
Pseudanthus is a genus of plants under the family Picrodendraceae. The genus is endemic to Australia described as a genus in 1827.

Wahlenbergia is a genus of around 260 species of flowering plants in the family Campanulaceae. Plants in this genus are perennial or annual herbs with simple leaves and blue to purple bell-shaped flowers, usually with five petals lobes. Species of Wahlenbergia are found on all continents except North America, and on some isolated islands, but the greatest diversity occurs in the Southern Hemisphere.

Pierre Edmond Boissier was a Swiss prominent botanist, explorer and mathematician. He was the son of Jacques Boissier (1784-1857) and Caroline Butini (1786-1836), daughter of Pierre Butini (1759-1838) a well-known physician and naturalist from Geneva. With his sister, Valérie Boissier (1813-1894), he received a strict education with lessons delivered in Italian and Latin. Edmond's interest in natural history stemmed from holidays in the company of his mother and his grandfather, Pierre Butini at Valeyres-sous-Rances. His hikes in the Jura and the Alps laid the foundation of his zest for later exploration and adventure. He attended a course at the Academy of Geneva given by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle.

Robert Wight MD FRS FLS was a Scottish surgeon in the East India Company, whose professional career was spent entirely in southern India, where his greatest achievements were in botany – as an economic botanist and leading taxonomist in south India. He contributed to the introduction of American cotton. As a taxonomist he described 110 new genera and 1267 new species of flowering plants. He employed Indian botanical artists to illustrate many plants collected by himself and Indian collectors he trained. Some of these illustrations were published by William Hooker in Britain, but from 1838 he published a series of illustrated works in Madras including the uncoloured, six-volume Icones Plantarum Indiae Orientalis (1838–53) and two hand-coloured, two-volume works, the Illustrations of Indian Botany (1838–50) and Spicilegium Neilgherrense (1845–51). By the time he retired from India in 1853 he had published 2464 illustrations of Indian plants. The standard author abbreviation Wight is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.

Millettia is a genus of legume in the family Fabaceae. It consists of about 150 species, which are distributed in the tropical and subtropical regions of the world. The genus was formerly known by the name Pongamia, but that name was rejected in favor of the name Millettia, and many species have been reclassified. Due to recent interest in biofuels, Pongamia is often the generic name used when referring to Millettia pinnata, a tree being explored for producing biodiesel.

Isonandra is a genus of plants in the family Sapotaceae found in tropical Asia, described as a genus in 1840.

Albrecht Wilhelm Roth was a physician and botanist born in Dötlingen, Germany.
Heteroderis is a genus of flowering plants in the dandelion family.
Rhanteriopsis is a genus of Middle Eastern plants in the golden samphire tribe daisy family.
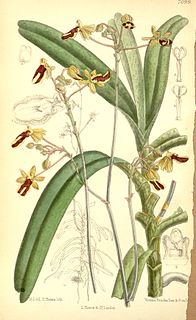
Cottonia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae: the only known species is Cottonia peduncularis. It is native to India and Sri Lanka. The genus was erected by Robert Wight and named after Major F. Cotton, an amateur botanist who served in the Madras Engineer Group and collected the species from Tellichery.

Trema orientalis is a species of flowering tree in the hemp family, Cannabaceae. It is known by many common names, including charcoal-tree, Indian charcoal-tree, pigeon wood, Oriental trema, and in Hawaii, where it has become naturalized, gunpowder tree, or nalita. It has a near universal distribution in tropical and warm temperate parts of the Old World, with a range extending from South Africa, through the Middle East, the Indian subcontinent and southern China to Southeast Asia and Australia.

Cleghornia is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae; its various species are distributed in Borneo, China, Laos, Malaysia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Diospyros ovalifolia, known as bastard ebony, is a tree in the family, Ebenaceae, endemic to the leeward side of South Sahyadri of Western Ghats of India and Sri Lanka.
Sida mysorensis, common name in India Mysore fanpetals, is a plant species native to South and Southeast Asia. It has been reported from the wild in Indonesia, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, India, Pakistan and southern China, and is cultivated elsewhere. It grows in grassy slopes, on roadsides, and in forest boundaries.
Lygisma is a plant genus in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1883. It is native to southern China, Indochina, Malaysia, and the Himalayas.
- Lygisma angustifolia(Wight) Hook.f. - Himalayas
- Lygisma flavum(Ridl.) Kerr - Peninsular Malaysia
- Lygisma inflexum(Costantin) Kerr - Vietnam, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan
- Lygisma nervosumKerr - Thailand

Impatiens jerdoniae is a species of flowering plant in the family Balsaminaceae. It is native to the Western Ghats of India. It was described and named by Robert Wight and commemorates Flora Jerdon, wife of Thomas C. Jerdon. It grows on rocks and as an epiphyte on trees.

Cullenia exarillata is a flowering plant evergreen tree species in the family Malvaceae endemic to the rainforests of the southern Western Ghats in India. It is one of the characteristic trees of the mid-elevation tropical wet evergreen rainforests and an important food plant for the endemic primate, the lion-tailed macaque.

Dorstenia indica is a small plant species in the family Moraceae native to Southern India and Sri Lanka. It was first described by Robert Wight in 1853.

Rungiah aka Rungia or Rungia Raju was a 19th-century Indian botanical illustrator, noted for producing a large number of images for Robert Wight's books on Indian flora. The Raju family were painters of the Kshatriya caste of Tanjore, and were originally from the Telugu-speaking region in the state of Andhra Pradesh.














