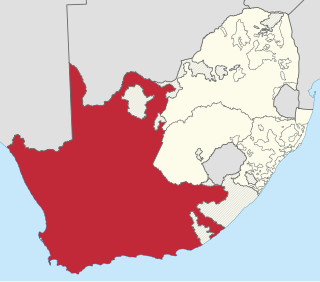
The Province of the Cape of Good Hope, commonly referred to as the Cape Province and colloquially as The Cape, was a province in the Union of South Africa and subsequently the Republic of South Africa. It encompassed the old Cape Colony, as well as Walvis Bay, and had Cape Town as its capital. In 1994, the Cape Province was divided into the new Eastern Cape, Northern Cape and Western Cape provinces, along with part of the North West.

Kimberley is the capital and largest city of the Northern Cape province of South Africa. It is located approximately 110 km east of the confluence of the Vaal and Orange Rivers. The city has considerable historical significance due to its diamond mining past and the siege during the Second Anglo-Boer war. British businessmen Cecil Rhodes and Barney Barnato made their fortunes in Kimberley, and Rhodes established the De Beers diamond company in the early days of the mining town.

The Griquas are a subgroup of mixed-race heterogeneous formerly Xiri-speaking nations in South Africa with a unique origin in the early history of the Dutch Cape Colony. Like the Boers they migrated inland from the Cape and in the 19th century established several states in what is now South Africa and Namibia. The Griqua consider themselves as being South Africa’s first multiracial nation with people descended directly from Dutch settlers in the Cape, and local peoples.

Griqualand West is an area of central South Africa with an area of 40,000 km2 that now forms part of the Northern Cape Province. It was inhabited by the Griqua people – a semi-nomadic, Afrikaans-speaking nation of mixed-race origin, who established several states outside the expanding frontier of the Cape Colony. It was also ancestral home to the Tswana and Khoisan peoples.

The High Court of South Africa is a superior court of law in South Africa. It is divided into nine provincial divisions, some of which sit in more than one location. Each High Court division has general jurisdiction over a defined geographical area in which it is situated. The decisions of a division are binding on magistrates' courts within its area of jurisdiction. The High Court has jurisdiction over all matters, but it usually only hears civil matters involving more than 400,000 rand, and serious criminal cases. It also hears any appeals or reviews from magistrates' courts and other lower courts.

Joseph Benjamin Robinson, was a South African gold and diamond mining magnate and Randlord. Only the top two knighthoods, KBE and GBE are entitled to be called Sir, thus JB Robinson is Mr. JB Robinson.

Griquas are a South African rugby union team that participates in the annual Currie Cup tournament. Their home ground is Griqua Park in Kimberley and they draw their players mostly from Northern Cape Province. They have won the Currie Cup three times – in 1899, 1911 and 1970 – and the Vodacom Cup a joint-record five times.

The South Africa Act 1909 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that created the Union of South Africa out of the former Cape, Natal, Orange River, and Transvaal colonies. The Act also allowed for potential admission of Rhodesia into the Union, a proposal rejected by Rhodesian colonists in a 1922 referendum. The draft proposal was supported by the four colonial parliaments, but was opposed by Cape Colony premier W. P. Schreiner, who raised concerns that it would strip rights from non-white South Africans.
The Cape Colonial Forces (CCF) were the official defence organisation of the Cape Colony in South Africa. Established in 1855, they were taken over by the Union of South Africa in 1910, and disbanded when the Union Defence Forces were formed in 1912.
Northern Cape is a first-class cricket team that nominally represents the South African province of Northern Cape in the CSA Provincial Competitions. The team is selected and supported by Northern Cape Cricket and plays its home games at the De Beers Diamond Oval in Kimberley.
The Supreme Court of South Africa was a superior court of law in South Africa from 1910 to 1997. It was made up of various provincial and local divisions with jurisdiction over specific geographical areas, and an Appellate Division which was the highest appellate court in the country.

The courts of South Africa are the civil and criminal courts responsible for the administration of justice in South Africa. They apply the law of South Africa and are established under the Constitution of South Africa or under Acts of the Parliament of South Africa.

The Western Cape Division of the High Court of South Africa is a superior court of law with general jurisdiction over the Western Cape province of South Africa. The division, which sits at Cape Town, consists of 31 judges led by Acting Judge President Patricia Goliath, former Acting Constitutional Court Justice.
The Eastern Cape Division of the High Court of South Africa is a superior court of law with general jurisdiction over the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. The main seat of the division is at Makhanda, with subordinate local seats at Gqeberha, East London, Bhisho and Mthatha. As of November 2017 the Judge President of the division is Selby Mbenenge.
The Free State Division of the High Court of South Africa is a superior court of law with general jurisdiction over the Free State province of South Africa. The division sits at Bloemfontein.

The KwaZulu-Natal Division of the High Court of South Africa is a superior court of law with general jurisdiction over the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa. The main seat of the division is at Pietermaritzburg, while a subordinate local seat at Durban has concurrent jurisdiction over the coastal region of the province. As of January 2024 the Judge President of the division is Thoba Poyo-Dlwati.
The North West Division of the High Court of South Africa is a superior court of law with general jurisdiction over the western part of North West province of South Africa. The division sits at Mahikeng.

In the colonial history of South Africa, the Griqualand West Annexation Act, was the act, passed in the Cape Colony Parliament on 27 July 1877, authorising the union of the Cape Colony with Griqualand West.

The Gauteng Division of the High Court of South Africa is a superior court of law which has general jurisdiction over the South African province of Gauteng and the eastern part of North West province. The main seat of the division is at Pretoria, while a local seat at Johannesburg has concurrent jurisdiction over the southern parts of Gauteng. Dunstan Mlambo has been the Judge President of the division since 1 November 2012.
The Cape Mounted Police was the principal law enforcement agency of the Cape Colony during its last three decades. In addition to its ordinary policing duties, it was a para-military organisation, which saw active service in several campaigns and operations, including the Anglo-Boer War (1899–1902). The force was fully militarised in 1913 and transferred to the new South African Army as a mounted rifle regiment.















