Podocarpus nivalis, the mountain or snow tōtara, is a species of conifer in the family Podocarpaceae. It is endemic to New Zealand.

The greater long-nosed bat or Mexican long-nosed bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found in Mexico and the United States. It chiefly consumes pollen and nectar, particularly from agave plants and cacti. Its habitat includes desert scrub and open woodlands, however, it is threatened by habitat loss.

The Heard Island shag, or Heard Island cormorant, is a marine cormorant native to the Australian territory comprising the Heard and McDonald Islands in the Southern Ocean, which is about 4,100 km south-west of Perth, Western Australia.

Rubus nivalis, commonly known as snow raspberry, is a species of flowering plant in the rose family. It is native to northwestern North America: British Columbia, Washington, Idaho, Oregon, and far northern California.

Urola nivalis, the snowy urola moth, is a moth of the family Crambidae. It is found from southern Canada and Maine, south to Florida and west to Illinois and Texas.

Lycaena nivalis, the lilac-bordered copper or nivalis copper, is a butterfly of the family Lycaenidae. It is found in the western mountains of North America.
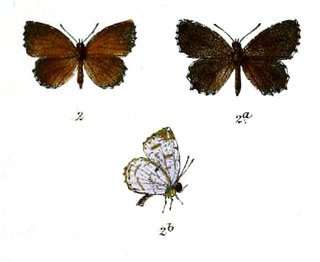
Allotinus nivalis is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It was described by Herbert Druce in 1873. It is found in Southeast Asia.

Amanita nivalis, the snow ringless amanita or mountain grisette, is a species of basidomycote fungus in the genus Amanita.
Luzula nivalis, commonly known as arctic wood-rush or less commonly as snowy wood-rush, is a species of perennial rush native to the North American Arctic and Northern Europe. It was described by Polunin (1940) as one of the most abundant, ubiquitous, and ecologically important of all arctic plants.
Carex nivalis is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1845. It is found from Afghanistan to southwest China. The name has also been used as a synonym for Carex micropoda.
Erigeron nivalis is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, called the northern daisy. It is widespread across much of western North America from Alaska east to Northwest Territories and south as far as California and New Mexico.
















