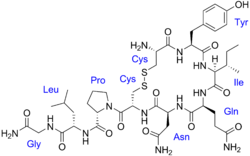

An oxytocin receptor agonist is a compound that acts as an agonist of the oxytocin receptor. [1] [2] They include peptides like oxytocin and carbetocin and small-molecules like LIT-001. [1] [2] Peptide oxytocin receptor agonists are used medically to induce labor, promote lactation, and for certain other uses. [3]
Contents
Oxytocin receptor agonists are of theoretical interest for the potential treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders with social symptoms, such as autism, social anxiety, and psychopathy. [1] [2] [4] Small-molecule oxytocin receptor agonists are considered to be more promising for such uses due to better potential pharmacokinetic profiles, such as blood–brain barrier permeability, elimination half-lives, and oral bioavailability. [1] [2]