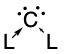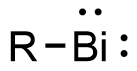In organic chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is R−:C−R' or R=C: where the R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms.
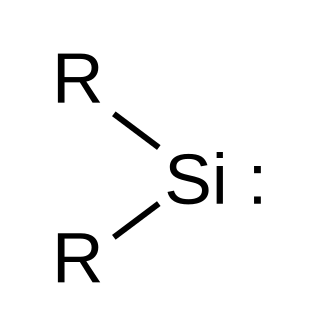
Silylene is a chemical compound with the formula SiR2. It is the silicon analog of carbene. Due to presence of a vacant p orbital, silylene rapidly reacts in a bimolecular manner when condensed. Unlike carbenes, which can exist in the singlet or triplet state, silylene (and all of its derivatives) are singlets.
A transition metal carbene complex is an organometallic compound featuring a divalent carbon ligand, itself also called a carbene. Carbene complexes have been synthesized from most transition metals and f-block metals, using many different synthetic routes such as nucleophilic addition and alpha-hydrogen abstraction. The term carbene ligand is a formalism since many are not directly derived from carbenes and most are much less reactive than lone carbenes. Described often as =CR2, carbene ligands are intermediate between alkyls (−CR3) and carbynes (≡CR). Many different carbene-based reagents such as Tebbe's reagent are used in synthesis. They also feature in catalytic reactions, especially alkene metathesis, and are of value in both industrial heterogeneous and in homogeneous catalysis for laboratory- and industrial-scale preparation of fine chemicals.

A persistent carbene is an organic molecule whose natural resonance structure has a carbon atom with incomplete octet, but does not exhibit the tremendous instability typically associated with such moieties. The best-known examples and by far largest subgroup are the N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC), in which nitrogen atoms flank the formal carbene.
In organic chemistry, umpolung or polarity inversion is the chemical modification of a functional group with the aim of the reversal of polarity of that group. This modification allows secondary reactions of this functional group that would otherwise not be possible. The concept was introduced by D. Seebach and E.J. Corey. Polarity analysis during retrosynthetic analysis tells a chemist when umpolung tactics are required to synthesize a target molecule.

Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.

Borirenes are a unique class of three-membered heterocyclic compounds characterized by an unsaturated boron atom within their ring structure. First computationally predicted by John Pople and Paul von Rague Schleyer in 1981, the simplest borirene, (CH)2BH, is isoelectronic with the cyclopropenium cation and exhibits Hückel aromaticity. Borirenes undergo ring-opening reactions with polar reagents and form Lewis adducts, due to the significant ring strain in its three-membered structure and the presence of an empty p orbital on the boron atom. The balance of these two properties leads to unique properties as a ligand for transition metals, in addition to observation of photochemical rearrangement and ring expansion. While borirenes were first discovered in the 1980s, new derivatives such as benzoborirenes have led to renewed interest in the field, with their potential applications yet to be fully explored.
Carbene analogs in chemistry are carbenes with the carbon atom replaced by another chemical element. Just as regular carbenes they appear in chemical reactions as reactive intermediates and with special precautions they can be stabilized and isolated as chemical compounds. Carbenes have some practical utility in organic synthesis but carbene analogs are mostly laboratory curiosities only investigated in academia. Carbene analogs are known for elements of group 13, group 14, group 15 and group 16.

Germylenes are a class of germanium(II) compounds with the general formula :GeR2. They are heavier carbene analogs. However, unlike carbenes, whose ground state can be either singlet or triplet depending on the substituents, germylenes have exclusively a singlet ground state. Unprotected carbene analogs, including germylenes, has a dimerization nature. Free germylenes can be isolated under the stabilization of steric hindrance or electron donation. The synthesis of first stable free dialkyl germylene was reported by Jutzi, et al in 1991.
Digermynes are a class of compounds that are regarded as the heavier digermanium analogues of alkynes. The parent member of this entire class is H-Ge≡Ge-H, which has only been characterized computationally, but has revealed key features of the whole class. Because of the large interatomic repulsion between two Ge atoms, only kinetically stabilized digermyne molecules can be synthesized and characterized by utilizing bulky protecting groups and appropriate synthetic methods, for example, reductive coupling of germanium(II) halides.
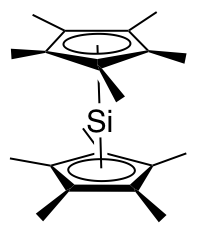
Decamethylsilicocene, (C5Me5)2Si, is a group 14 sandwich compound. It is an example of a main-group cyclopentadienyl complex; these molecules are related to metallocenes but contain p-block elements as the central atom. It is a colorless, air sensitive solid that sublimes under vacuum.

