
Rio Grande do Sul is a state in the southern region of Brazil. It is the fifth-most populous state and the ninth-largest by area. Located in the southernmost part of the country, Rio Grande do Sul is bordered clockwise by Santa Catarina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Uruguayan departments of Rocha, Treinta y Tres, Cerro Largo, Rivera, and Artigas to the south and southwest, and the Argentine provinces of Corrientes and Misiones to the west and northwest. The capital and largest city is Porto Alegre. The state has the highest life expectancy in Brazil, and the crime rate is relatively low compared to the Brazilian national average. Despite the high standard of living, unemployment is still high in the state, as of 2017. The state has 5.4% of the Brazilian population and it is responsible for 6.6% of the Brazilian GDP.

Paubrasilia echinata is a species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae, that is endemic to the Atlantic Forest of Brazil. It is a Brazilian timber tree commonly known as Pernambuco wood or brazilwood and is the national tree of Brazil. This plant has a dense, orange-red heartwood that takes a high shine, and it is the premier wood used for making bows for stringed instruments. The wood also yields a historically important red dye called brazilin, which oxidizes to brazilein.
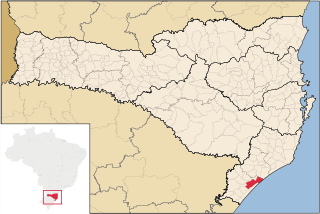
Araranguá is a city located in the southern part of Santa Catarina state, in the south of Brazil. It has 68,867 inhabitants and was settled mainly by Portuguese and Italians. Araranguá is known as "A Cidade das Avenidas" because of its wide roads.

Polish Brazilians refers to Brazilians of full or partial Polish ancestry who are aware of such ancestry and remain connected, to some degree, to Polish culture, or Polish-born people permanently residing in Brazil. Also, a Polish Brazilian may have one Polish parent.

Eugenia brasiliensis, with common names Brazil cherry and grumichama, or the Brazilian cherry is medium-sized tree endemic (native) to southern Brazil which bears small fruits that are purple to black in color, and have a sweet cherry to plum-like flavor.
Hospital das Clínicas or Hospital de Clínicas is a denomination traditionally reserved for teaching hospitals in Brazil. Another common denomination is Hospital Universitário.

Brava Linhas Aéreas Ltda, formerly known as NHT Linhas Aéreas, was a domestic airline based in Porto Alegre, Brazil founded in 2006. The airline has been grounded since late 2013 after the National Civil Aviation Agency of Brazil (ANAC) suspended the company's Transportation Operating Certificate. The airline does not currently operate any flights. Jorge Barouki, president of the company, has stated that Brava requested the suspension since the airline no longer had the capital to pay its employees.

The Araucaria moist forests, officially classified as mixed ombrophilous forest in Brazil, are a montane subtropical moist forest ecoregion. The forest ecosystem is located in southern Brazil and northeastern Argentina. The ecoregion is a southern portion of the Atlantic Forest. The ecoregion also includes select areas of open field called "campos de cima da serra" or "coxilhas".

Lithraea molleoides is a tree that is native to South America, specially in Argentina, Uruguay, Bolivia, and Cerrado vegetation of Brazil.

Inga sellowiana is an endangered species of legume in the family Fabaceae, endemic to Brazil. It is an evergreen, perennial shrub or small tree, 1–8 metres (3.3–26.2 ft) in height. Common names include ingá mirim, ingá ferro, ingá xixica and ingá xixi.

Trithrinax brasiliensis is a species of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae. It is known as carandá, burití or leque. It is considered a rare and endemic species in southern Brazil. It occurs in Argentina, southern Brazil, and eastern Bolivia, where it is popularly known to Spanish speakers as saó or saocito and to speakers of Chiquitano as baixhíxh. Nowadays it is considered a threatened species belonging to the category "In Danger" in the List of Threatened species of Rio Grande do Sul state, southern Brazil.

Ocotea porosa, commonly called imbuia or Brazilian walnut, is a species of plant in the Lauraceae family. Its wood is very hard, and it is a major commercial timber species in Brazil.

Ocotea odorifera is a species of plant in the family Lauraceae. It is an evergreen tree in the genus Ocotea.
Neocabreria is a genus of Brazilian flowering plants in the tribe Eupatorieae within the family Asteraceae.
Symphyopappus is a genus of South American plants in the tribe Eupatorieae within the family Asteraceae.
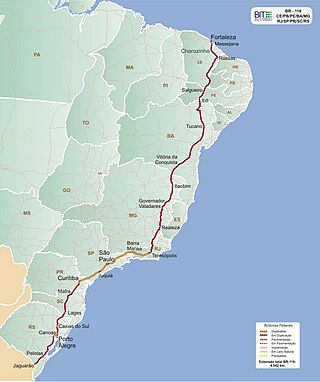
BR-116 is a federal route of highways of Brazil and the longest highway in the country, with 4,542 km (2,822 mi) of extension. The road connect Fortaleza, Ceará, one of the largest Northeast Brazil metropolises, to the southern city of Jaguarão, Rio Grande do Sul, in the border with Uruguay. It is also the longest highway in the country to be completely paved. It is considered one of the most important highways in the country, along with BR-101.
The SOS Mata Atlântica Foundation was created in 1986 as a non-governmental and non-profit organization, with the goal of defending what remains of Mata Atlântica in Brazil. Its actions are divided in six areas: public policies; campaigns; documentation, information and communication for conservation; environmental education and good citizenship; institutional development; and sustainable development, protection and handling of ecosystems.
Renato Martins Seabra is a former Brazilian cyclist. He competed at the 2000 Summer Olympics.
The 2019 Copa do Brasil final stages were the final stages of the 2019 Copa do Brasil football competition. They were played from 15 May to 18 September 2019. A total of 16 teams competed in the final stages to decide the champions of the 2019 Copa do Brasil.














