Related Research Articles

The Miller Range is a mountain range extending south from Nimrod Glacier for 80 km (50 mi) along the western edge of the Marsh Glacier in Antarctica.
The Neptune Range is a mountain range, 112 km (70 mi) long, lying WSW of Forrestal Range in the central part of the Pensacola Mountains in Antarctica. The range is composed of Washington Escarpment with its associated ridges, valleys and peaks, the Iroquois Plateau, and the Schmidt and Williams Hills. It was discovered and photographed on 13 January 1956 on a US Navy transcontinental plane flight from McMurdo Sound to Weddell Sea and return.
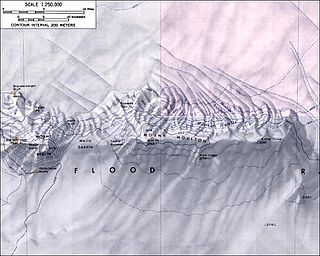
The Flood Range is an Antarctic range of large snow-covered mountains extending in an E-W direction for about 96 km (60 mi) and forming a right angle with the southern end of the Ames Range in Marie Byrd Land.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.
Foundation Ice Stream is a major ice stream in Antarctica's Pensacola Mountains. The ice stream drains northward for 150 nautical miles along the west side of the Patuxent Range and the Neptune Range to enter the Ronne Ice Shelf westward of Dufek Massif. The United States Geological Survey mapped the stream from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1956–66. The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names named the stream in recognition of the National Science Foundation, which provided major support to the U.S. Antarctic Research Program during this period.

The Herbert Mountains are a conspicuous group of rock summits on the east side of Gordon Glacier in the Shackleton Range of Antarctica. They were first mapped in 1957 by the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition and named for Sir Edwin S. Herbert, Chairman of the Finance Committee and a Member of the Committee of Management of the expedition, 1955–58.
Arthur Glacier is a valley glacier in Antarctica. It is about 25 nautical miles (50 km) long, and flows west to Sulzberger Ice Shelf between the Swanson Mountains on the north and Mount Rea and Mount Cooper on the south, in the Ford Ranges of Marie Byrd Land. It was discovered by members of West Base of the United States Antarctic Service, in aerial flights and from ground surveys in November–December 1940. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Rear Admiral Arthur C. Davis, a leader in aviation in the U.S. Navy.

Otter Highlands is a group of peaks and ridges extending northwest-southeast for 17 nautical miles from Mount Lowe to Wyeth Heights, located west of Blaiklock Glacier and forming the west end of the Shackleton Range. Surveyed by the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition in 1957. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1972 after the De Havilland Otter aircraft which supported the CTAE.

Mount Ojakangas is an elongated mountain rising to about 2,450 m, 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) northwest of Mount Washburn in Gromshin Heights in the north part of the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains. It surmounts Vicha Glacier to the east and Newcomer Glacier to the west.
Mount Crooker is a gable-shaped mountain with much exposed rock, located on the north side of Ryder Glacier and at the south end of the Pegasus Mountains, in Palmer Land. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Allen R. Crooker, a United States Antarctic Research Program biologist at Palmer Station in 1972.
Mount Krokisius is a mountain 0.6 nautical miles (1.1 km) northeast of Moltke Harbor, South Georgia. Named by the German group of the International Polar Year Investigations, 1882–83, for Corvette Captain Krokisius, commander of the Marie, one of the two ships of the expedition.

Sullivan Heights is a compact group of mountains in western Antarctica rising to 2,760 m (9,060 ft) in Mount Levack centered 11.5 nautical miles east-northeast of Mount Tyree in the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains. Roughly elliptical in plan and 11 nautical miles long, the feature includes sharp mountain peaks, rugged ridges, and steep peripheral scarps. The heights are encompassed by the flow of the Crosswell, Ellen, and Dater Glaciers, with their interior drained also by Pulpudeva and Strinava Glaciers. Separated from Vinson Massif to the south-southwest by Vranya Pass.

Mount Goldthwait is a prominent mountain located 2.5 nautical miles (4.6 km) south of Mount Dalrymple in the north part of the Sentinel Range, Antarctica. Discovered by the Marie Byrd Land Traverse Party of 1957–58, under Charles R. Bentley, and named for Richard P. Goldthwait, consultant, Technical Panel on Glaciology, U.S. National Committee for the IGY, and later Director, Institute of Polar Studies, Ohio State University.
Moulder Peak is a sharp peak 3 nautical miles (6 km) southeast of Mount Rosenthal in the Liberty Hills of the Heritage Range, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for storekeeper Andrew B. Moulder, U.S. Navy, who was fatally injured in a cargo unloading accident at South Pole Station, February 13, 1966.
Mount Mill is a mountain, 735 metres (2,410 ft), standing 2 nautical miles (4 km) west of Mount Balch on the northeast shore of Waddington Bay, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was first charted by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1897–99, and was named by the Fourth French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, for British geographer Hugh Robert Mill, an Antarctic historian and author in 1905 of The Siege of the South Pole.

La Grange Nunataks is a scattered group of nunataks extending west for 22 nautical miles (41 km) from the mouth of Gordon Glacier, on the north side of the Shackleton Range, Antarctica. They were first mapped in 1957 by the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE), and were photographed in 1967 by U.S. Navy aircraft. They were named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Johannes J. La Grange, a South African meteorologist with the CTAE. Not: Beney Nunataks.

The Liberty Hills are a line of rugged hills and peaks with bare rock eastern slopes, about 10 nautical miles (19 km) long, standing 7 nautical miles (13 km) northwest of the Marble Hills and forming part of the west wall of Horseshoe Valley, in the Heritage Range, Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. The Liberty Hills were mapped by the United States Geological Survey from ground surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–66. The name was applied by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in association with the name Heritage Range. The remarkable High Nunatak towers east of the Hills.

Della Pia Glacier is a glacier that descends the east slope of Craddock Massif and flows between Mount Mohl and Elfring Peak into Thomas Glacier in the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica.

Knutzen Peak is a sharp, rocky summit of elevation 3,373 metres (11,066 ft) standing on the north edge of Taylor Ledge in the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It surmounts Branscomb Glacier to the east and south.

Schmidt Glacier is a glacier, 20 nautical miles long, in the Pioneer Heights of the Heritage Range, Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The glacier originates near Hall Peak and drains north along the west side of Thompson Escarpment and Gross Hills to coalesce with the lower part of Splettstoesser Glacier, north of Mount Virginia. It was named by the University of Minnesota Ellsworth Mountains Party, 1961–62, for Paul G. Schmidt, geologist with the party.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Rosenthal". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Mount Rosenthal". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
