Related Research Articles

North Ossetia, officially the Republic of North Ossetia–Alania, is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe. Its population according to the 2021 Census was 687,357. The republic's capital city is the city of Vladikavkaz, located on the foothills of the Caucasus Mountains.

The Alans were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the 1st century CE. At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From 215–250 CE the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe.
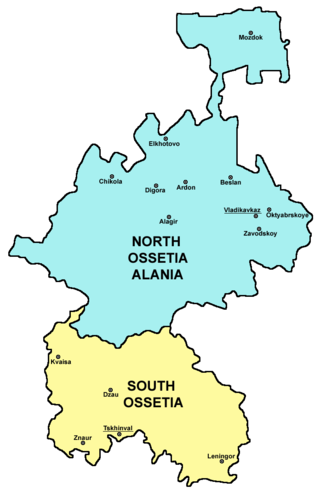
Ossetia is an ethnolinguistic region located on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. The Ossetian language is part of the Eastern Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages. Most countries recognize the Ossetian-speaking area south of the main Caucasus ridge as lying within the borders of Georgia, but it has come under the control of the de facto government of the Russian-backed Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania. The northern portion of the region consists of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania within the Russian Federation.

Nowruz is the Iranian or Persian New Year celebrated by various ethnicities worldwide. It is a festival based on the Iranian Solar Hijri calendar, on the spring equinox—on or around 21 March on the Gregorian calendar.

The Ossetians are an Iranian ethnic group who are indigenous to Ossetia, a region situated across the northern and southern sides of the Caucasus Mountains. They natively speak Ossetic, an Eastern Iranian language of the Indo-European language family, with most also being fluent in Russian as a second language.

South Ossetia, officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated population of just over 56,500 people (2022), who live in an area of 3,900 square kilometres (1,500 sq mi), on the south side of the Greater Caucasus mountain range, with 33,000 living in the capital city, Tskhinvali. Only Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru, and Syria recognise South Ossetia as a sovereign state. Although Georgia does not control South Ossetia, the Georgian government and the United Nations consider the territory part of Georgia.

Makar(a) Sankranti, also referred to as Uttarayana, Makar, or simply Sankranti, is a Hindu observance and a festival. Usually falling on the date of January 15 annually, this occasion marks the transition of the sun from the zodiac of Sagittarius (dhanu) to Capricorn (makara). Since the sun has made this transition which vaguely coincides with moving from south to north, the festival is dedicated to the solar deity, Surya, and is observed to mark a new beginning. Many native multi-day festivals are organised on this occasion all over India.

Lohri is a popular winter Punjabi folk festival celebrated primarily in Northern India. The significance and legends about the Lohri festival are many and these link the festival to the Punjab region. It is believed by many that the festival marks the passing of the winter solstice. Lohri marks the end of winter, and is a traditional welcome of longer days and the sun's journey to the northern hemisphere by people in the northern region of the Indian subcontinent. It is observed the night before Maghi, according to the solar part of the lunisolar Punjabi calendar, and almost always falls on 13 January.

The Georgian–Ossetian conflict is an ethno-political conflict over Georgia's former autonomous region of South Ossetia, which evolved in 1989 and developed into a war. Despite a declared ceasefire and numerous peace efforts, the conflict remained unresolved. In August 2008, military tensions and clashes between Georgia and South Ossetian separatists erupted into the Russo-Georgian War. Since then, South Ossetia has been under Russian occupation.

Nykhas Uastyrdzhi is the name of Saint George in Ossetian folklore. Uastyrdzhi is the patron of the male sex and travellers as well as being a guarantor of oaths, like his Iranian counterpart Mithra with whom he shares a common origin. It is forbidden for women to pronounce his name; instead, they must refer to him as лӕгты дзуар laegty dzuar.

Puthandu, also known as Puthuvarudam, and the Tamil New Year, is the first day of year on the Tamil calendar, traditionally celebrated as a festival by Tamil Hindus. The festival date is set with the solar cycle of the lunisolar Hindu calendar, as the first day of the Tamil month Chittirai. It falls on or about 14 April every year on the Gregorian calendar. The same day is observed elsewhere in South and South East Asia as the traditional new year, but is known by other names such as Vishu in Kerala, and Vaisakhi or Baisakhi in central and northern India.

