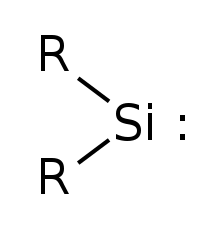
 Simplest silylene has R=Hydrogen | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Silylene | |
| Systematic IUPAC name Silylidene [1] | |
| Other names Hydrogen silicide(−II) Silicene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H2Si | |
| Molar mass | 30.101 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Silylene is a chemical compound with the formula SiR2 (R = H). It is the silicon analog of carbene. Silylenes decomposes rapidly when condensed.
Contents
Silylenes are formal derivatives of silylene with its hydrogens replaced by other substituents. [2] Most examples feature amido (NR2) or organyl groups. [3] [4]
Silylenes have been proposed as reactive intermediates. They are carbene analogs. [5]


