
Siphonostomatoida is an order of copepods, containing around 75% of all the copepods that parasitise fishes. Their success has been linked to their possession of siphon-like mandibles and of a "frontal filament" to aid attachment to their hosts. Most are marine, but a few live in fresh water. There are 40 recognised families:

The Cyclopoida are an order of small crustaceans from the subclass Copepoda. Like many other copepods, members of Cyclopoida are small, planktonic animals living both in the sea and in freshwater habitats. They are capable of rapid movement. Their larval development is metamorphic, and the embryos are carried in paired or single sacs attached to first abdominal somite.
Bomolochidae is a family of copepods parasitic on marine fishes. Most species parasitize the gills of fish, but some species live in the nostrils or on the eyes of their hosts. The family contains just over 150 species from the following genera:
Acantholochus is a genus of parasitic copepods belonging to the family Bomolochidae. Its members can only be distinguished from the closely related genus Hamaticolax by the absence of an accessory process on the claw of the maxillipeds.
Shiinoidae is a family of parasitic copepods found on marine teleosts.
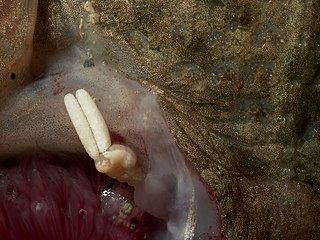
Chondracanthidae is a family of parasitic copepods, usually found infecting the branchial chamber of demersal fishes. It comprises the following genera:

Pennellidae is a family of parasitic copepods. When anchored on a host, they have a portion of the body on the outside of the host, whereas the remaining anterior part of the parasite is hidden inside tissues of the host.

Caligus is a genus of sea lice in the family Caligidae. The species are parasites of marine fishes and could be vectors of viruses. As of 2017, the World Register of Marine Species includes the following species:
Hamaticolax is a genus of parasitic copepods belonging to the family Bomolochidae. Its members can only be distinguished from the closely related genus Acantholochus by the presence of an accessory process on the claw of the maxillipeds. It includes the following species:
Speleophriidae is a family of copepods, comprising seven genera. All are restricted to anchialine caves, with the exception of Archimisophria, which is found in the hyperbenthos of the depths of the Atlantic Ocean. The genera are:

Misophrioida is an order of copepods, containing the following families:

Nicothoë astaci or the 'lobster louse' is an ectoparasitic copepod that parasitises the gills of the European lobster species Homarus gammarus. The lobster louse was first reported in 1826 by Audoin & Milne-Edwards. N. astaci has been found on lobsters inhabiting locations including Scotland, Lundy Island in the Bristol Channel and as far south as France and Portugal. The louse possesses a narrow suctorial mouthpart to feed on host haemolymph. Internally, In its adult form, Nicothoe is barely mobile and most likely remains in the same position for most of its life. The parasite occurs in groups, particularly near the base of the gills, and study has gone into its effects on the lobsters, which are considerably important, commercially. Not much is known about its life cycle, since there are significant gaps in knowledge of certain stages of its growth.

Nicothoidae is a family of copepods, containing the following genera:

Augaptilidae is a family of copepods.

Lernaeopodidae is a family of parasitic copepods. The females are typically large and fleshy, and attach to the host permanently using a plug made of chitin called the bulla. The males cling on to the females using their antennae. They parasitize both marine and freshwater fish. Some lernaeopodids, including Clavella and Salmincola, can have negative impacts on fish in aquaculture.
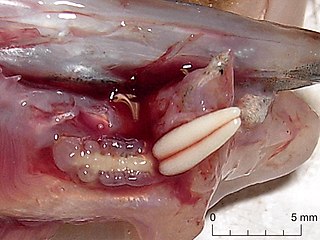
Acanthochondria limandae is a species of copepods in the family Chondracanthidae. They are host-specific ectoparasites of two species of flatfish: the common dab and the European flounder. They attach themselves to the bases of the gill arches of their hosts. They can infest as much as 2 to 30% of fish in a given population.
Chondracanthus is a parasitic copepod genus in the family Chondracanthidae, containing the following species:

Acanthochondria is a genus of copepods, containing the following species:

Lepeophtheirus is a genus of sea louse. The best-known species is L. salmonis, the salmon louse. Other species include L. pectoralis, which uses flatfish as its host, particularly the European flounder, and is also the type species of the genus Lepeophtheirus.

Arietellidae is a family of copepods belonging to the order Calanoida.