The South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast was an autonomous oblast of the Soviet Union created within the Georgian SSR on April 20, 1922. Its autonomy was revoked on December 11, 1990 by the Supreme Soviet of the Georgian SSR, leading to the First South Ossetian War. Currently, its territory is controlled by the breakaway Republic of South Ossetia.
The Dvals were a ethnographic group of Georgians, their lands lying on both sides of the central Greater Caucasus mountains, somewhere between the Darial and Mamison gorges. This historic territory mostly covers the north of Kartli, parts of the Racha and Khevi regions in Georgia and south of Ossetia in Russia.

Alania was a medieval kingdom of the Iranian Alans (proto-Ossetians) that flourished in the Northern Caucasus, roughly in the location of latter-day Circassia, Chechnya, Ingushetia, and modern North Ossetia–Alania, from its independence from the Khazars in the late 9th century until its destruction by the Mongol invasion in 1238–39. Its capital was Maghas, and it controlled a vital trade route through the Darial Pass. The kingdom reached its peak in the 11th century, under the rule of king Durgulel.
Ossetian mythology is the collective term for the beliefs and practices of the Ossetian people of the Caucasus region, which contains several gods and supernatural beings. The religion itself is believed to be of Scythian origin, but contains many later elements from Christianity, with Ossetian gods often being identified with Christian saints. The gods play a role in the famous stories about a race of semi-divine heroes called the Narts.
The Vainakh peoples of the North Caucasus were Islamised comparatively late, during the early modern period, and Amjad Jaimoukha (2005) proposes to reconstruct some of the elements of their pre-Islamic religion and mythology, including traces of ancestor worship and funerary cults. The Nakh peoples, like many other peoples of the North Caucasus such as Circassians and Ossetians, practised tree worship, and believed that trees were the abodes of spirits. Vainakh peoples developed many rituals to serve particular kinds of trees. The pear tree held a special place in the faith of Vainakhs.
An international diplomatic crisis between Georgia and Russia began in 2008, when Russia announced that it would no longer participate in the Commonwealth of Independent States economic sanctions imposed on Abkhazia in 1996 and established direct relations with the separatist authorities in Abkhazia and South Ossetia. The crisis was linked to the push for Georgia to receive a NATO Membership Action Plan and, indirectly, the unilateral declaration of independence by Kosovo.

The 2008 Russo-Georgian War was a war between Georgia, on one side, and Russia and the Russian-backed self-proclaimed republics of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, on the other. The war took place in August following a period of worsening relations between Russia and Georgia, both formerly constituent republics of the Soviet Union. The fighting took place in the strategically important South Caucasus region. It is regarded as the first European war of the 21st century.

The Armed Forces of South Ossetia is the military of the partially recognised state of South Ossetia. The force consists of 16,000 soldiers: 2,500 officers and active-duty soldiers and 13,500 reservists. It includes an Army and an Air Corps.
South Ossetia is an autonomous region in Georgia, approximately 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) above sea level on the slopes of the Greater Caucasus. Although it declared independence in 2008, only a few countries acknowledge it. The region is inhabited by Ossetians, an Iranian ethnic group. According to Russia, Nicaragua, Venezuela, Syria and Nauru, it is one of the world's newest independent states. All other states and international organisations consider South Ossetia an autonomous region of Georgia, functioning as a de facto state for twenty years after declaring independence and conducting a successful armed rebellion. Its Georgian inhabitants have been displaced. South Ossetia has been a source of tension for a number of years, with Georgia and Russia's political differences impeding peaceful independence and breeding a turbulent series of events which undermine the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
References
- ↑ John Colarusso; Tamirlan Salbiev (28 June 2016). Tales of the Narts: Ancient Myths and Legends of the Ossetians. Princeton University Press. pp. 25–. ISBN 978-0-691-17040-4.
- ↑ Irina Molodikova; Alan Watt (3 January 2014). Growing Up in the North Caucasus: Society, Family, Religion and Education. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-317-93190-4.
- ↑ Chirikba, Viacheslav (2015). "Between Christianity and Islam: Heathen Heritage in the Caucasus". Brill. Retrieved 2020-03-13.
- ↑ "Во Владикавказе отметили национальный праздник Ногбон". 2019-01-14. Retrieved 2020-03-13.