
Hawaii is an island state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. It is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics.

The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major volcanic islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaiʻi in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll. Formerly called the Sandwich Islands by Europeans, the present name for the archipelago is derived from the name of its largest island, Hawaiʻi.

The Oceanian realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms and is unique in not including any continental land mass. It has the smallest land area of any of the WWF realms.

Metrosideros is a genus of approximately 60 trees, shrubs, and vines mostly found in the Pacific region in the family Myrtaceae. Most of the tree forms are small, but some are exceptionally large, the New Zealand species in particular. The name derives from the Ancient Greek metra or "heartwood" and sideron or "iron". Perhaps the best-known species are the pohutukawa, northern and southern rātā of New Zealand, and ʻōhiʻa lehua, from the Hawaiian Islands.
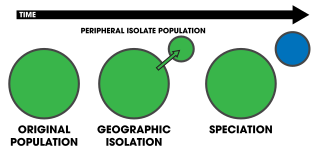
Peripatric speciation is a mode of speciation in which a new species is formed from an isolated peripheral population. Since peripatric speciation resembles allopatric speciation, in that populations are isolated and prevented from exchanging genes, it can often be difficult to distinguish between them., and peripatric speciation may be considered one type or model of allopatric speciation. The primary distinguishing characteristic of peripatric speciation is that one of the populations is much smaller than the other, as opposed to allopatric speciation, in which similarly-sized populations become separated. The terms peripatric and peripatry are often used in biogeography, referring to organisms whose ranges are closely adjacent but do not overlap, being separated where these organisms do not occur—for example on an oceanic island compared to the mainland. Such organisms are usually closely related ; their distribution being the result of peripatric speciation.

The TanagerExpedition was a series of five biological surveys of the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands conducted in partnership between the Bureau of Biological Survey and the Bishop Museum, with the assistance of the United States Navy. Four expeditions occurred from April to August 1923, and a fifth in July 1924. Led by Lieutenant Commander Samuel Wilder King on the minesweeper USS Tanager (AM-5), and Alexander Wetmore directing the team of scientists, the expedition studied the plant animal life, and geology of the central Pacific islands. Noted members of the team include archaeologist Kenneth Emory and herpetologist Chapman Grant.

The Hawaiian hoary bat, also known as ʻōpeʻapeʻa, is a species of bat endemic to the islands of Hawaiʻi. The Hawaiian hoary bat occupies the major Hawaiian islands, making it the only extant and native terrestrial mammal in the islands. Some studies report that the mainland hoary bat lives in sympatry on the Hawaiian Islands alongside the Hawaiian hoary bat, although this is disputed. The Hawaiian hoary bat was officially named the state land mammal of Hawaiʻi in 2015. It is a federally listed endangered taxon of the United States.

Achatinellidae is a family of tropical air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Pupilloidea.

The Hawaiʻi hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located near the namesake Hawaiian Islands, in the northern Pacific Ocean. One of the best known and intensively studied hotspots in the world, the Hawaii plume is responsible for the creation of the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain, a 6,200-kilometer (3,900 mi) mostly undersea volcanic mountain range. Four of these volcanoes are active, two are dormant; more than 123 are extinct, most now preserved as atolls or seamounts. The chain extends from south of the island of Hawaiʻi to the edge of the Aleutian Trench, near the eastern coast of Russia.

Opogona is a genus of the fungus moth family, Tineidae. Therein, it belongs to the subfamily Hieroxestinae. As it includes Opogona omoscopa, the type species of the now-abolished genus Hieroxestis, it is the type genus of its subfamily.

Opogona omoscopa is a moth of the family Tineidae.

Opogona sacchari, the banana moth, is a moth of the family Tineidae. The species was first described by Wenceslas Bojer in 1856. It is native to the humid tropical and subtropical regions of sub-Saharan Africa, where it is also found in Madagascar, Mauritius, Réunion, Rodrigues Island, the Seychelles and St. Helena. It was first reported from the Canary Islands in the 1920s. In the 1970s, it was introduced into Brazil and Central America, and also appeared in Europe. It has been reported from Florida since 1986.
Opogona purpuriella is a moth of the family Tineidae. It was first described by Otto Swezey in 1913. It has been recorded from Hawaii and Tonga. It has also been reported as a port interception in California.
Opogona bicolorella is a moth of the family Tineidae. It was described by Shōnen Matsumura in 1931. It is found in Japan and Taiwan.











