
The Anacardiaceae, commonly known as the cashew family or sumac family, are a family of flowering plants, including about 83 genera with about 860 known species. Members of the Anacardiaceae bear fruits that are drupes and in some cases produce urushiol, an irritant. The Anacardiaceae include numerous genera, several of which are economically important, notably cashew, mango, Chinese lacquer tree, yellow mombin, Peruvian pepper, poison ivy, poison oak, sumac, smoke tree, marula and cuachalalate. The genus Pistacia is now included, but was previously placed in its own family, the Pistaciaceae.

Combretum, the bushwillows or combretums, make up the type genus of the family Combretaceae. The genus comprises about 272 species of trees and shrubs, most of which are native to tropical and southern Africa, about 5 to Madagascar, but there are others that are native to tropical Asia, New Guinea and the Bismarck Archipelago, Australia, and tropical America. Though somewhat reminiscent of willows (Salix) in their habitus, they are not particularly close relatives of these.

The Sapotaceae are a family of flowering plants belonging to the order Ericales. The family includes about 800 species of evergreen trees and shrubs in around 65 genera. Their distribution is pantropical.

Chrysophyllum is a group of trees in the Sapotaceae described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1753.

Palaquium is a genus of about 120 species of trees in the family Sapotaceae. Their range is from India across Southeast Asia, Malesia, Papuasia, and Australasia, to the western Pacific Islands.

Manilkara is a genus of trees in the family Sapotaceae. They are widespread in tropical and semitropical locations, in Africa, Madagascar, Asia, Australia, and Latin America, as well as various islands in the Pacific and in the Caribbean. A close relative is the genus Pouteria.

The Simaroubaceae, also known as the quassia family, are a small, mostly tropical, family in the order Sapindales. In recent decades, it has been subject to much taxonomic debate, with several small families being split off. A molecular phylogeny of the family was published in 2007, greatly clarifying relationships within the family. Together with chemical characteristics such as the occurrence of petroselinic acid in Picrasma, in contrast to other members of the family such as Ailanthus, this indicates the existence of a subgroup in the family with Picrasma, Holacantha, and Castela.

Irvingiaceae is a small family of flowering plants, consisting of about 13 species; it was erected by Exell and Mendonça in 1951.

Commiphora is the most species-rich genus of flowering plants in the frankincense and myrrh family, Burseraceae. The genus contains approximately 190 species of shrubs and trees, which are distributed throughout the (sub-) tropical regions of Africa, the western Indian Ocean islands, the Arabian Peninsula, India, and South America. The genus is drought-tolerant and common throughout the xerophytic scrub, seasonally dry tropical forests, and woodlands of these regions.

Anisophyllea is a genus of plant in the family Anisophylleaceae. The generic name is from the Greek meaning "unequal leaf", referring to the dimorphism of the leaves.
Hannoa is a genus of plant in the family Simaroubaceae. Found in tropical parts of Africa.
Pierreodendron is a genus of plants in the family Simaroubaceae.
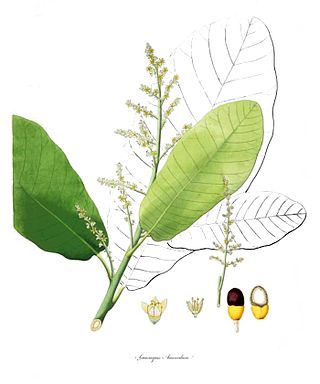
Semecarpus is a genus of plants in the family Anacardiaceae. It includes 87 species native to the Indian subcontinent, Indochina, Malesia, Taiwan, Papuasia, Queensland, and the South Pacific.

Vepris is a genus of plant in family Rutaceae. It comprises around 90 species, mainly from tropical Africa, Madagascar and the Mascarene Islands and at a lesser extent Arabia and India.

Jean Baptiste Louis Pierre, also known as J. B. Louis Pierre, was a French botanist known for his Asian studies.

The Sapotoideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Sapotaceae. Plants in the subfamily are characterized by their leather-like leaves, often growing in a stipule fashion.

Dichapetalum is a genus in the plant family Dichapetalaceae. The plants are tropical lianas native mainly to tropical regions of Africa, Asia, Malesia, the West Indies, Australia and Latin America. Some species are known to be poisonous due to the presence of toxic fluorinated compounds such as fluorocarboxylic acid and dichapetalins, a unique class of cytotoxic compounds that are only found within this genus.
Cleistopholis is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Annonaceae.

Rhaphiostylis is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Metteniusaceae.
Scytopetalum is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Lecythidaceae.