Trisilaallene is a subclass of silenes derivatives where a central silicon atom forms double bonds with each of two terminal silicon atoms, with the generic formula R2Si=Si=SiR2. Trisilaallene is a silicon-based analog of an allene, but their chemical properties are markedly different.

Silylones are a class of zero-valent monatomic silicon complexes, characterized as having two lone pairs and two donor-acceptor ligand interactions stabilizing a silicon(0) center. Synthesis of silylones generally involves the use of sterically bulky carbenes to stabilize highly reactive Si(0) centers. For this reason, silylones are sometimes referred to siladicarbenes. To date, silylones have been synthesized with cyclic alkyl amino carbenes (cAAC) and bidentate N-heterocyclic carbenes (bis-NHC). They are capable of reactions with a variety of substrates, including chalcogens and carbon dioxide.

Phosphasilenes or silylidenephosphanes are a class of compounds with silicon-phosphorus double bonds. Since the electronegativity of phosphorus (2.1) is higher than that of silicon (1.9), the "Si=P" moiety of phosphasilene is polarized. The degree of polarization can be tuned by altering the coordination numbers of the Si and P centers, or by modifying the electronic properties of the substituents. The phosphasilene Si=P double bond is highly reactive, yet with the choice of proper substituents, it can be stabilized via donor-acceptor interaction or by steric congestion.

Plumbylenes (or plumbylidenes) are divalent organolead(II) analogues of carbenes, with the general chemical formula, R2Pb, where R denotes a substituent. Plumbylenes possess 6 electrons in their valence shell, and are considered open shell species.
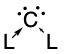
Carbones are a class of molecules containing a carbon atom in the 1D excited state with a formal oxidation state of zero where all four valence electrons exist as unbonded lone pairs. These carbon-based compounds are of the formula CL2 where L is a strongly σ-donating ligand, typically a phosphine (carbodiphosphoranes) or a N-heterocyclic carbene/NHC (carbodicarbenes), that stabilises the central carbon atom through donor-acceptor bonds. Carbones possess high-energy orbitals with both σ- and π-symmetry, making them strong Lewis bases and strong π-backdonor substituents. Carbones possess high proton affinities and are strong nucleophiles which allows them to function as ligands in a variety of main group and transition metal complexes. Carbone-coordinated elements also exhibit a variety of different reactivities and catalyse various organic and main group reactions.

An N-heterocyclic carbene boryl anion is an isoelectronic structure of an N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC), where the carbene carbon is replaced with a boron atom that has a -1 charge. NHC boryl anions have a planar geometry, and the boron atom is considered to be sp2-hybridized. They serve as extremely strong bases, as they are very nucleophilic. They also have a very strong trans influence, due to the σ-donation coming from the boron atom. NHC boryl anions have stronger electron-releasing character when compared to normal NHCs. These characteristics make NHC boryl anions key ligands in many applications, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and more commonly low oxidation state main group element bonding.
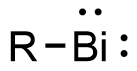
Bismuthinidenes are a class of organobismuth compounds, analogous to carbenes. These compounds have the general form R-Bi, with two lone pairs of electrons on the central bismuth(I) atom. Due to the unusually low valency and oxidation state of +1, most bismuthinidenes are reactive and unstable, though in recent decades, both transition metals and polydentate chelating Lewis base ligands have been employed to stabilize the low-valent bismuth(I) center through steric protection and π donation either in solution or in crystal structures. Lewis base-stabilized bismuthinidenes adopt a singlet ground state with an inert lone pair of electrons in the 6s orbital. A second lone pair in a 6p orbital and a single empty 6p orbital make Lewis base-stabilized bismuthinidenes ambiphilic. Recently, a triplet bismuthinidene is reported by Cornella et al.
A ketenyl anion contains a C=C=O allene-like functional group, similar to ketene, with a negative charge on either terminal carbon or oxygen atom, forming resonance structures by moving a lone pair of electrons on C-C-O bond. Ketenes have been sources for many organic compounds with its reactivity despite a challenge to isolate them as crystal. Precedent method to obtain this product has been at gas phase or at reactive intermediate, and synthesis of ketene is used be done in extreme conditions. Recently found stabilized ketenyl anions become easier to prepare compared to precedent synthetic procedure. A major feature about stabilized ketene is that it can be prepared from carbon monoxide (CO) reacting with main-group starting materials such as ylides, silylene, and phosphinidene to synthesize and isolate for further steps. As CO becomes a more common carbon source for various type of synthesis, this recent finding about stabilizing ketene with main-group elements opens a variety of synthetic routes to target desired products.

