
Synbranchiformes, often called swamp eels, is an order of ray-finned fishes that are eel-like but have spiny rays, indicating that they belong to the superorder Acanthopterygii.

The cutlassfishes are about 45 species of predatory fish in the family Trichiuridae found in seas throughout the world. Fish of this family are long, slender, and generally steely blue or silver in colour, giving rise to their name. They have reduced or absent pelvic and caudal fins, giving them an eel-like appearance, and large fang-like teeth.

The Eel is a 1997 film directed by Shohei Imamura and starring Kōji Yakusho, Misa Shimizu, Mitsuko Baisho, and Akira Emoto. The film is loosely based on the novel On Parole by celebrated author Akira Yoshimura, combined with elements from the director's 1966 film The Pornographers. It shared the Palme d'Or at the 1997 Cannes Film Festival with Taste of Cherry. It also won the 1998 Kinema Junpo Award for Best Film of the Year.

The Japanese eel is a species of anguillid eel found in Japan, Korea, China, and Vietnam, as well as the northern Philippines. Like all the eels of the genus Anguilla and the family Anguillidae, it is catadromous, meaning it spawns in the sea, but lives parts of its life in fresh water. The spawning area of this species is in the North Equatorial Current in the western North Pacific to the west of the Mariana Islands. The larvae are called leptocephali and are carried westward by the North Equatorial Current and then northward by the Kuroshio Current to East Asia, where they live in rivers, lakes, and estuaries. The Japanese eel is an important food fish in East Asia, where it is raised in aquaculture ponds in most countries in the region. In Japan, where they are called unagi, they are an important part of the food culture, with many restaurants serving grilled eel, which is called kabayaki.
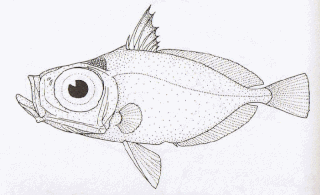
Zenion is a genus of zeniontid fish that is known from the fossil record, but is still extant.

An eel is a ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes, which consists of eight suborders, 19 families, 111 genera, and about 800 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage, and most are predators.
The Nepalese snowtrout is a cyprinid fish species of the genus Schizothorax. This snowtrout was first collected in 1979 in the alpine fresh water Rara Lake located in Nepal's Rara National Park.
Tatsuya Kamohara is a former Japanese football player.

Pterygotrigla is a genus of searobins native to the Indian and Pacific oceans.
Parabathymyrus is a genus of eels in the family Congridae.
Meadia is a genus of eels in the cutthroat eel family Synaphobranchidae. It currently contains the following species:
Glyptophidium is a genus of cusk-eels.
The Highlands long-finned eel is an eel in the family Anguillidae. It was described by Gilbert Percy Whitley in 1938. It is a tropical eel known from freshwaters in eastern New Guinea. The eels spend most of their lives in freshwater but migrate to the ocean to breed. Males can reach a maximum total length of 80 centimetres.
Owstonia is a genus of fish in the family Cepolidae found in deep-waters of the Indian and Pacific Ocean.
Parabathymyrus brachyrhynchus is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Henry Weed Fowler in 1934, originally under the genus Ariosoma. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a maximum depth of 289 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 33 centimetres.
Parabathymyrus fijiensis is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Emma Stanislavovna Karmovskaya in 2004. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from Fiji, in the western Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 478–500 metres. Females can reach a total length of 36 centimetres.
Parabathymyrus karrerae is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Emma Stanislavovna Karmovskaya in 1991. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from Cape Tala and Madagascar, in the western Indian Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 260–405 metres.
The flapnose conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from French Guiana, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 210 metres.
The Abyssal cutthroat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Toshiji Kamohara in 1938. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific, including Brazil, the Hancock Seamount, the Hawaiian and Society islands, Japan, Mauritius, and Réunion. It is found off the continental slope, and dwells at a depth range of 100–329 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 73 centimetres.






