
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity (hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure.

Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Present in animals since early stages of evolution, in humans it plays roles in behavior that include social bonding, love, reproduction, childbirth, and the period after childbirth. Oxytocin is released into the bloodstream as a hormone in response to sexual activity and during childbirth. It is also available in pharmaceutical form. In either form, oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions to speed up the process of childbirth.

Empathogens or entactogens are a class of psychoactive drugs that induce the production of experiences of emotional communion, oneness, relatedness, emotional openness—that is, empathy or sympathy—as particularly observed and reported for experiences with 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). This class of drug is distinguished from the classes of hallucinogen or psychedelic, and amphetamine or stimulants. Major members of this class include MDMA, MDA, MDEA, MDOH, MBDB, 5-APB, 5-MAPB, 6-APB, 6-MAPB, methylone, mephedrone, GHB, αMT, and αET, MDAI among others. Most entactogens are phenethylamines and amphetamines, although several, such as αMT and αET, are tryptamines. When referring to MDMA and its counterparts, the term MDxx is often used. Entactogens are sometimes incorrectly referred to as hallucinogens or stimulants, although many entactogens such as ecstasy exhibit psychedelic or stimulant properties as well.

The supraoptic nucleus (SON) is a nucleus of magnocellular neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus of the mammalian brain. The nucleus is situated at the base of the brain, adjacent to the optic chiasm. In humans, the SON contains about 3,000 neurons.

Vasopressin analogues are synthetic peptides structurally and functionally similar to arginine vasopressin (AVP), a naturally occurring hormone in mammals. These compounds have been developed to target specific vasopressin receptors with varying affinities, allowing for more tailored therapeutic applications. These analogues have been developed to address limitations of endogenous vasopressin, such as short half-life and lack of receptor selectivity, and to potentially reduce side effects associated with non-selective vasopressin receptor activation.

Vasopressin receptor 1A (V1AR), or arginine vasopressin receptor 1A is one of the three major receptor types for vasopressin, and is present throughout the brain, as well as in the periphery in the liver, kidney, and vasculature.

Vasopressin V1b receptor (V1BR) also known as vasopressin 3 receptor (VPR3) or antidiuretic hormone receptor 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AVPR1B gene.

Vasopressin receptor 2 (V2R), or arginine vasopressin receptor 2, is a protein that acts as receptor for vasopressin. AVPR2 belongs to the subfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors. Its activity is mediated by the Gs type of G proteins, which stimulate adenylate cyclase.
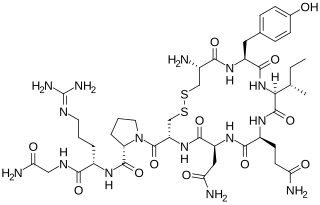
Vasotocin is an oligopeptide homologous to oxytocin and vasopressin found in all non-mammalian vertebrates and possibly in mammals during the fetal stage of development. Arginine vasotocin (AVT), a hormone produced by neurosecretory cells within the posterior pituitary gland (neurohypophysis) of the brain, is a major endocrine regulator of water balance and osmotic homoeostasis and is involved in social and sexual behavior in non-mammalian vertebrates. In mammals, it appears to have biological properties similar to those of oxytocin and vasopressin. It has been found to have effects on the regulation of REM sleep. Evidence for the existence of endogenous vasotocin in mammals is limited and no mammalian gene encoding vasotocin has been confirmed.

The oxytocin receptor, also known as OXTR, is a protein which functions as receptor for the hormone and neurotransmitter oxytocin. In humans, the oxytocin receptor is encoded by the OXTR gene which has been localized to human chromosome 3p25.

Carbetocin, sold under the brand names Pabal among others, is a medication used to prevent excessive bleeding after childbirth, particularly following Cesarean section. It appears to work as well as oxytocin. Due to it being less economical than other options, use is not recommended by NHS Scotland. It is given by injection into a vein or muscle.

L-371,257 is a compound used in scientific research which acts as a selective antagonist of the oxytocin receptor with over 800x selectivity over the related vasopressin receptors. It was one of the first non-peptide oxytocin antagonists developed, and has good oral bioavailability, but poor penetration of the blood–brain barrier, which gives it good peripheral selectivity with few central side effects. Potential applications are likely to be in the treatment of premature labour.

