
Puget Sound is a sound on the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins. A part of the Salish Sea, Puget Sound has one major and two minor connections to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, which in turn connects to the open Pacific Ocean. The major connection is Admiralty Inlet; the minor connections are Deception Pass and the Swinomish Channel.

Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams have two shells of equal size connected by two adductor muscles and have a powerful burrowing foot. They live in both freshwater and marine environments; in salt water they prefer to burrow down into the mud and the turbidity of the water required varies with species and location; the greatest diversity of these is in North America.

The Pacific geoduck is a species of very large saltwater clam in the family Hiatellidae. The common name is derived from the Lushootseed name, gʷidəq.

A siphon is an anatomical structure which is part of the body of aquatic molluscs in three classes: Gastropoda, Bivalvia and Cephalopoda.

Tresus capax is a species of saltwater clam, marine bivalve mollusk, common name the fat gaper, in the family Mactridae. It also shares the common name horse clam with Tresus nuttallii a species which is similar in morphology and lifestyle. Both species are somewhat similar to the geoduck, though smaller, with shells up to eight inches long (20 cm), weight to 3–4 lb (1.4–1.8 kg).

Hiatellidae is a taxonomic family of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs. This family is placed in the order Adapedonta.

Hiatella arctica, known as the wrinkled rock-borer, the arctic hiatella or the arctic saxicave, is a species of saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Hiatellidae. The white shell of this mollusc is thick and more or less rectangular, but generally irregular in shape. It is up to 45 mm long.

Panopea is a genus of large marine bivalve molluscs or clams in the family Hiatellidae. There are 10 described species in Panopea. Many of them are known under the common name "geoduck".

Panopea zelandica, commonly known as the deepwater clam or New Zealand geoduck, is a large species of marine bivalve mollusc in the Panopea (geoduck) genus of the family Hiatellidae. It is also sometimes called a king clam, or a gaper – in reference to the shell not being closed at either end.

Panopea smithae is a species of large marine bivalve mollusc in the Panopea (geoduck) genus of the family Hiatellidae, found in the waters surrounding New Zealand. While its relative Panopea zelandica lives in shallow waters, P. smithae lives in deeper waters, ranging from deep harbours to the outer continental shelf.

Amanita abrupta, commonly known as the American abrupt-bulbed amanita or the American abrupt-bulbed lepidella, is a possibly toxic species of fungus in the family Amanitaceae. Named for the characteristic shape of its fruit bodies, this white Amanita has a slender stem, a cap covered with conical white warts, and an "abruptly enlarged" swollen base. This terrestrial species grows in mixed woods in eastern North America and eastern Asia, where it is thought to exist in a mycorrhizal relationship with a variety of both coniferous and deciduous tree species.
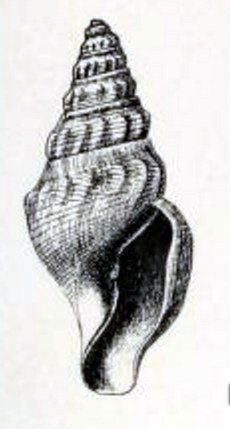
Borsonella is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Borsoniidae.

Tresus is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Mactridae. Many of them are known under the common name the horse clam or as species of gaper clam. They are similar to geoducks.

Tresus nuttallii, common name the Pacific gaper, is a species of saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Mactridae. It also shares the common name horse clam with Tresus capax, a species which is similar in morphology and lifestyle. Both species are somewhat similar to the Geoduck, though smaller, with shells up to eight inches long (20 cm), weight to 3–4 lb (1.4–1.8 kg).

Turbonilla abrupta, common name the abrupt turbonilla, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Pyramidellidae, the pyrams and their allies.

Geoduck aquaculture or geoduck farming is the practice of cultivating geoducks for human consumption. The geoduck is a large edible saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusk, that is native to the Pacific Northwest.

Panopea glycimeris is a species of large marine bivalve mollusc in the family Hiatellidae.
Panopea dockensis is an extinct species of marine bivalve mollusc from the Pliocene–Pleistocene Waccamaw Formation of North Carolina. It was a close relative of the well-known Pacific geoduck. It gets its name from the locality of Old Dock in Columbus County, where it was first discovered.

Panopea bitruncata is a species of marine bivalve commonly known as the Atlantic geoduck or Atlantic geoduck clam. These clams like their more famous Pacific relative P. generosa have an enlarged siphon that can extend to great lengths or contract to just barely poke out of the shell. They are generally smaller in comparison to the Pacific species though still constitute a sizable mollusc as they cannot fully retract their siphon.














