See also
| | This article about a location in the Interior of British Columbia, Canada is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
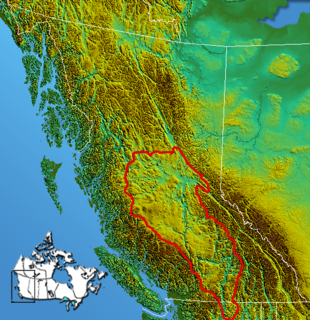
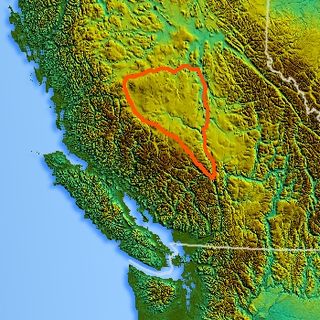
The Nechako Country, also referred to as the Nechako District or simply "the Nechako" is one of the historical geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia, located southwest of the city of Prince George and south of Hwy 16 on the inland side of the Hazelton Mountains (an inland subrange of the Coast Mountains), and comprising the basin of the Nechako River and its tributaries. "Nechako" is an anglicization of netʃa koh, its name in the indigenous Carrier language which means "big river".
The area is sparsely populated, mostly by members of the Carrier people, and is noted for its many large lakes, including Ootsa Lake Reservoir, which is the source of water for the Kemano Powerhouse on a neighbouring coastal inlet, which is the power supply for the aluminum smelter at Kitimat.
To the north of the Nechako Country are the Omineca Country and Bulkley Valley, while to its south is the Chilcotin Country and to the southeast the Cariboo Country.

The Dakelh or Carrier are the indigenous people of a large portion of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada.
New Caledonia was a fur-trading district of the Hudson's Bay Company that comprised the territory of the north-central portions of present-day British Columbia, Canada. Though not a British colony, New Caledonia was part of the British claim to North America. Its administrative centre was Fort St. James. The rest of what is now mainland British Columbia was called the Columbia Department by the British, and the Oregon Country by the Americans. Even before the partition of the Columbia Department by the Oregon Treaty in 1846, New Caledonia was often used to describe anywhere on the mainland not in the Columbia Department, such as Fort Langley in the Fraser Valley.

The Regional District of Bulkley–Nechako (RDBN) is a regional district in the Canadian province of British Columbia, Canada. As of the 2016 census, the population was 37,896. The area is 73,419.01 square kilometres. The regional district offices are in Burns Lake.

The Nechako River arises on the Nechako Plateau east of the Kitimat Ranges of the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, and flows north toward Fort Fraser, then east to Prince George where it enters the Fraser River. "Nechako" is an anglicization of netʃa koh, its name in the indigenous Carrier language which means "big river".
The Interior Plateau comprises a large region of the Interior of British Columbia, and lies between the Cariboo and Monashee Mountains on the east, and the Hazelton Mountains, Coast Mountains and Cascade Range on the west. The continuation of the plateau into the United States is known there as the Columbia Plateau.
The Chilcotin Plateau is part of the Fraser Plateau, a major subdivision of the Interior Plateau of British Columbia. The Chilcotin Plateau is physically near-identical with the region of the same name, i.e. "the Chilcotin", which lies between the Fraser River and the southern Coast Mountains and is defined by the basin of the Chilcotin River and so includes montane areas beyond the plateau. East of the Chilcotin Plateau, across the Fraser River, is the Cariboo Plateau, while to the north beyond the West Road (Blackwater) River is the Nechako Plateau. West and south of the Chilcotin Plateau are various subdivisions of the Coast Mountains, including the Chilcotin Ranges which lie along the plateau's southwest.
The Stuart River or Nak'alkoh is one of the largest tributaries of the Nechako River in northeastern British Columbia, Canada. The Nechako is in turn one the more important tributaries of the Fraser River. The Stuart River flows 187 kilometres (116 mi) from Stuart Lake to its junction with the Nechako River. The river drains a portion of the Nechako Plateau—a gently-rolling region characterized by small lakes and tributaries. Low but impressive ridges interact with the river, creating high bluffs and hoodoos.

The Omineca Mountains, also known as "the Ominecas", are a group of remote mountain ranges in the Boreal Cordillera of north-central British Columbia, Canada. They are bounded by the Finlay River on the north, the Rocky Mountain Trench on the east, the Nation Lakes on the south, and the upper reaches of the Omineca River on the west. They form a section of the Continental Divide, that, in this region, separates water drainage between the Arctic and Pacific Oceans. The lower course of the Omineca River flows through the heart of the range. To the south of the Ominecas is the Nechako Plateau, to the west the Skeena Mountains and Hazelton Mountains, to the north the Spatsizi Plateau and the Stikine Ranges, while east across the Rocky Mountain Trench are the Muskwa Ranges.

