
The Latidae, known as the lates perches, are a family of perch-like fish found in Africa, Asia, and the Indian and western Pacific Oceans. Including about 13 species, the family, previously classified subfamily Latinae in family Centropomidae, was raised to family status in 2004 after a cladistic analysis showed the original Centropomidae were paraphyletic.

The brook lamprey, also known as the European brook lamprey and the western brook lamprey is a small European lamprey species that exclusively inhabits freshwater environments. The species is related to, but distinct from, the North American western brook lamprey.

The belted sandfish, also known as the dwarf sea bass or stubby sea bass, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea bass from the subfamily Serraninae, classified as part of the family Serranidae which includes the groupers and anthias. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean. This species is found in the aquarium trade.

The Arctic lamprey, also known as the Japanese river lamprey or Japanese lampern, is a species of lamprey, a jawless fish in the order Petromyzontiformes. It inhabits coastal freshwater habitat types in the Arctic. Some populations are anadromous, spending part of their lives in the ocean. It is the most common and widespread lamprey in the Arctic region.

The broadgilled hagfish or New Zealand hagfish, also known by its Māori language name tuere, is a hagfish found around New Zealand and the Chatham Islands as well as around the south and east coasts of Australia, at depths between 1 and 900 metres.

The redspotted catshark, also known as the Chilean catshark, is a species of catshark commonly found in the coastal waters of the southeastern Pacific, from central Peru to southern Chile. They are typically found in the rocky sublittoral areas at the edge of the continental shelf, in waters down to 100 m in depth. They spend the spring, summer, and fall in rocky subtidal areas, but winter in deeper offshore waters due to the strong currents at that time of year.

The Florida gar is a species of gar found in the US from the Savannah River and Ochlockonee River watersheds of Georgia and throughout peninsular Florida. Florida gar can reach a length over 3 ft (91 cm). The young feed on zooplankton and insect larvae, as well as small fish. Adults mainly eat fish, shrimp, and crayfish. Although edible, they are not popular as food. The roe is highly toxic to many animals, including humans and birds.

The bulbous dreamer, or cosmoplitan dreamer, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep-sea anglerfishes. This fish has a circumglobal distribution in tropical and temperate oceans.

The Izak catshark or simply Izak is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, common off the coasts of South Africa and southern Namibia. It typically inhabits the outer continental shelf at depths of 100–300 m (330–980 ft), with the males found deeper than the females and juveniles. The Izak catshark has a short, wide, flattened head and a robust body tapering to a long, slender tail. It can be identified by its ornate color pattern of dark brown spots or reticulations and blotches on a light yellowish background, as well as by the enlarged dermal denticles over its pectoral fins and along its dorsal midline from the snout to the second dorsal fin. This species reaches 69 cm (27 in) in length, with the males larger than females.

The bristly catshark is a cat shark of the family Scyliorhinidae, found from southeastern India and the Andaman Islands, between latitudes 15° N and 5° N, at depths between 200 and 300 m. Its length usually ranges from around 20–26 cm, and it is regarded as the smallest catshark of Bythaelurus.

The African sawtail catshark is a species of catshark, part of the family Scyliorhinidae. Demersal in nature, it is found at depths of 160–720 m (520–2,360 ft) off the western African coast from Morocco to South Africa. This slender species has a rather long, pointed snout, a series of dark saddles along the back and tail, and a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the upper edge of the caudal fin. Its maximum known length is 46 cm (18 in).
Squalus nasutus, the western longnose spurdog, is a dogfish of the family Squalidae, found on the continental shelf off the northwest and southwest coasts of Western Australia, at depths between 300 and 510 m. Its length is at least 55 cm.

The Pacific hagfish is a species of hagfish. It lives in the mesopelagic to abyssal Pacific Ocean, near the ocean floor. It is a jawless fish and has a body plan that resembles early Paleozoic fish. They are able to excrete prodigious amounts of slime in self-defense.
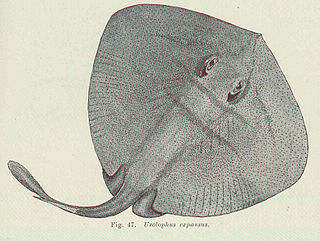
The wide stingaree is a little-known species of stingray in the family Urolophidae, found off southwestern Australia. It typically occurs over sand in water 200–300 m (660–980 ft) deep around the edge of the continental shelf. This species has a broad diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc, a slightly pointed snout, and a tail with a leaf-like caudal fin, skin folds along either side, and no dorsal fins. Between its nostrils is a skirt-shaped curtain of skin. It is grayish green above, with faint bluish lines beside and behind the eyes. The maximum length on record is 52 cm (20 in).

The shortnose gar is a primitive freshwater fish of the family Lepisosteidae. It is native to the United States where its range includes the Mississippi and Missouri River basins, ranging from Montana to the west and the Ohio River to the east, southwards to the Gulf Coast. It inhabits calm waters in large rivers and their backwaters, as well as oxbow lakes and large pools. It is a long, slender fish, brown or olive green above and whitish below. It typically grows to about 60 cm (24 in) and is armored by rows of interlocking, rhomboidal ganoid scales.

The southern hagfish is a hagfish of the genus Myxine.
Eptatretus bischoffii is a common hagfish of the genus Eptatretus. Its maximum length is 55 centimetres (22 in). It lives in a demersal, non-migratory, marine habitat with its depth range between 8–50 m. It can survive in only temperate zones. These organisms are found in the South Pacific, mainly, Chile. It is harmless to humans.
The least brook lamprey is a common, non-parasitic lamprey distributed in the Mississippi River watershed, and a limited range along the Atlantic coast.
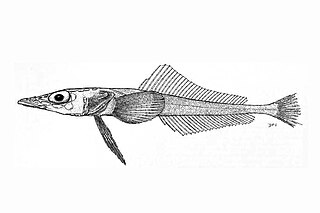
Akarotaxis is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Bathydraconidae, the Antarctic dragonfish. There are two species: Akarotaxis nudiceps and Akarotaxis gouldae. They are found in the Southern Ocean along the continental shelf of Antarctica.

Myxine circifrons, the whiteface hagfish, is a marine bathydemersal species of fish in the family Myxinidae. It is found off Southern California, Peru, and Chile and grows to 65 centimetres (26 in) total length.















