
Artemisia vulgaris, the common mugwort, is a species of flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae. It is one of several species in the genus Artemisia commonly known as mugwort, although Artemisia vulgaris is the species most often called mugwort. It is also occasionally known as riverside wormwood, felon herb, chrysanthemum weed, wild wormwood, old Uncle Henry, sailor's tobacco, naughty man, old man, or St. John's plant. Mugworts have been used medicinally and as culinary herbs.

The Pyraloidea are a moth superfamily containing about 16,000 described species worldwide, and probably at least as many more remain to be described. They are generally fairly small moths, and as such, they have been traditionally associated with the paraphyletic Microlepidoptera.
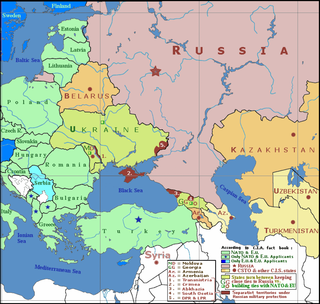
In international relations, a frozen conflict is a situation in which active armed conflict has been brought to an end, but no peace treaty or other political framework resolves the conflict to the satisfaction of the combatants. Therefore, legally the conflict can start again at any moment, creating an environment of insecurity and instability.

The Central Asian red deer is a deer species with a sparse distribution in Central Asia. It is considered possibly extirpated from Pakistan. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. It was first described in the mid-19th century.

Ostrinia is a genus of moths in the family Crambidae described by Jacob Hübner in 1825. Several of them, including the European corn borer, are agricultural pests.

Ostrinia palustralis is a species of moth in the family Crambidae described by Jacob Hübner in 1796. It has a trans-Palearctic distribution. In Europe, it is found from Sweden south to Italy and east through eastern Europe to Russia. However, it is absent from the western part of the Balkan Peninsula.
Ostrinia quadripunctalis is a species of moth in the family Crambidae. It is found in Norway, Germany, the Czech Republic, Austria, Italy, Slovakia, Hungary, the Republic of Macedonia, Albania, Ukraine and Russia.
Ostrinia scapulalis, the adzuki bean borer or adzuki bean worm, is a species of moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1859. It is one of 20 moths in the genus Ostrinia and is of Eurasian origin. The larvae have a gray mid-dorsal line and can be light pink or beige. The adult adzuki bean borer has a yellowish-brown forewing with jagged lines and variable darker shading, with a wingspan that ranges from 20 to 32 mm. The moths of this species are nocturnal and tend to be attracted to light.

Ostrinia furnacalis is a species of moth in the family Crambidae, the grass moths. It was described by Achille Guenée in 1854 and is known by the common name Asian corn borer since this species is found in Asia and feeds mainly on corn crop. The moth is found from China to Australia, including in Java, Sulawesi, the Philippines, Borneo, New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, and Micronesia. The Asian corn borer is part of the species complex, Ostrinia, in which members are difficult to distinguish based on appearance. Other Ostrinia such as O. orientalis, O. scapulalis, O. zealis, and O. zaguliaevi can occur with O. furnacalis, and the taxa can be hard to tell apart.
The 2014 Russian hacker password theft is an alleged hacking incident resulting in the possible theft of over 1.2 billion internet credentials, including usernames and passwords, with hundreds of millions of corresponding e-mail addresses. The data breach was first reported by the New York Times after being allegedly discovered and reported by Milwaukee-based information security company, Hold Security.
Rajendra Tiku, is an Indian sculptor and art teacher known for his outdoor stone sculptures. He was honoured by the Government of India, in 2013, by bestowing on him the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award, for his contributions to the field of art.
Ostrinia dorsivittata is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Frederic Moore in 1888. It is found in Darjeeling, India and China.
Ostrinia erythrialis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1913. It is found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Malawi, Nigeria and South Africa.
Ostrinia kurentzovi is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Akira Mutuura and Eugene G. Munroe in 1970. It is found in the Russian Far East (Ussuri).
Ostrinia latipennis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Warren in 1892. It is found in Japan and the Russian Far East.
Ostrinia putzufangensis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Akira Mutuura and Eugene G. Munroe in 1970. It is found in China.
Ostrinia sanguinealis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Warren in 1892. It is found in China, Japan and Russia.
Ostrinia zaguliaevi is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Akira Mutuura and Eugene G. Munroe in 1970. It is found in the Russian Far East, Japan and China.

Ostrinia zealis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Achille Guenée in 1854. It is found in the Russian Far East, Japan, China and India.

Jammu and Kashmir is a region administered by India as a union territory and consisting of the southern portion of the larger Kashmir region, which has been the subject of a dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947, and between India and China since 1962. The Line of Control separates Jammu and Kashmir from the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan in the west and north. It lies to the north of the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab and to the west of Ladakh, which is also subject to the dispute as a part of Kashmir, and administered by India as a union territory.








