Related Research Articles

Jayapura is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of 940.0 km2 (362.9 sq mi). The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sudarso Bay to the north, the country of Papua New Guinea to the east, Keerom Regency to the south, and Jayapura Regency to the west.

The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Tolai languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic.

The Western Oceanic languages is a linkage of Oceanic languages, proposed and studied by Ross (1988). They make up a majority of the Austronesian languages spoken in New Guinea.
The Ngero–Vitiaz languages form a linkage of Austronesian languages in northern Papua New Guinea. They are spoken, from west to east, in Madang Province, Morobe Province, and New Britain.

The Papuan Tip languages are a branch of the Western Oceanic languages consisting of 60 languages.
The Sarmi-Jayapura Bay languages consist of half a dozen languages spoken on the northern coast of Papua province of Indonesia:
The Schouten languages are a linkage of Austronesian languages in northern Papua New Guinea. They are in contact with various North Papuan languages, particularly the Skou and some Torricelli languages.
The Huon Gulf languages are Western Oceanic languages spoken primarily in Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea. They may form a group of the North New Guinea languages, perhaps within the Ngero–Vitiaz branch of that family.
Sulka is a language isolate of New Britain, Papua New Guinea. In 1991, there were 2,500 speakers in eastern Pomio District, East New Britain Province. Villages include Guma in East Pomio Rural LLG. With such a low population of speakers, this language is considered to be endangered. Sulka speakers had originally migrated to East New Britain from New Ireland.

The Southern Oceanic languages are a linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in Vanuatu and New Caledonia. It was proposed by John Lynch in 1995 and supported by later studies. It appears to be a linkage rather than a language family with a clearly defined internal nested structure.

Western Pantar, sometimes referred to by the name of one of its dialects, Lamma, is a Papuan language spoken in the western part of Pantar island in the Alor archipelago of Indonesia. Western Pantar is spoken widely in the region by about 10,000 speakers. Although speakers often use Malay in political, religious, and educational contexts, Western Pantar remains the first language of children of the region, and is acquired to some extent by immigrants.
Arop-Lokep is an Oceanic language spoken by 3,015 people on four islands in the Siassi chain in the Vitiaz Strait in Papua New Guinea.
Malcolm David Ross is an Australian linguist. He is the emeritus professor of linguistics at the Australian National University.
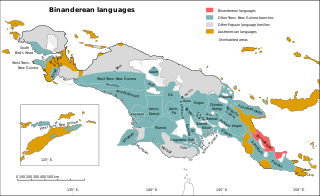
The Greater Binanderean or Guhu-Oro languages are a language family spoken along the northeast coast of the Papuan Peninsula – the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea – and appear to be a recent expansion from the north. They were classified as a branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages by Stephen Wurm (1975) and Malcolm Ross (2005), but removed by Timothy Usher (2020). The Binandere family proper is transparently valid; Ross connected it to the Guhu-Semane isolate based on pronominal evidence, and this has been confirmed by Smallhorn (2011). Proto-Binanderean has been reconstructed in Smallhorn (2011).

The West Trans–New Guinea languages are a suggested linguistic linkage of Papuan languages, not well established as a group, proposed by Malcolm Ross in his 2005 classification of the Trans–New Guinea languages. Ross suspects they are an old dialect continuum, because they share numerous features that have not been traced to a single ancestor using comparative historical linguistics. The internal divisions of the languages are also unclear. William A. Foley considers the TNG identity of the Irian Highlands languages at least to be established.
The family of Northwest Solomonic languages is a branch of the Oceanic languages. It includes the Austronesian languages of Bougainville and Buka in Papua New Guinea, and of Choiseul, New Georgia, and Santa Isabel in Solomon Islands.

Sarmi Regency is one of the regencies (kabupaten) in Papua Province of Indonesia. It was formed from the western districts which had until then been part of Jayapura Regency with effect from 12 November 2002. It covers an area of 18,034.0 km2, and had a population of 32,971 at the 2010 Census and 41,515 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 42,680. The regency's administrative centre is at the town of Sarmi.
Kwerba is a Papuan language of Indonesia. Alternate names are Airmati (Armati), Koassa, Mataweja, Naibedj, Segar Tor, Tekutameso.
Yetfa and Biksi are dialects of a language spoken in Jetfa District, Pegunungan Bintang Regency, Highland Papua, Indonesia, and across the border in Papua New Guinea. It is a trade language spoken in Western New Guinea up to the PNG border.
Sarmi is a coastal town and the administrative center of Sarmi Regency in the province of Papua in Indonesia.
References
- Ross, Malcolm (1988). Proto Oceanic and the Austronesian languages of western Melanesia. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.