The Hazelton Mountains are a grouping of mountain ranges on the inland lee of the Kitimat Ranges of the Coast Mountains in northwestern British Columbia, Canada, spanning the area of Hazelton south to the Nechako Reservoir. Defined by the British Columbia geographic names office, they span from the Nass River to the Nechako Plateau, and between the Coast Mountains and the Bulkley River, they are considered by geographers to be part of the Interior Mountains complex, though in local perspective they are considered to be part of the Coast Mountains. They are neighboured on the west by the Kitimat Ranges and on the east by the southernmost section of the Skeena Mountains; beyond the Nass River, which is their northern boundary, are the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains. To their southeast is the Nechako Plateau, including the Quanchus Range on the near-island between Ootsa and Eutsuk Lakes of the Nechako Reservoir.

The Nechako Plateau is the northernmost subdivision of the Interior Plateau, one of the main geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia. It spans the basin of the Nechako River and its tributaries the Stuart River and Endako Rivers, and is bounded on the south by the West Road River, south of which is the Chilcotin Plateau and on the north by the Nation River and the valleys of Babine and Takla Lakes, beyond which are the Omineca Mountains (N) and Skeena Mountains (NW). To the west, it abuts the various ranges of the Hazelton Mountains while on its east it is bounded by the pass between Prince George, British Columbia and the Parsnip Arm of Williston Lake, beyond which is the McGregor Plateau, which skirts the Northern Rockies. Some classification systems include the plateau area on the east bank of the Fraser River beyond the city of Prince George; this area neighbours the northernmost reaches of the Quesnel Highland and Cariboo Mountains.

The Nadleh Whut'en First Nation is a First Nations government of the Dakelh people, whose territory is located in the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada, around the east end of Fraser Lake. The nation has seven reserves which Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Development Canada refer to as IR#1-9.. Until 1990, it was referred to as the Fraser Lake Indian Band.

The Alexander MacKenzie Heritage Trail is a 420 km (260 mi) long historical overland route between Quesnel and Bella Coola, British Columbia, Canada. Of the many grease trails connecting the Coast with the Interior, it is the most notable and often is referred to as the Grease Trail.

The British Columbia Interior, popularly referred to as the BC Interior or simply the Interior, is a geographic region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. While the exact boundaries are variously defined, the British Columbia Interior is generally defined to include the 14 regional districts that do not have coastline along the Pacific Ocean or Salish Sea, and are not part of the Lower Mainland. Other boundaries may exclude parts of or even entire regional districts, or expand the definition to include the regional districts of Fraser Valley, Squamish–Lillooet, and Kitimat–Stikine.
The Kenney Dam is a rock-fill embankment dam on the Nechako River in northwestern British Columbia, built in the early 1950s. The impoundment of water behind the dam forms the Nechako Reservoir, which is also commonly known as the Ootsa Lake Reservoir. The dam was constructed to power an aluminum smelter in Kitimat, British Columbia by Alcan, although in the late 1980s the company increased their economic activity by selling excess electricity across North America. The development of the dam caused various environmental problems along with the displacement of the Cheslatta T'En First Nation, whose traditional land was flooded.

The Nechako Reservoir, sometimes called the Ootsa Lake Reservoir, is a hydroelectric reservoir in British Columbia, Canada that was formed by the Kenney Dam making a diversion of the Nechako River through a 16-km intake tunnel in the Kitimat Ranges of the Coast Mountains to the 890 MW Kemano Generating Station at sea level at Kemano to service the then-new Alcan aluminum smelter at Kitimat. When it was constructed on the Nechako River in 1952, it resulted in the relocation of over 75 families. It was one of the biggest reservoirs built in Canada until the completion of the Columbia Treaty Dams and the W.A.C. Bennett Dam that created Lake Williston. The water level may swing 10 feet between 2790 and 2800 feet.

Knewstubb Lake is an arm or stretch of the Ootsa Lake Reservoir in the Nechako Country of the western Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It forms part of the south arm of the reservoir, which includes adjoining stretches such as Eutsuk Lake and Natalkuz Lake, which are "upstream" to the southwest. Ootsa Lake was formed by the damming and diversion of the flow of the Nechako River, the bulk of which is now drained beneath the spine of the Coast Mountains to the west to the Kemano Powerhouse, which is the power supply for the aluminum smelter at Kitimat, to the southeast of Terrace.
The Cheslatta Carrier Nation or Cheslatta T'En, of the Dakelh or Carrier people (Ta-cullies, meaning "people who go upon water", whose traditional lands where originally where the Kitimat Kemano Project I was built, form a large portion of the Central Interior of present-day British Columbia, Canada, is a First Nation of the Nechako River at the headwaters of the Fraser River.
The Nechako Region is the second-largest economic development region in British Columbia and covers an area of 200,023 km2, from the Nechako plateau, in central British Columbia, northward to the border with Yukon Territory.
The Cheslatta River is a tributary of the Nechako River, one of the main tributaries of the Fraser River, in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It flows through the Nechako Plateau. Before the construction of Kenney Dam in the early 1950s the Cheslatta was a minor tributary of the Nechako. Today the Nechako River is dry above the Cheslatta, which provides all its source water.

Cheslatta Lake is a large freshwater lake located between François Lake and the western end of the Nechako Reservoir, Range 4 Coast Land District. It is in the Regional District of Bulkley-Nechako, British Columbia.