
Aeger is a genus of fossil prawns. They first occur in the Early Triassic, and died out at the end of the Late Cretaceous. A total of 21 species are known.
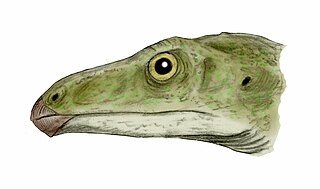
Shuvosaurus is a genus of beaked, bipedal poposauroid pseudosuchian from the Late Triassic of western Texas. Despite superficially resembling a theropod dinosaur, especially the ostrich-like ornithomimids, it is instead more closely related to living crocodilians than to dinosaurs. Shuvosaurus is known by the type and only species S. inexpectatus, and is closely related to the very similar Effigia within the clade Shuvosauridae. Shuvosaurus was originally described from a restored skull and very few fragmentary postcranial bones as a probable ornithomimosaur, or at least a very ornithomimosaur-like early theropod. The true pseudosuchian affinities of Shuvosaurus were only recognised after the discovery of Effigia linked the skull of Shuvosaurus with similar poposauroid skeletal remains found in the same quarry.

Semionotus is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish found throughout Northern Pangaea during the late Triassic, becoming extinct in the Early Jurassic.

Ceratodus is an extinct genus of lungfish. It has been described as a "catch all", and a "form genus" used to refer to the remains of a variety of lungfish belonging to the extinct family Ceratodontidae. Fossil evidence dates back to the Early Triassic. A wide range of fossil species from different time periods have been found around the world in places such as the United States, Argentina, Greenland, England, Germany, Egypt, Madagascar, China, and Australia. Ceratodus is believed to have become extinct sometime around the beginning of the Eocene Epoch.

Ceratites is an extinct genus of ammonite cephalopods. These nektonic carnivores lived in marine habitats in what is now Europe, during the Triassic, from the upper-most Anisian to the lower Ladinian age.
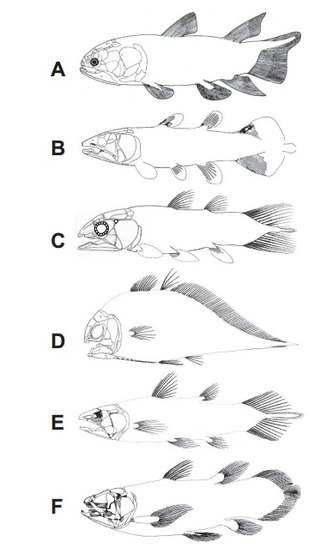
Rhabdoderma is an extinct genus of coelacanth fish in the class Sarcopterygii. It lived in the Carboniferous and Early Triassic (Induan), and its fossils have been found in Europe, Madagascar and North America. The type species was originally described as Coelacanthus elegans. Five species are considered valid in 1981.
Dictyocephalus is an extinct genus of prehistoric temnospondyls; the only species is Dictyocephalus elegans. This taxon was one of the first metoposaurids to be discovered in North America, being discovered by Ebeneezer Emmons and briefly described by Joseph Leidy in 1856 in the Newark supergroup exposures of Chatham County, North Carolina. At the time, Leidy was uncertain of much of the anatomy of D. elegans, which is represented only by a small partial skull and made only brief descriptions and measurements of a few elements, with an estimated size based on the long-snouted trematosaur Trematosaurus. Emmons provided the first figures of the specimen the following year. Romer (1947) briefly mentioned that the specimen was indistinguishable from "Buettneria" (Koskinonodon).
Helichthys is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Early Triassic epoch in what is now South Africa.
Platycraniellus is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodonts from the Early Triassic. It is known from the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone of the Normandien Formation in South Africa. P. elegans is the only species in this genus based on the holotype specimen from the Ditsong National Museum of Natural History in Pretoria, South Africa. Due to limited fossil records for study, Platycraniellus has only been briefly described a handful of times.

Matoniaceae is one of the three families of ferns in the Gleicheniales order of the Polypodiopsida class. Fossil records reveal that Matoniaceae ferns were abundant during the Mesozoic era, during which they lived on every continent, including Antarctica, with eight genera and 26 species, with the oldest known specimens being from the Middle Triassic of Antarctica. Today the family is much less abundant, and also less diverse, with only two extant genera and four species, which are limited to portions of southeastern Asia.
Polycynodon is an extinct genus of therocephalians from the Late Permian of South Africa. It is known from the Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone. The type species was first described as Octocynodon elegans by South African paleontologist Robert Broom in 1940, but the name Octocynodon was preoccupied by a genus of labrid fish first described in 1904. Along with John T. Robinson, Broom instated Polycynodon as a replacement name for O. elegans in 1948. Polycynodon is classified in Baurioidea, although its relationship to other baurioid therocephalians is uncertain.
Diegocanis is an extinct genus of cynodonts from the Late Triassic (Carnian) of Argentina. The type species, Diegocanis elegans, was named in 2013 from fossils found in the Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin. Diegocanis was classified within a new family of probainognathian cynodonts called Ecteniniidae, along with the genera Ecteninion and Trucidocynodon.

Ceratitidae is an extinct family of ammonite cephalopods.
C. elegans most commonly refers to the model round worm Caenorhabditis elegans. It may also refer to any of the species below. They are listed, first in taxonomic order and, second, alphabetically.
Cheilotomona is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine gastropods in the family Goniasmatidae. The species C. elegans is from a Pelsonian/Illyrian marine shale/marl in the Triassic Qingyan Formation of Guizhou Province, China.
Cubanothyris is an extinct genus of prehistoric brachiopods in the extinct family Angustothyrididae. Species are from the Triassic of China, the Russian Federation and Tajikistan. The type species, C. elegans, is found only at River Kuna.

Nemacanthus is an extinct genus of prehistoric sharks in the family Palaeospinacidae.
The Normandien Formation is a Triassic-age rock formation located in Free State, South Africa. It is where the fossils of Ericiolacerta, a subtaxa of Ericiolacertidae, were found.

Teffichthys is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish from the Early Triassic epoch. Fossils have been found in Madagascar and China, and possibly also in Angola, Canada, Greenland, and Svalbard.