Stibinidenes represent a class of organoantimony compounds in which the antimony center exhibits a formal oxidation state of +1. Structurally, stibinidenes adopt the general formula R–Sb, with the antimony center possessing two lone pairs of electrons and a vacant 5p orbital. Due to the unusual low oxidation state of antimony, stibinidenes are highly reactive and prone to oxidation, often transitioning to the more stable +3 oxidation state. Historically, stibinidenes were only known in their oligomeric forms or in coordination complexes with transition metal centers. In such coordination states, the reactive lone pair centers are effectively blocked, limiting the potential applications of these compounds. However, the use of sterically bulky ligands, such as 2,4,6-tris[bis(trimethylsilyl)methyl]phenyl, 2,6-bis-[bis(trimethylsilyl)methyl]-4-[tris(trimethylsilyl)methyl]phenyl, and various m-terphenyl ligands, has enabled the isolation of stable heavier-element dipnictenes of the general formula RSb=SbR. So, the synthesis of monomeric stibinidene molecules necessitates the combined application of kinetic and thermodynamic stabilization strategies. This approach has successfully yielded stabilized monomeric stibinidenes with carbene ligands, bulky N,C,N-pincer ligands, phosphinebased and gallium based ligand. Based on computational studies, ⲡ-donating substituents, such as nitrogen- and phosphorus-based anionic ligands attached to the pnictogen atom, significantly stabilize the singlet ground state of stibinidenes. In this state, the molecule features one stereochemically inactive lone pair with predominantly s-character and another lone pair with predominantly p-character, accompanied by a vacant p orbital, making stibinidenes ambiphilic. In contrast, σ-type ligands, such as hydride and alkyl groups, favor the triplet ground state, where two unpaired electrons occupy two 5p orbitals and one lone pair resides in the 5s orbital. Notably, the isolation of a triplet stibinidene was achieved only recently using a highly bulky σ-type ligand, hydrindacene.
![.mw-parser-output .template-chem2-su{display:inline-block;font-size:80%;line-height:1;vertical-align:-0.35em}.mw-parser-output .template-chem2-su>span{display:block;text-align:left}.mw-parser-output sub.template-chem2-sub{font-size:80%;vertical-align:-0.35em}.mw-parser-output sup.template-chem2-sup{font-size:80%;vertical-align:0.65em}
[tBuN-CH=CH-tBuN]Si: (N,N'-Di-tert-butyl-1,3-diaza-2-silacyclopent-4-en-2-ylidene) The first stable NHSi. First Stable NHSi.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/57/First_Stable_NHSi.svg/220px-First_Stable_NHSi.svg.png)
![Synthesis of
[tBuN-CH=CH-tBuN]Si Margin general synth no English.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b6/Margin_general_synth_no_English.svg/633px-Margin_general_synth_no_English.svg.png)












![Contour map based on Atoms in Molecules analysis of the archetypal unsaturated NHSi [HN-CH=CH-NH]Si: showing second derivative of charge density. Solid line indicate a positive Laplacian and striped indicate a negative Laplacian. NHSi contour map.png](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/82/NHSi_contour_map.png/335px-NHSi_contour_map.png)