
Nepita is a monotypic moth genus in the subfamily Arctiinae erected by Frederic Moore in 1860. Its only species, Nepita conferta, the footman moth, was first described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in India and Sri Lanka.

Arsacia is a monotypic moth genus of the family Noctuidae. Its only species is Arsacia rectalis. Both the genus and species were described by Francis Walker, the genus in 1866 and the species in 1863. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics of India, Sri Lanka to Queensland and the Solomon Islands.

Mythimna decisissima is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Francis Walker in 1856. It is found from India across south-east Asia including Hong Kong, Japan, Taiwan and Australia in Queensland and New South Wales. It is also present in South Africa.

Acrapex carnea is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae first described by George Hampson in 1905. It is found in Africa, including South Africa.

Acrapex spoliata is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Francis Walker in 1863. It is found in Africa, including Sierra Leone and South Africa.

Eudocima phalonia, the common fruit-piercing moth, is a fruit piercing moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1763 Centuria Insectorum. It is found in large parts of the tropics, mainly in Asia, Africa and Australia but introduced into other areas such as Hawaii, New Zealand and the Society Islands. It is one of major fruit pests in the world.

Penicillaria jocosatrix, the mango shoot borer, is a moth of the family Euteliidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found from southeast Asia to the Pacific. Records include Borneo, Guam, Hawaii, India, Sri Lanka, Thailand and in Australia, Western Australia, the Northern Territory and Queensland.

Chilo suppressalis, the Asiatic rice borer or striped rice stemborer, is a moth of the family Crambidae. It is a widespread species, known from Iran, India, Sri Lanka, China, eastern Asia, Japan, Taiwan, Malaysia to the Pacific.

Ischyja manlia is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Pieter Cramer in 1776. It is found in the Indian subregion, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, China, Okinawa, Sundaland, Sulawesi, Korea, the southern Moluccas, Australia (Queensland) and Palau.

Mythimna pallidicosta is a moth in the family Noctuidae first described by George Hampson in 1894. It is found from north-eastern India to western China, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Sundaland, Flores, the Philippines and Japan.

Banisia myrsusalis, the sapodilla borer or sapota midrib folder, is a species of moth of the family Thyrididae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1859 and is found in North America, Brazil, Australia, southern Asia and Africa.
Eriopithex recensitaria is a moth in the family Geometridae first described by Francis Walker in 1862. It is found in Sri Lanka, Taiwan, on Borneo and in the Australian state of Queensland.
Gymnoscelis imparatalis, the flower-looper moth, is a moth in the family Geometridae. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics of India, Sri Lanka, east to the Society Islands and the Marquesas Archipelago. The habitat consists of both lowland and montane ecosystems.
Gymnoscelis deleta is a moth in the family Geometridae. It is found in India, Korea, Japan, Taiwan and probably in Sri Lanka according to Hampson.

Hypomecis separata is a species of moth of the family Geometridae. It was first described by Francis Walker in 1863. It is found in Sri Lanka, India, Java and Borneo.

Autoba abrupta is a species of moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in Papua New Guinea, Thailand, and Australia. The species is largely used by the name Eublemma abrupta in Indian and Sri Lankan texts.
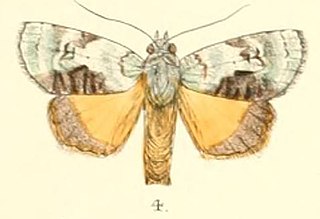
Blenina donans is a moth of the family Nolidae first described by Francis Walker in 1858. It is found from India, Sri Lanka to the Pacific region.
Surattha invectalis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1863. It is found in Sri Lanka, India, Java, Indonesia, Myanmar, and Kenya.

Hyposidra talaca, the black looper or black inch worm, is a moth of the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1860. It is found from India to Indochina, Sundaland, Sulawesi, the Philippines, Sri Lanka, the Solomon Islands, Thailand, Taiwan, New Guinea and Australia, where it has been recorded from Queensland. It is a major defoliating pest in tea plantations.

Chrysocraspeda abhadraca is a species of moth in the family Geometridae described by Francis Walker in 1861. It is found in Indian subregion including India and Sri Lanka, Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra and Borneo.