WAY-267464 is a potent, selective, non-peptide agonist for the oxytocin receptor, with negligible affinity for the vasopressin receptors. Contradictorily however, though originally described as selective for the oxytocin receptor and lacking affinity for the vasopressin receptors, it has since been reported to also act as a potent vasopressin V1A receptor antagonist. WAY-267464 has been shown to cross the blood–brain barrier to a significantly greater extent than exogenously applied oxytocin, and in animal tests produces centrally-mediated oxytocinergic actions such as anxiolytic effects, but with no antidepressant effect evident. It was developed by a team at Ferring Pharmaceuticals. WAY-267464 was under investigation for the potential clinical treatment of anxiety disorders by Wyeth, and reached the preclinical stage of development, but no development has been reported as of 2011.
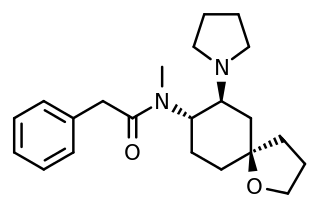
U-69,593 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective κ1-opioid receptor agonist. In animal studies it has been shown to produce antinociception, anti-inflammation, anxiolysis, respiratory depression, and diuresis, while having little effect on gastrointestinal motility. It also inhibits the peripheral, though not central secretion of oxytocin and vasopressin in rats.

Epelsiban is an orally bioavailable drug which acts as a selective and potent oxytocin receptor antagonist. It was initially developed by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) for the treatment of premature ejaculation in men and then as an agent to enhance embryo or blastocyst implantation in women undergoing embryo or blastocyst transfer associated with in vitro fertilization (IVF)., and was also investigated for use in the treatment of adenomyosis.
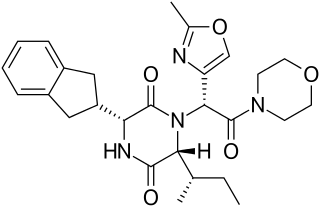
Retosiban also known as GSK-221,149-A is an oral drug which acts as an oxytocin receptor antagonist. It is being developed by GlaxoSmithKline for the treatment of preterm labour. Retosiban has high affinity for the oxytocin receptor and has greater than 1400-fold selectivity over the related vasopressin receptors
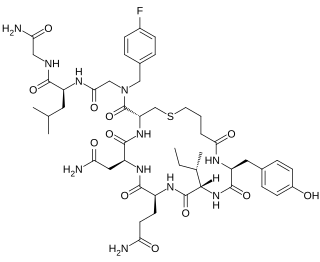
Merotocin (INN) (developmental code name FE-202767), also known as carba-1-(4-FBzlGly7)dOT, is a peptidic agonist of the oxytocin receptor that was derived from oxytocin. It is under development by Ferring Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of preterm mothers with lactation failure requiring lactation support, and is in phase II clinical trials for this indication. Merotocin is potent (EC50 < 0.1 nM) and highly selective (>1000-fold over the related vasopressin receptors).

Synthetic oxytocin, sold under the brand name Pitocin among others, is a medication made from the peptide oxytocin. As a medication, it is used to cause contraction of the uterus to start labor, increase the speed of labor, and to stop bleeding following delivery. For this purpose, it is given by injection either into a muscle or into a vein.

An oxytocin receptor agonist is a compound that acts as an agonist of the oxytocin receptor. Examples include peptide oxytocin receptor agonists like oxytocin, carbetocin, and demoxytocin (Sandopart) and small-molecule oxytocin receptor agonists like TC OT 39, WAY-267464, and LIT-001. Oxytocin receptor agonists are used medically to induce labor, promote lactation, and for other uses. In addition, oxytocin receptor agonists are of theoretical interest for the potential treatment of social disorders, such as autism and social anxiety. Small-molecule oxytocin receptor agonists are considered to be more promising for such uses due to better pharmacokinetic profiles, such as blood–brain barrier permeability, elimination half-lives, and potential for oral bioavailability.
LIT-001 is a small-molecule oxytocin receptor agonist and vasopressin receptor mixed agonist and antagonist that was first described in the literature in 2018. Along with TC OT 39 and WAY-267464, it is one of the first small-molecule oxytocin receptor agonists to have been developed. LIT-001 has greatly improved pharmacokinetic properties relative to oxytocin, reduces social deficits in animal models, and may have potential as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of social disorders like autism in humans.

















