| Panay cloudrunner | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Muridae |
| Genus: | Crateromys |
| Species: | C. heaneyi |
| Binomial name | |
| Crateromys heaneyi Gonzales & Kennedy, 1996 | |
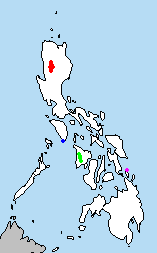 | |
| Range in green | |
The Panay cloudrunner (Crateromys heaneyi) is the second-largest cloud rat, a squirrel-like rodent that is found on the island of Panay in the Philippines. It is the most endangered rodent species in Panay, and one of the only few known cloud rat species in the world.
